Optimal configuration of 5G base station energy storage
Feb 1, 2022 · The high-energy consumption and high construction density of 5G base stations have greatly increased the demand for backup energy storage batteries. To maximize overall
Get Started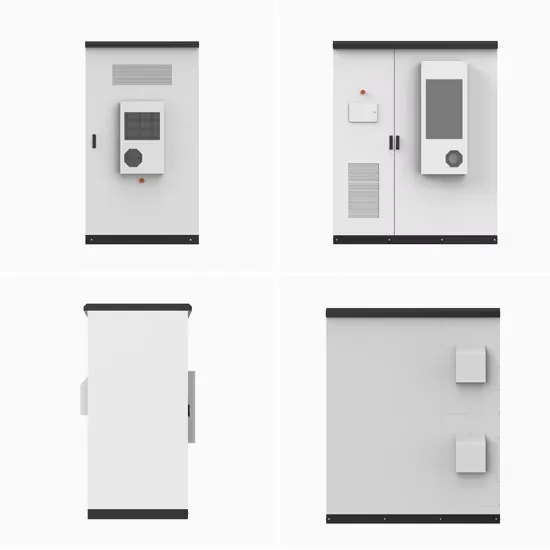
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT FOR THE
Dec 3, 2022 · ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT FOR THE PROPOSED GUINAS TELECOMMUNICATION BASE TRANSCEIVER STATION (BTS) TOWER AT GUINAS,
Get Started
Environmental-economic analysis of the secondary use of
Nov 30, 2022 · Frequent electricity shortages undermine economic activities and social well-being, thus the development of sustainable energy storage systems (ESSs) becomes a center
Get Started
Environmental Planning and Assessment Regulation 2021
Dec 17, 2021 · Explanatory note The object of this Regulation is to remake, with amendments, certain provisions of the Environmental Planning and Assessment Regulation 2000, which is
Get Started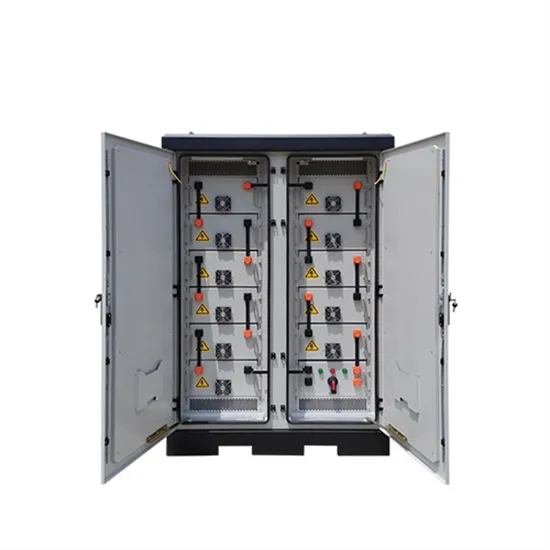
Communication Base Station Inverter
Dec 14, 2023 · The power requirements of inverters for communication base stations vary depending on the size of the site, equipment requirements and
Get Started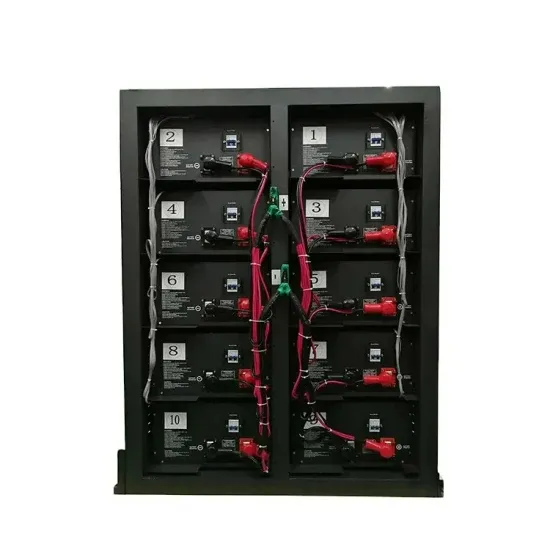
Environmental Impact Assessment of Power Generation
Aug 19, 2013 · Resumen Hybrid power systems were used to minimize the environmental impact of power generation at GSM (global systems for mobile communication) base station sites.
Get Started
Environmental-economic analysis of the secondary use of
Nov 30, 2022 · This study examines the environmental and economic feasibility of using repurposed spent electric vehicle (EV) lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) in the ESS of
Get Started
Carbon emissions and mitigation potentials of 5G base station
Jul 1, 2022 · However, a significant reduction of ca. 42.8% can be achieved by optimizing the power structure and base station layout strategy and reducing equipment power consumption.
Get Started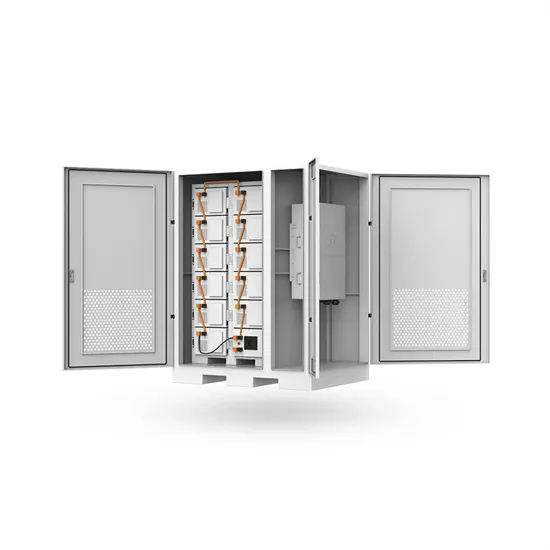
Base Station and Electromagnetic Fields Management-FETnet
Jun 25, 2025 · In addition to addressing the most pressing concerns regarding base station construction regulations, norms, and clarifications on electromagnetic waves and health, it is
Get Started
The 2020 EIA Regulations
From 1st January 2021 Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) Projects listed in Schedule 1 of the 2020 EIA Regulations are subject to an EIA process as required by regulation 5 (1).
Get Started
ENVIRONMENTAL SCOPING REPORT DATE: NOV 2022
Dec 3, 2022 · ENVIRONMENTAL SCOPING REPORT DATE: NOV 2022 REFRENCE NUMBER:221126000489 ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT FOR THE PROPOSED
Get Started
4507 handbook cover a/w TG
Mar 26, 2014 · Annex I and Annex II of the Directive are transposed by Schedule 1 and Schedule 2 of the Town & Country Planning (Environmental Impact Assessment) Regulations 1999, SI
Get Started
Final
Jul 2, 2023 · Radio wave strength is generally much greater from radio and television broadcast stations than from cellular phone communication base transceiver stations. Microwave and
Get Started
Environmental Impact Assessment
Article 2 (4) of the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Directive provides for the possibility for Member States to exempt a specific project from the requirements of the Directive in
Get Started
Base-station network planning including environmental impact control
Jul 25, 2004 · The authors present a method for planning a base station''s position in a mobile communication system taking into account both the requirement to minimise the environmental
Get Started
Improved Model of Base Station Power System
Nov 29, 2023 · An improved base station power system model is proposed in this paper, which takes into consideration the behavior of converters. And through
Get Started
Some types of TD base stations can be exempted from environmental
According to relevant regulations in my country, the electromagnetic radiation of communication base stations must be less than 40μW/cm2, and only when it reaches 8μW/cm2 or less can it
Get Started
《5G移动通信基站电磁辐射环境监测方法(试行)》_中华
Mar 1, 2021 · 为贯彻《中华人民共和国环境保护法》,保护环境,防治电磁辐射环境污染,规范 5G 移动通信基 站电磁辐射环境监测,制定本标准。 本标准规定了 5G 移动通信基站电磁辐射
Get Started
NSW Telecommunications Facilities Guideline, Including
Mar 6, 2023 · The Guideline explains the state-wide planning provisions and development controls for telecommunication facilities in NSW, as outlined in State Environmental Planning
Get Started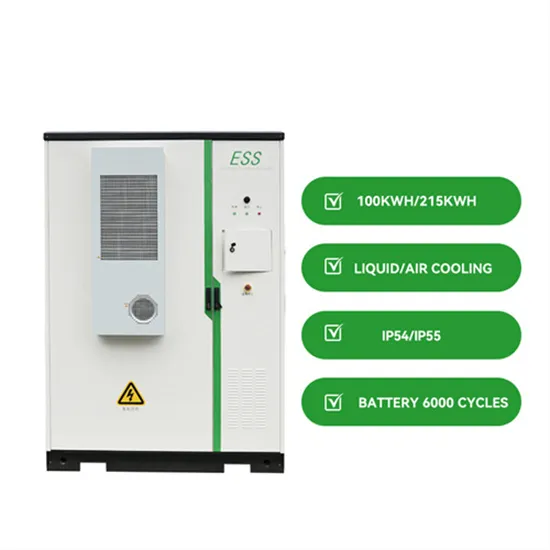
The Environmental Assessment of Plans and Programmes Regulations
Aug 6, 2025 · These Regulations implement Directive 2001/42/EC of the European Parliament and Council on the assessment of the effects of certain plans and programmes on the
Get Started
Low-Carbon Sustainable Development of 5G Base Stations in
May 4, 2024 · In order to increase the contribution of the communication industry to mitigate the global greenhouse effect, future efforts must focus on reducing the carbon emissions
Get Started
5G Mobile Communication Base Station Electromagnetic
Dec 15, 2023 · The current national policies and technical requirements related to electromagnetic radiation administration of mobile communication base stations in China are described,
Get Started
Environmental EMF Evaluation for Mobile Communication Base Stations
Aug 28, 2021 · Environmental EMF assessment for epidemiological studies is important. It obviously differs from the measurements for compliance test with the safety limits. We
Get Started
Microsoft Word
Dec 12, 2012 · POLICY AND GUIDELINES FOR THE ERECTION OF TELECOMMUNICATION INFRASTRUCTURE 1. Introduction Base stations and cellular telephone masts form part of
Get Started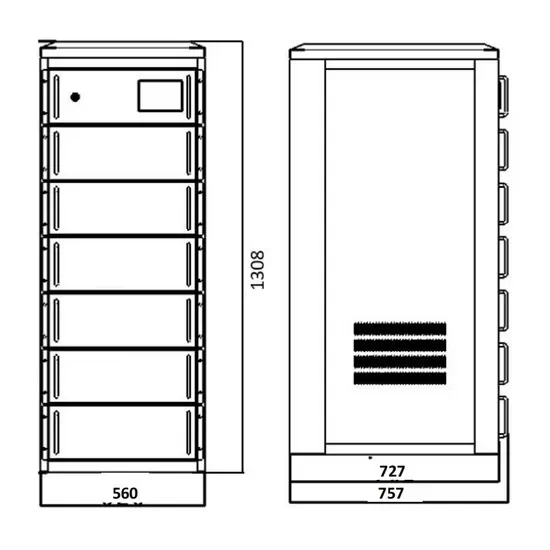
Base-station network planning including environmental
Jun 25, 2004 · The authors present a method for planning a base station''s position in a mobile communication system taking into account both the requirement to minimise the environmental
Get Started
Planning environmental impact assessment law in China:
Jul 1, 2023 · Abstract As the primary form of strategic environmental assessment (SEA) mandated by law in China, the planning environmental impact assessment (PEIA) serves to anticipate
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Communication Base Station Inverter Planning Environmental Assessment Regulations]
What is the system boundary of 5G base station?
The system boundary of the CO 2 of 5G base station The civil construction of 5G base stations is typically carried out using the existing infrastructure of 4G base stations, resulting in less material input during the construction phase. The primary focus on carbon emission generation is during the use phase due to power consumption.
Why are micro base stations important in 5G planning?
Micro base stations, on the other hand, are smaller and more flexible, allowing them to supplement the peripheral communication that cannot be covered by macro stations, thereby improving communication quality and capacity. Therefore, micro stations play a critical role in 5G planning.
How can base stations be improved?
Currently, limited research (Tala't et al., 2017) is focused on improving the power supply mode of base stations, such as replacing traditional thermal power generation with renewable energy (photovoltaic systems, wind power) and equipping micro base stations with solar cells.
Can macro base stations be deployed on a large scale?
As 5G operates at a higher frequency than 4G, its coverage capability is lower and the signal penetration is poor, causing significant signal attenuation. Thus, deploying macro base stations on a large scale is not feasible for 5G networks.
What is the main mode of transport of base station equipment?
The road transportation mode is the main mode of transporting the base station equipment. The main energy consumption is related to fuel usage.
How much power does a micro base station use?
The power consumption of a single macro base station is approximately 5 kW, whereas a Pico Cell requires only about 10 W (Bolla et al., 2012; Deruyck et al., 2014; Hu & Yi, 2014). Deploying multiple micro base stations to cover the blind spots of a macro base station will reduce power consumption during operation, thereby reducing carbon emissions.
Related Articles
-
 Communication base station wind power environmental assessment regulations
Communication base station wind power environmental assessment regulations
-
 Communication base station inverter grid connection planning adjustment range
Communication base station inverter grid connection planning adjustment range
-
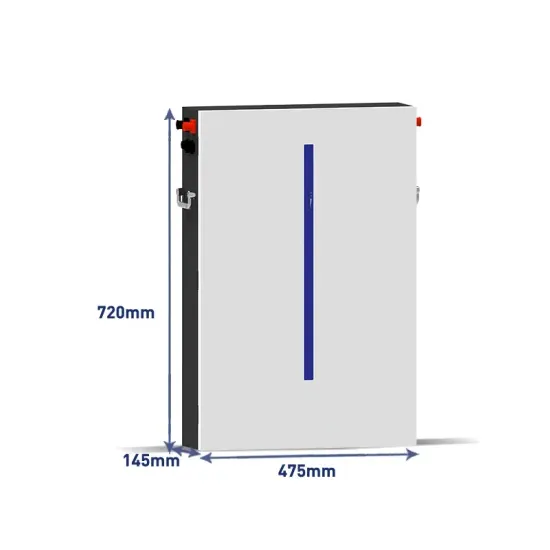 Praia Communication Base Station Inverter Expansion Project
Praia Communication Base Station Inverter Expansion Project
-
 How to connect the grid-connected optical cable of the communication base station inverter
How to connect the grid-connected optical cable of the communication base station inverter
-
 How to check the inverter of local communication base station
How to check the inverter of local communication base station
-
 Asuncion 5G communication base station inverter grid connection solution
Asuncion 5G communication base station inverter grid connection solution
-
 The lifespan of the inverter connected to the grid in the communication base station in Djibouti
The lifespan of the inverter connected to the grid in the communication base station in Djibouti
-
 Portugal communication base station inverter grid connection operation and maintenance work
Portugal communication base station inverter grid connection operation and maintenance work
-
 Belmopan communication base station inverter photovoltaic power generation
Belmopan communication base station inverter photovoltaic power generation
-
 Bangladesh communication base station inverter grid-connected maintenance project
Bangladesh communication base station inverter grid-connected maintenance project
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


