How Does An Inverter Work? | Its Components,
Jan 25, 2025 · What Is An Inverter? An inverter is an essential electronic device that plays a crucial role in converting direct current (DC) into alternating
Get Started
Inverter Battery Voltage Chart
Nov 9, 2024 · An inverter battery voltage chart shows the relationship between a battery''s charge level and its voltage. Battery voltage charts describe the
Get Started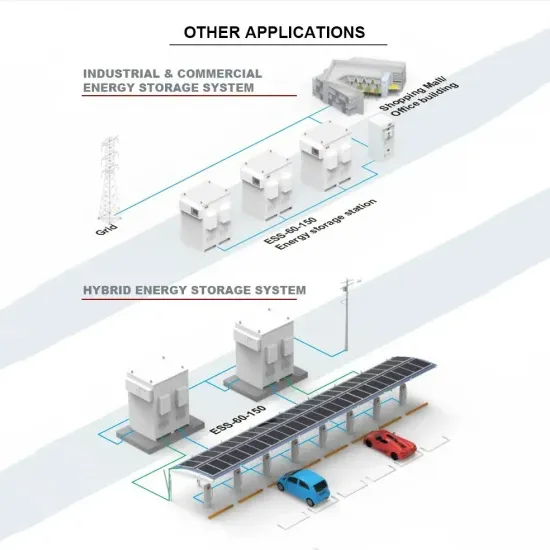
The 3 Most Common Faults on Inverters and
At IDS we have a wealth of inverter experience. We have been an ABB Partner for over 20 years and are used to supporting clients with a variety of inverter
Get Started
What is Current Source Inverter? Working,
Dec 17, 2021 · The current I L supplied to the single phase transistorised inverter is adjusted by the combination of variable dc voltage and inductance L. The
Get Started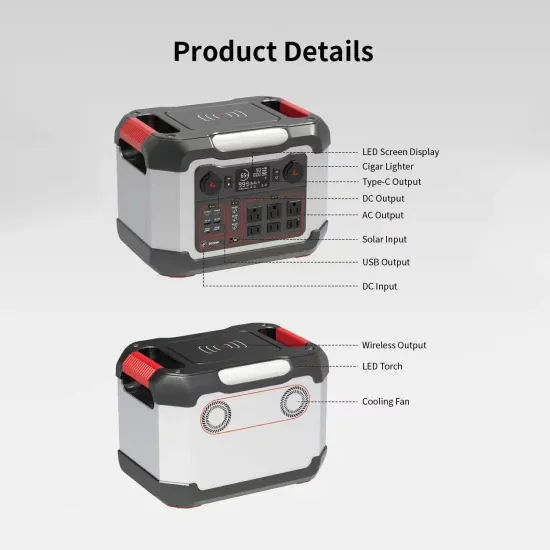
Inverter Voltage Calculator, Formula, Inverter Voltage
3 days ago · Inverter Voltage Formula: Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes
Get Started
What is Inverter? – Meaning, Types and
Jul 26, 2020 · The DC power input to the inverter is obtained from an existing power supply source or from a rotating alternator through a rectifier or a
Get Started
difference between PV input and MPPT range
Aug 31, 2021 · this is my solar inverter datasheet i don''t get the difference between the MPPT and The PV input voltage my each pv in series should equal to 500v? or to 425?
Get Started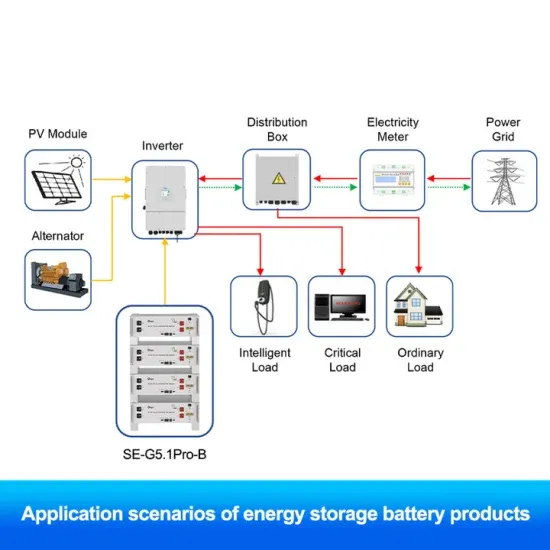
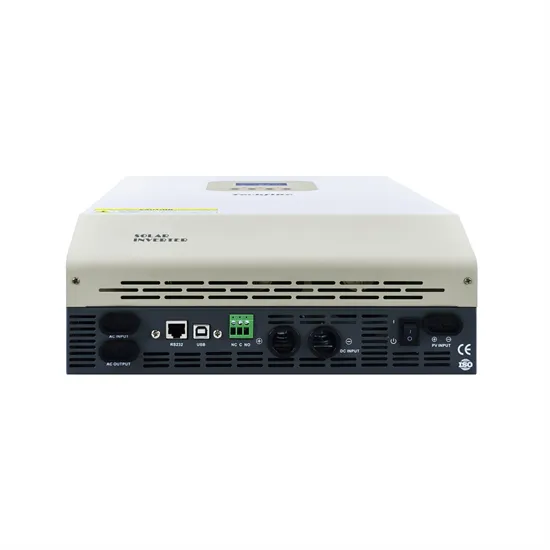
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
Nov 17, 2023 · Solar inverter specifications include input and output specs highlighting voltage, power, efficiency, protection, and safety features.
Get Started
Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition,
Dec 16, 2024 · The term inverter voltage in electric power systems world is a familiar thing. However, some people still do not understand what an inverter
Get Started
What is an inverter? | inverter
Aug 11, 2019 · An inverter or power inverter, refers to an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). In our daily life, we often convert 110V or 220V AC
Get Started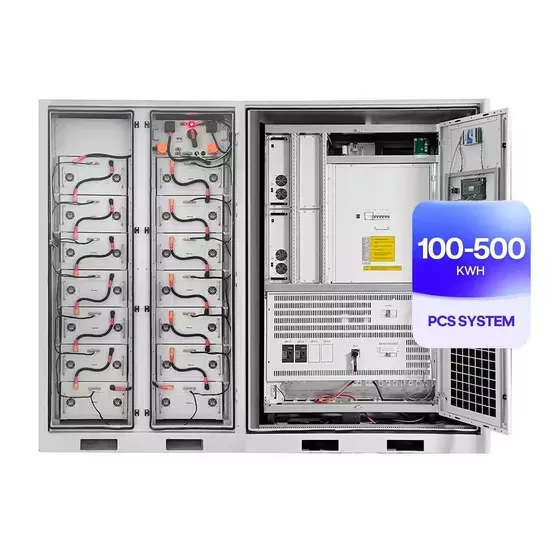
Power Inverter Basics
Mar 25, 2020 · The power inverter, and also called inverter is an electronic circuit that converts DC electricity to AC electricity. Actually, the inverter does not
Get Started
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
Dec 18, 2024 · For 12V inverters, the inverter start voltage is typically between 10V and 12V. This threshold ensures that the inverter can reliably start
Get Started
What is equation for inverter output voltage?
Dear Rinku, welcome, In the full bridge inverter the output peak voltage of the inverter is equal to the input DC voltage VDC lowered by the voltage drop on
Get Started
Current Source Inverter : Circuit Diagram and Its
What is Current Source Inverter? The current source inverter is also known as current fed inverter which converts the input dc into ac and its output can be
Get Started
Single Phase Inverter
Jul 23, 2025 · Single Phase Inverter A single-phase inverter is a type of inverter that converts DC source voltage into single-phase AC output voltage at a
Get Started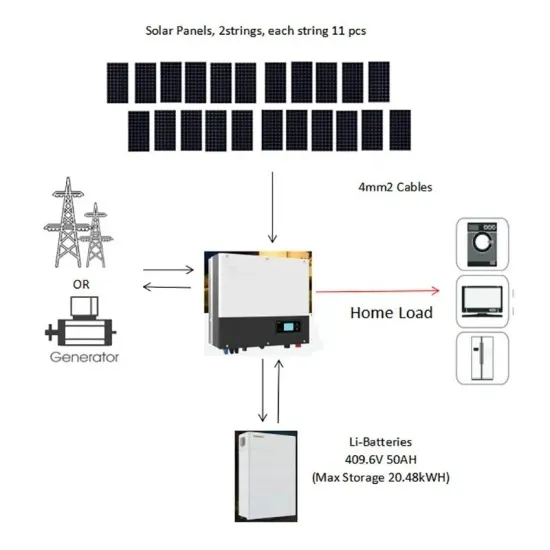
How Inverters Work
Dec 15, 2017 · How do Inverters work? In this article we''ll be learning how inverters work, starting from the very basics. We''ll cover Pulse Width
Get Started
Understanding Inverter Voltage: Definition,
Dec 16, 2024 · Inverter voltage is a voltage generated by the inverter after several electrons that converts a series of direct current (DC) into alternating current
Get Started
How Does Input Voltage Affect a Grid-Tie Inverter?
Aug 29, 2019 · In the photovoltaic grid-tie inverter, there are many input voltage technical parameters: Maximum DC input voltage, MPPT operating voltage
Get Started
Inverter Basics: Classification and Applications
Jan 3, 2021 · Inverter Basics: Resonant Inverters This is the class of inverters in which output voltage or current is passed though zero to minimize switching
Get Started
Inverter Voltage Calculator & Formula Online Calculator Ultra
Oct 3, 2024 · To calculate the inverter voltage, the formula is: [ VI = V_ {dc} times dm ] where: (dm) is the difference in modulation indices. For a system with a DC bus voltage of 95 volts
Get Started
Inverter Voltage Calculator, Formula, Inverter Voltage
3 days ago · Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes the output voltage of an
Get Started
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications: A
Jun 5, 2024 · How to read solar inverter specifications: A simple guide to understanding technical details like efficiency ratings, input/output specs,
Get Started
Understanding inverter voltage
Jan 10, 2024 · Inverter voltage typically falls into three main categories: 12V, 24V, and 48V. These values signify the nominal direct current (DC) input voltage required for the inverter to function
Get Started
CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
Mar 27, 2016 · With this method, the inverter monitors the output voltage, the output current, and the encoder feedback from the motor. The encoder feedback is used to adjust the output
Get Started
Frequently Asked Questions about Inverters
Modern inverters generate a sine wave-shaped output current similar to or even better than that of the public grid and perfectly suited to powering sensitive equipment. Trapezoidal inverters,
Get Started
Voltage Source Inverter : Construction, Phases
The external commutation inverters, acquire sources externally from motors or power supply and the self-commutated inverters control the circuit with the
Get Started
Voltage Inverter : Circuit, Working and Its
Mar 30, 2019 · Inverters are used in a large number of electrical power applications. Voltage inverters are divided into three categories, Pulse-width
Get Started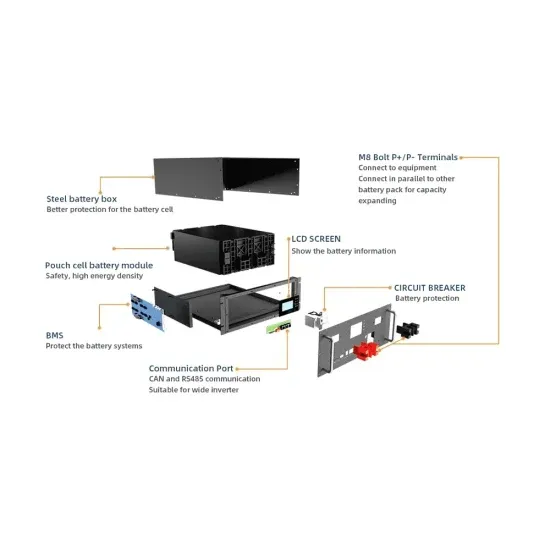
What Is Inverter Voltage?
What Is Inverter Voltage? Inverters are crucial components in energy systems, converting direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for household appliances. Understanding inverter
Get Started
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters:
The Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters can be done in two ways. by varying the dc link voltage by varying the ac voltage at the output using a
Get Started
Voltage Source Inverter
Voltage Source Inverters abbreviated as VSI are the type of inverter circuits that converts a dc input voltage into its ac equivalent voltage at the output. It is
Get Started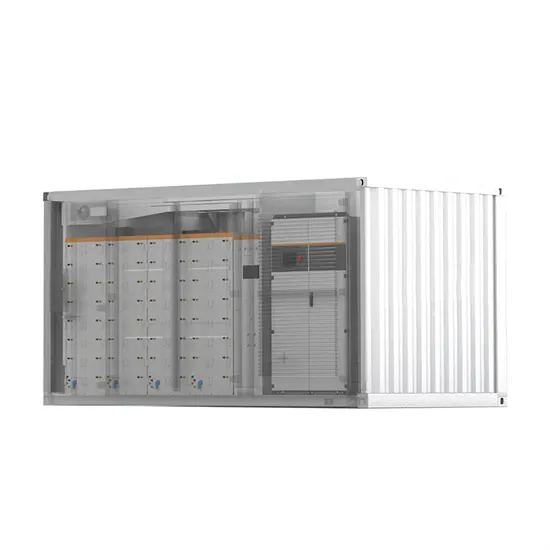
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Jul 8, 2025 · Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
Get Started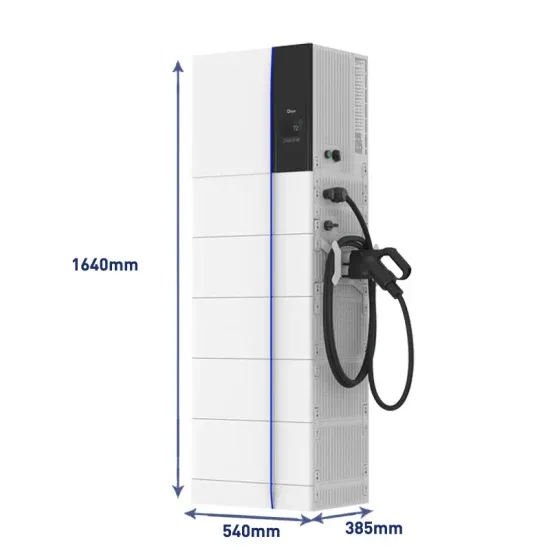
Power Inverter Basics
Mar 25, 2020 · The three parameters will be determined based on your load characteristics / requirements; whether its 50Hz or 60Hz, and whether its
Get Started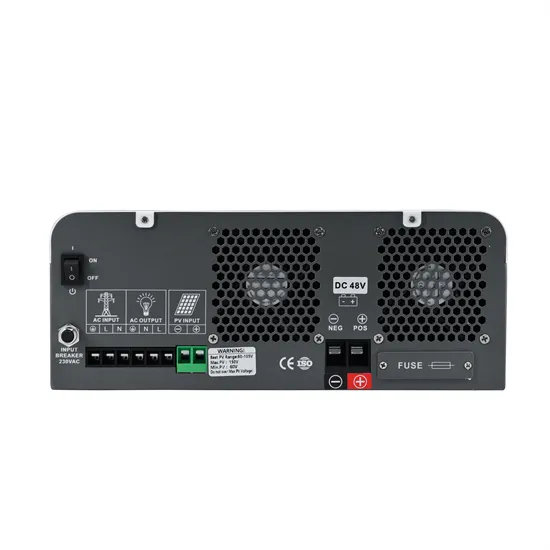
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
Dec 17, 2019 · Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working
Get Started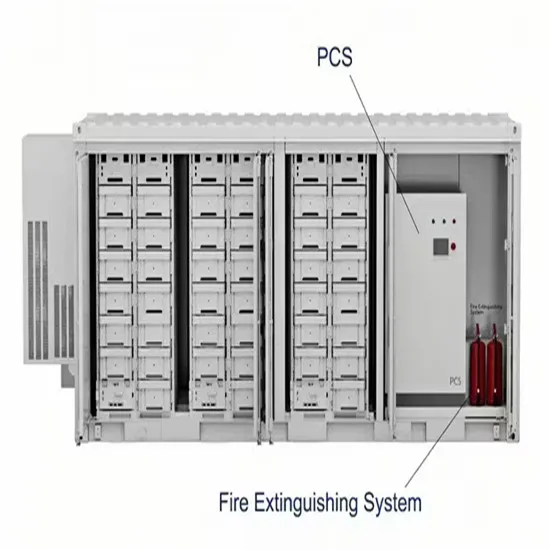
6 FAQs about [What is the voltage of the inverter ]
What is inverter voltage?
Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC).
Why is inverter voltage calculation important?
Inverter technology plays a pivotal role in modern power electronics, converting DC (Direct Current) into AC (Alternating Current). This process is crucial for applications ranging from renewable energy systems to the control of electric motors. The inverter voltage calculation is a fundamental aspect of designing and analyzing these systems.
What is a DC inverter?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working Principle: Inverters use power electronics switches to mimic the AC current’s changing direction, providing stable AC output from a DC source.
What is an example of a power inverter?
Common examples are refrigerators, air-conditioning units, and pumps. AC output voltage This value indicates to which utility voltages the inverter can connect. For inverters designed for residential use, the output voltage is 120 V or 240 V at 60 Hz for North America. It is 230 V at 50 Hz for many other countries.
What voltage is a 12V inverter?
Inverters come in various configurations, each designed for specific power systems. Common rated input voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V. The choice depends on the application, the size of the power system, and the available power source. A 12V inverter is commonly used for smaller applications, such as in vehicles or small off-grid setups.
What determines the output voltage of an inverter?
The output voltage of an inverter is determined by the DC input voltage and the modulation index. The modulation index represents the ratio of the inverter’s AC output voltage to its maximum possible AC output voltage.
Related Articles
-
 What is the voltage of the inverter
What is the voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the voltage of a low voltage inverter
What is the voltage of a low voltage inverter
-
 What is the tracking voltage of the inverter
What is the tracking voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the input voltage of the communication inverter
What is the input voltage of the communication inverter
-
 What is the input voltage of the inverter
What is the input voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the input voltage range of the 48v inverter
What is the input voltage range of the 48v inverter
-
 Sunshine PV inverter DC voltage
Sunshine PV inverter DC voltage
-
 What to do if the communication base station inverter is connected to the grid and is struck by lightning
What to do if the communication base station inverter is connected to the grid and is struck by lightning
-
 What inverter to use for 12v2000ma
What inverter to use for 12v2000ma
-
 Inverter DC voltage is 1500v
Inverter DC voltage is 1500v
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


