
Improving frequency stability in grid-forming inverters with
May 13, 2025 · The increasing utilization of renewable energy sources in low-inertia power systems demands advanced control strategies for grid-forming inverters (GFMs).
Get Started
Single phase grid-connected inverter: advanced control
Jul 28, 2025 · Advanced control techniques such as proportional-resonant control, deadbeat control, and model predictive control are analyzed for their effectiveness in achieving high
Get Started
Advanced Control for Grid-Connected System
May 5, 2022 · Self-adaptive virtual synchronous generator (SDVSG) controlled grid-connected inverters can provide virtual damping and inertia to support the
Get Started
Power instruction correction based frequency response strategy for grid
Jan 1, 2024 · Grid forming (GFM) inverter interfaced energy storage system can offer frequency support for islanded microgrids (IMGs), and the frequency response relies on the GFM
Get Started
Harmonic characteristics and control strategies of grid
Nov 1, 2022 · The current research on grid-connected PV systems usually adopts an impedance modeling method that only considers a single disturbance frequency, which is difficult to truly
Get Started
How a Grid-tied PV System Works with Hybrid
Dec 19, 2022 · Against the backdrop of today''s global energy transition, grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems, as an important component of
Get Started
Improving frequency stability in grid-forming inverters
May 13, 2025 · Grid-Forming Inverters in Virtual Synchronous Machine (VSM) mode have become a pivotal technology for frequency stability and increasing damping in power systems
Get Started
Dynamic Grid Frequency Support using a Self-Synchronising Grid
May 27, 2021 · This paper uses a self-synchronising grid-following inverter to provide dynamic frequency support for a low inertia grid system. The approach uses frequency dev
Get Started
Active and reactive power regulation in grid-connected
Jul 30, 2025 · d voltage output whose magnitude and frequency can be controlled. Under normal condition the control strategy of inverter determines: 1) the level of the active power injected
Get Started
A Review of Adaptive Control Methods for Grid
Jan 21, 2025 · In order to enhance the adaptability of grid-connected inverters under these abnormal conditions, this research systematically summarizes
Get Started
PLL and Self-Synchronized Synchonverter: An
Mar 26, 2016 · Similar to other grid-connected inverters, it needs a dedicated synchronization unit, e.g., a phase-locked loop (PLL), to provide the phase,
Get Started
Review on novel single-phase grid-connected solar inverters:
Mar 1, 2020 · A micro inverter operating in grid-connected mode should satisfy the grid connection standards in terms of power quality, THD ratios, islanding detection, grid interfacing limits for
Get Started
Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes,
Jan 1, 2024 · With the development of modern and innovative inverter topologies, efficiency, size, weight, and reliability have all increased dramatically. This paper provides a thorough
Get Started
Self-Synchronization Grid Forming Inverters Connected to a
Oct 29, 2023 · Synchronization must be implemented before and after connecting an inverter to a power grid. Virtual synchronous generator-controlled grid-forming (VSG-GFM) inv
Get Started
Fundamental‐Frequency Bus‐Impedance Analysis of Power
Jun 16, 2025 · This article investigates how the placement of grid-forming (GFM) and grid-following (GFL) inverters influences the equivalent fundamental-frequency impedance at
Get Started
Enhancing photovoltaic grid integration with hybrid energy
Jun 1, 2025 · This paper introduces an innovative approach to improving power quality in grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems through the integration of a hybrid energy storage,
Get Started
Grid frequency disturbance analysis based virtual
May 1, 2025 · To address the issue, a grid frequency disturbance analysis based VSG control strategy is proposed in this paper. Unlike the existing methods that add zero/pole pairs to the
Get Started
A modified control strategy for seamless switching of virtual
Jun 1, 2024 · A new modified control strategy for seamless switching is introduced in this study for the VSG inverter during the transition from off-grid to on-grid mode. The operation of the VSG
Get Started
Design of a Non-PLL Grid-Forming Inverter for Smooth
Sep 23, 2020 · Use self-generated phase before and after disconnection, no change in phase angle. Keep the same phase without need for compensation. A synchronization scheme of a
Get Started
A comprehensive review of grid-connected solar
Jun 1, 2023 · This manuscript presents various standards of grid-interactive solar PV inverters and their detailed analysis in section 2. The requirements of the grid-connected solar power
Get Started
SolarEdge Inverters, Power Control Options —
May 6, 2024 · Installation Note for Three Phase Inverters If power control is enabled, the order of connection of grid lines to the inverter is important. A 120-degree phase difference between L1
Get Started
Next generation power inverter for grid resilience:
Nov 15, 2024 · The capacity of inverters to function in grid-following and grid-forming control modes is known as the self-governing feature for grid-interactive inverters. The self-adapting
Get Started
Control interaction analysis of hybrid system with grid
Nov 1, 2024 · • A control interaction analysis method is proposed based on admittance decomposition. • The potential threat of grid-following inverters on the low-frequency mode of
Get Started
Inverters: A Pivotal Role in PV Generated Electricity
Dec 15, 2021 · Requirements for generating plants to be connected in parallel with distribution networks Grid connection code for RPPs in South Africa Grid connection of energy systems
Get Started
Grid Connected Self-Synchronized Inverter
Apr 25, 2017 · Abstract: The paper discuss the idea of operating an inverter to mimic a synchronous generator(SG) ing such inverters,the theory or algorithms used to control
Get Started
Grid-connected isolated PV microinverters: A review
Jan 1, 2017 · Galvanic isolation in grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) microinverters is a very important feature concerning power quality and safety issues. However, high-frequency
Get Started
Grid-Forming Inverters: Shaping the Future of
Jul 5, 2023 · These inverters are designed to follow the grid''s voltage and frequency, rendering them unable to continue supplying power and
Get Started
A composite strategy for designing efficient harmonic
Feb 1, 2024 · The harmonic controlling schemes are very important for renewable energy applications. The power efficient applications are playing significant role in grid connected
Get Started
Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study
Mar 20, 2025 · Grid-forming inverters (GFMIs) are recognized as critical enablers for the transition to power systems with high renewable energy penetration.
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Inverter self-frequency reduction and grid connection]
How can grid-forming inverters improve grid stability?
The increased penetration of inverter-interfaced renewable energy resources in modern power grids has significantly reduced system inertia, which is critical for maintaining frequency stability. Among emerging solutions, Grid-Forming Inverters (GFMs) have proven pivotal in simulating inertia and enhancing grid stability.
What is a pic-based frequency response strategy for grid forming inverter?
A PIC-based frequency response strategy for grid forming inverter is proposed. PIC strategy can enhance the frequency stability of IMGs under large disturbances. PIC strategy can be implemented in IMGs and complex multi-machine systems.
Can grid-forming inverters be used in low-inertia power systems?
Scientific Reports 15, Article number: 16540 (2025) Cite this article The increasing utilization of renewable energy sources in low-inertia power systems demands advanced control strategies for grid-forming inverters (GFMs).
What is a grid forming inverter?
A grid-forming inverter operating in Virtual Synchronous Machine (VSM) mode emulates the behavior of a synchronous generator by establishing the grid’s reference voltage and frequency. In doing so, it contributes virtual inertia and damping to stabilize frequency and voltage while facilitating power sharing among inverter-based resources.
What is a grid-connected inverter?
In the grid-connected inverter, the associated well-known variations can be classified in the unknown changing loads, distribution network uncertainties, and variations on the demanded reactive and active powers of the connected grid.
Can grid-connected PV inverters improve utility grid stability?
Grid-connected PV inverters have traditionally been thought as active power sources with an emphasis on maximizing power extraction from the PV modules. While maximizing power transfer remains a top priority, utility grid stability is now widely acknowledged to benefit from several auxiliary services that grid-connected PV inverters may offer.
Related Articles
-
 Communication base station inverter grid connection process
Communication base station inverter grid connection process
-
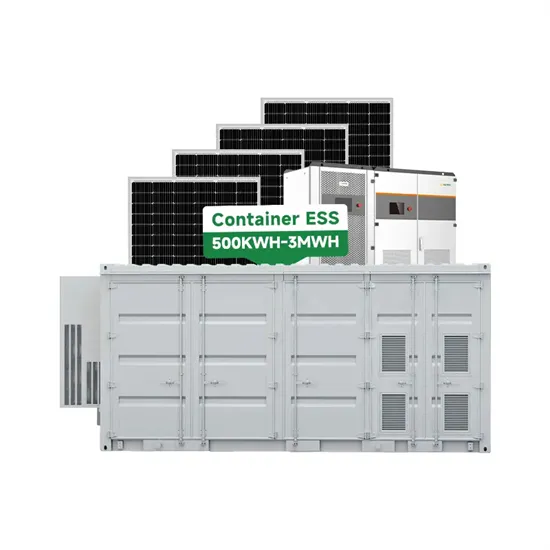 Communication base station inverter grid connection disappears
Communication base station inverter grid connection disappears
-
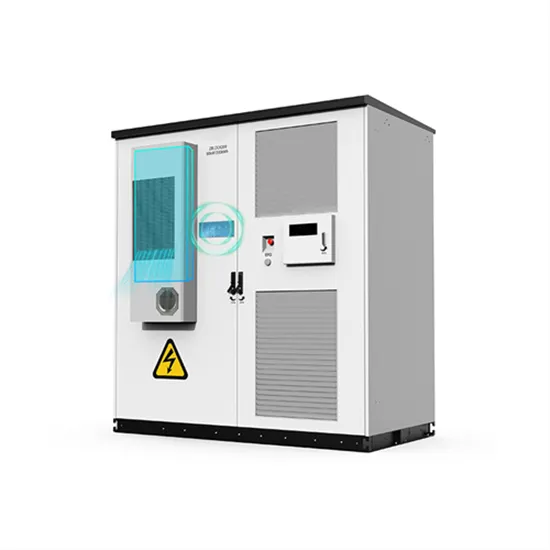 Additional communication base station inverter grid connection application
Additional communication base station inverter grid connection application
-
 Communication base station inverter grid connection setup plan
Communication base station inverter grid connection setup plan
-
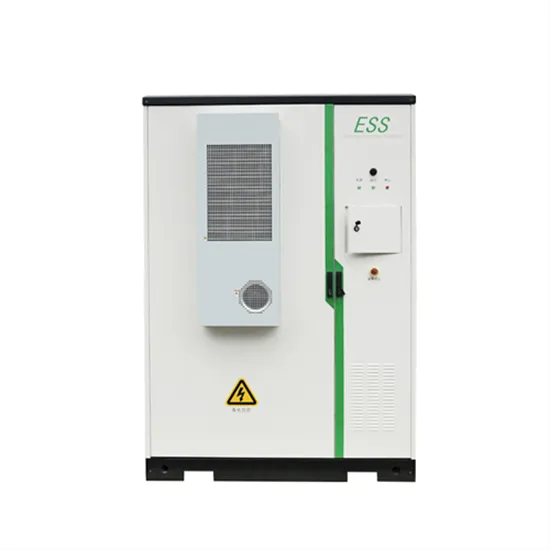 Inverter output and grid connection
Inverter output and grid connection
-
 Photovoltaic power station inverter grid connection
Photovoltaic power station inverter grid connection
-
 Abuja communication base station inverter grid connection lac
Abuja communication base station inverter grid connection lac
-
 Mobile company 5g communication base station inverter grid connection
Mobile company 5g communication base station inverter grid connection
-
 Inverter scr grid connection standard
Inverter scr grid connection standard
-
 What are the functions of the virtual communication base station inverter grid connection
What are the functions of the virtual communication base station inverter grid connection
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

