The Future of Energy Storage | MIT Energy
MITEI''s three-year Future of Energy Storage study explored the role that energy storage can play in fighting climate change and in the global adoption of clean
Get Started
The most comprehensive guide to thermal energy storage
Aug 21, 2023 · Thermal energy storage technology (TES) temporarily stores energy (solar heat, geothermal, industrial waste heat, low-grade waste heat, etc.) by heating or cooling the energy
Get Started
Energy Storage
Sep 11, 2020 · Energy storage is a technology that holds energy at one time so it can be used at another time. Building more energy storage allows renewable
Get Started
A review of battery energy storage systems and advanced
May 1, 2024 · This review highlights the significance of battery management systems (BMSs) in EVs and renewable energy storage systems, with detailed insights into voltage and current
Get Started
Chapter 1: Fundamentals of high temperature thermal energy storage
Nov 27, 2020 · Abstract (100-150 words): Renewable energy generation is inherently variable. For example solar energy shows seasonally (summer-winter), daily (day-night) and hourly (clouds)
Get Started
Sensible Heat Storage
Sensible heat storage refers to the storage or release of heat energy through the temperature change of the heat storage material itself, utilizing materials such as water, water vapor, and
Get Started
Introduction to thermal energy storage systems
Jan 1, 2021 · Thermal energy storage (TES) systems can store heat or cold to be used later, at different temperature, place, or power. The main use of TES is to overcome the mismatch
Get Started
Thermal Energy Storage
Oct 11, 2023 · Energy demand both in industry and domestic households, including buildings, typically follows a pattern of demand that can be burdensome for the energy grid during peak
Get Started
Latent thermal energy storage technologies and applications
Aug 1, 2020 · The achievement of European climate energy objectives which are contained in the European Union''s (EU) "20–20–20″ targets and in the European Commission''s (EC) Energy
Get Started
Thermal Energy Storage
Jul 11, 2025 · Thermal energy storage (TES) is a type of energy storage system that stores energy in the form of heat or cold, allowing for the retention and
Get Started
Critical review of energy storage systems
Jan 1, 2021 · This review article critically highlights the latest trends in energy storage applications, both cradle and grave. Several energy storage applications
Get Started
6 Low-temperature thermal energy storage
Sensible storage of heat and cooling uses a liquid or solid storage medium witht high heat capacity, for example, water or rock. Latent storage uses the phase change of a material to
Get Started
Thermal Energy Storage Systems Unveiled: The Best Factors
May 8, 2025 · Thermal Energy Storage Systems (TES) are transforming energy management by storing excess thermal energy for later use, enhancing sustainability. They come in three
Get Started
Thermochemical Storage
Thermal storage is defined as a method that stores thermal energy by heating or cooling a storage medium, enabling the stored energy to be utilized later for power generation, typically
Get Started
Full article: Exploring heat storage: innovations, risks, and
Jun 2, 2025 · ABSTRACT Heat storage is the process of capturing thermal energy for use at a later time, playing a key role in enhancing energy efficiency and enabling renewable energy
Get Started
Recent advancement in energy storage technologies and
Jul 1, 2024 · Throughout this concise review, we examine energy storage technologies role in driving innovation in mechanical, electrical, chemical, and thermal systems with a focus on
Get Started
What is Thermal Energy Storage?
Dec 12, 2023 · Thermal energy storage involves heating or cooling a substance to preserve energy for later use. In its simplest form, this process includes
Get Started
These 4 energy storage technologies are key to
Apr 23, 2021 · Pumped hydro, batteries, thermal and mechanical energy storage store solar, wind, hydro and other renewable energy to supply peaks in
Get Started
Thermal Energy Storage
Apr 11, 2022 · Thermal energy storage systems can be either centralised or distributed systems. Centralised applications can be used in district heating or cooling systems, large industrial
Get Started
How Does Thermal Energy Storage Work?
May 25, 2024 · Thermal energy storage systems can be primarily classified into three types based on how the energy is stored: sensible heat, latent heat, and
Get Started
Advanced Compressed Air Energy Storage Systems:
Mar 1, 2024 · The "Energy Storage Grand Challenge" prepared by the United States Department of Energy (DOE) reports that among all energy storage technologies, compressed air energy
Get Started
Thermal Storage Systems: Types, Components,
Jul 19, 2024 · Thermal storage systems can be categorized into three main types: sensible heat storage, latent heat storage, and thermochemical storage. Each
Get Started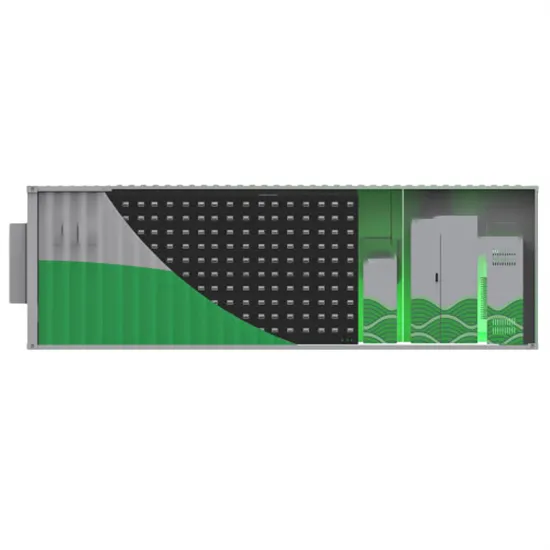
An overview of thermal energy storage systems
Feb 1, 2018 · Due to humanity''s huge scale of thermal energy consumption, any improvements in thermal energy management practices can significantly benefit the soci
Get Started
What Are the Types of Energy Storage Systems?
Apr 22, 2024 · If you''re curious about energy storage, you''re in the right place! In this guide, we''ll explore the different types of energy storage systems that are
Get Started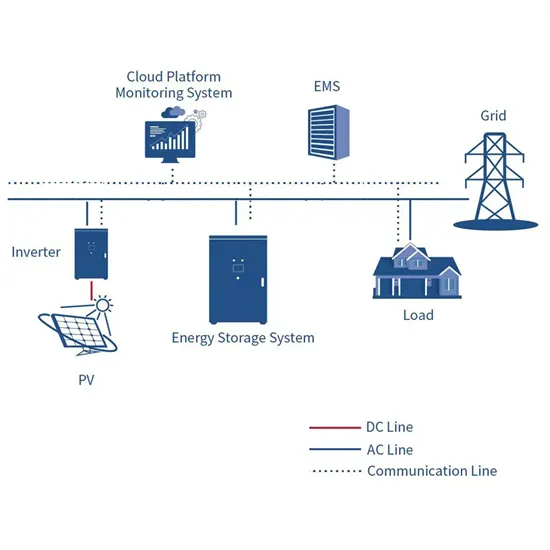
What are the types of thermal energy storage
Aug 16, 2025 · Thermal Energy Storage systems are a cornerstone of modern energy infrastructure, enabling efficient, sustainable, and reliable heating and
Get Started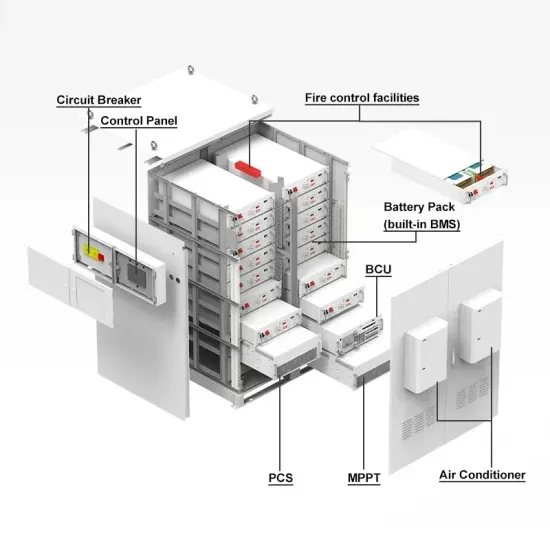
The most comprehensive guide to thermal
Aug 21, 2023 · This article will elaborate on the concept, classification, types, use scenario technology development, energy conversion process and prospects
Get Started
Renewable Energy Storage Systems
Efficient renewable energy storage systems enhance grid stability, store excess energy from solar and wind, and ensure a reliable, sustainable power supply.
Get Started
Thermal Energy Storage: A Key to Sustainable
Nov 9, 2024 · Thermal Energy Storage refers to the process of storing excess thermal energy produced during times of high demand and releasing it when
Get Started
6 FAQs about [What are the temperature energy storage systems ]
How does a thermal energy storage system work?
Energy Collection: Thermal energy is captured from a heat source. This heat might come from natural sources like solar heat (captured using solar thermal panels), industrial waste heat, or even off-peak electricity converted to heat via an electric heater. Energy Storage: The captured heat is transferred to a TES medium.
What are the different types of thermal energy storage?
Sensible Heat Storage: This is the most common type of thermal energy storage. It involves storing energy by raising the temperature of a solid or liquid, without a phase change. Common materials used for sensible heat storage include water, sand, and rocks.
What are thermal energy storage materials for chemical heat storage?
Thermal energy storage materials for chemical heat storage Chemical heat storage systems use reversible reactions which involve absorption and release of heat for the purpose of thermal energy storage. They have a middle range operating temperature between 200 °C and 400 °C.
What are some examples of thermal energy storage technologies?
For example, liquids or solids are used to store excess electrical and thermal energy. The stored heat is then used to provide thermal energy for the generator to generate electricity. 2. Types of thermal energy storage technologies
Which material properties are used in thermal energy storage applications?
Different material properties are utilized in Thermal Energy Storage (TES) applications, categorized into three methods based on thermal mechanisms: sensible heat, latent heat, and thermochemical heat. 1. Sensible thermal energy storage is a viable option for lowering energy consumption and CO 2 emissions, particularly in residential buildings.
What is a thermal storage system?
Thermal storage systems have found diverse applications in both buildings and industrial settings, driven by the need for energy efficiency and sustainability. In residential and commercial buildings, these systems are increasingly integrated into heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to optimize energy use.
Related Articles
-
 What are the compressed air energy storage power generation systems
What are the compressed air energy storage power generation systems
-
 What are the losses in energy storage systems
What are the losses in energy storage systems
-
 What are the manufacturers of battery energy storage systems for Comoros communication base stations
What are the manufacturers of battery energy storage systems for Comoros communication base stations
-
 What is the temperature of the energy storage cabinet liquid cooling cabinet
What is the temperature of the energy storage cabinet liquid cooling cabinet
-
 What are the liquid-cooled battery energy storage systems
What are the liquid-cooled battery energy storage systems
-
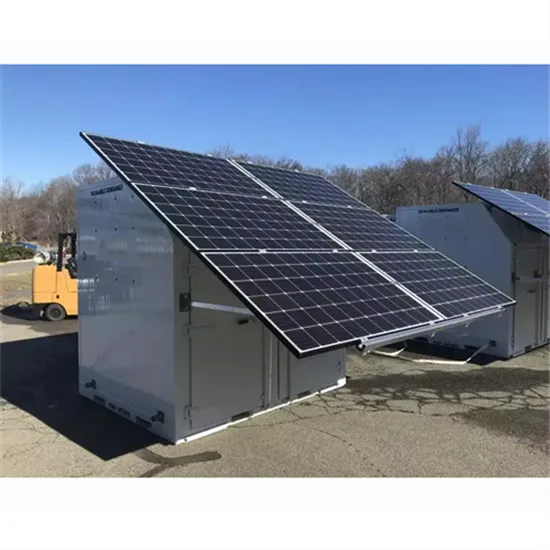 What are the photovoltaic energy storage systems in Freetown
What are the photovoltaic energy storage systems in Freetown
-
 What are the operation and maintenance technologies of battery energy storage systems for communication base stations
What are the operation and maintenance technologies of battery energy storage systems for communication base stations
-
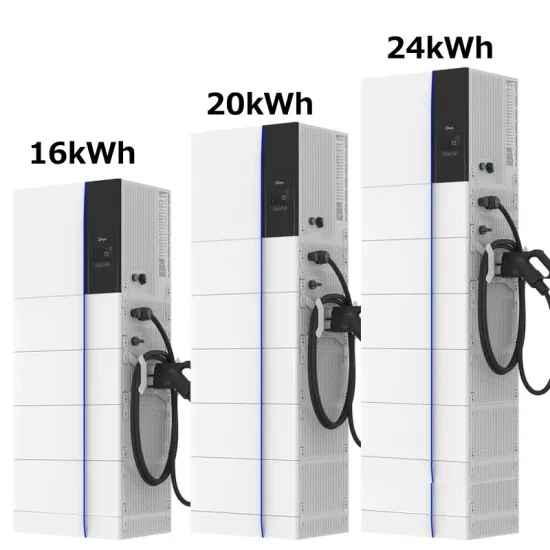 What are the fire protection systems of the energy storage station in Sao Paulo Brazil
What are the fire protection systems of the energy storage station in Sao Paulo Brazil
-
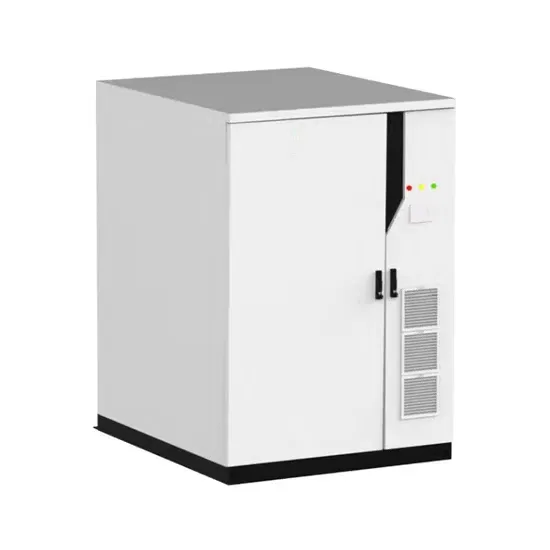 What is the battery capacity of the energy storage container
What is the battery capacity of the energy storage container
-
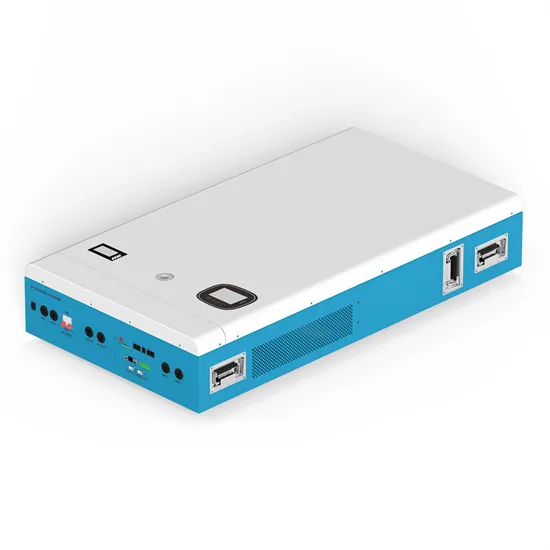 Recommended manufacturers of simple energy storage systems
Recommended manufacturers of simple energy storage systems
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


