Inverter Current Calculator, Formula, Inverter Calculation
5 days ago · Inverter Current Formula: Inverter current is the electric current drawn by an inverter to supply power to connected loads. The current depends on the power output required by the
Get Started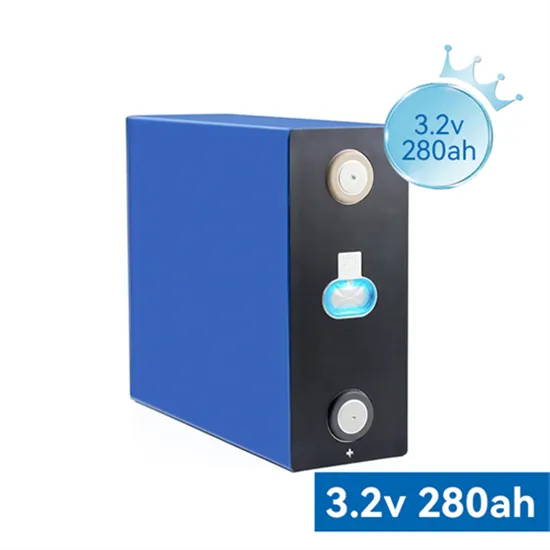
Understanding Inverters: How They Convert DC
The Basics of Power Conversion: An inverter''s primary function is to convert DC, the type of electricity stored in batteries or generated by solar panels, into AC,
Get Started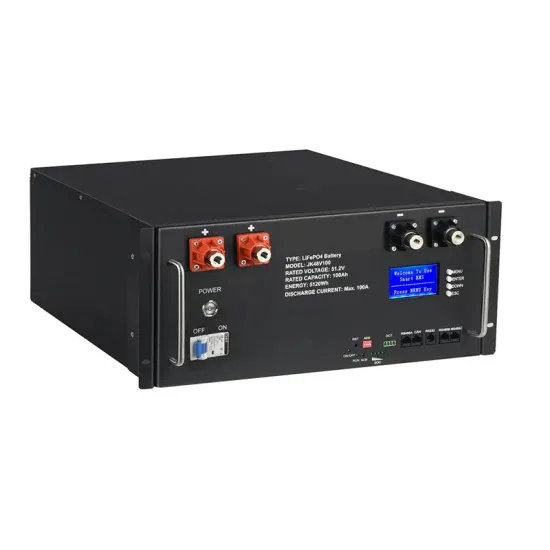
Designing an Efficient Power Inverter Circuit
Learn how to build a power inverter circuit diagram to convert DC power into AC power for various applications. Step-by-step guide and circuit diagram.
Get Started
What Is An Inverter? | Definition, Types, Uses,
Jan 25, 2025 · An inverter is a vital electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is used to power many household
Get Started
Inverter | Efficiency & Output Waveform
Jan 15, 2019 · A power inverter controls voltage and current between the source (PV array, wind turbine, or other types of DC source) and the electrical loads
Get Started
What is a Power Inverter, and How Does It Work?
Jan 21, 2020 · A power inverter is an electronic unit that converts AC power to DC power. And how do power inverters work? Power inverters behave just the
Get Started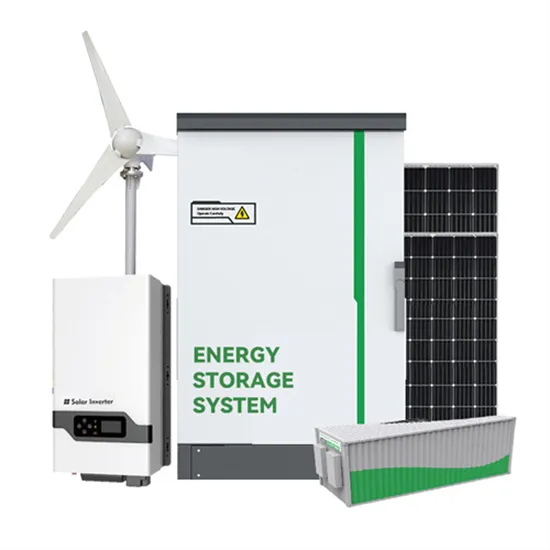
Inverter Peak Power vs Rated Power: What it is
Apr 21, 2025 · Peak power of common devices Understanding the peak power of commonly used appliances is a critical step in selecting an inverter. The
Get Started
What is an Inverter?
2 days ago · In short, an inverter converts direct current into alternating current. Direct current is used in many of the small electrical equipment such as solar
Get Started
Inverter Power Calculator, Formula,Inverter Calculation
4 days ago · Inverter power (Pi) refers to the power output provided by an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources such as batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC)
Get Started
A Compilation of the Best Power Inverters and
Oct 31, 2024 · The Power Behind Modern Energy Systems: Inverters and Converters Differences Between Inverters and Converters What is an
Get Started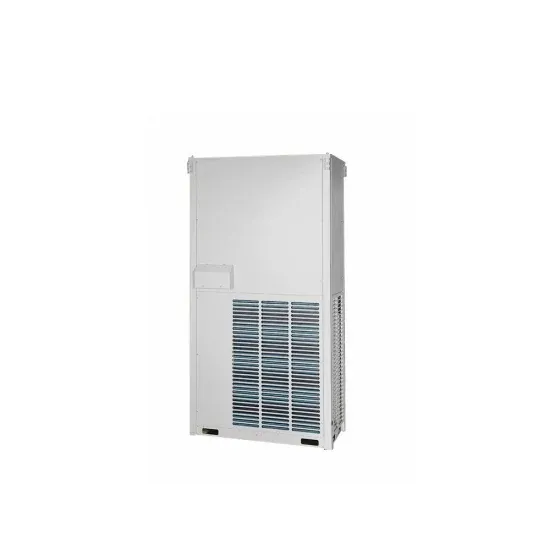
Inverter Power Calculator, Formula,Inverter Calculation
4 days ago · Inverter Power Formula: Imagine a solar panel system. The panels generate direct current (DC) electricity. But most appliances run on alternating current (AC). Here''s where
Get Started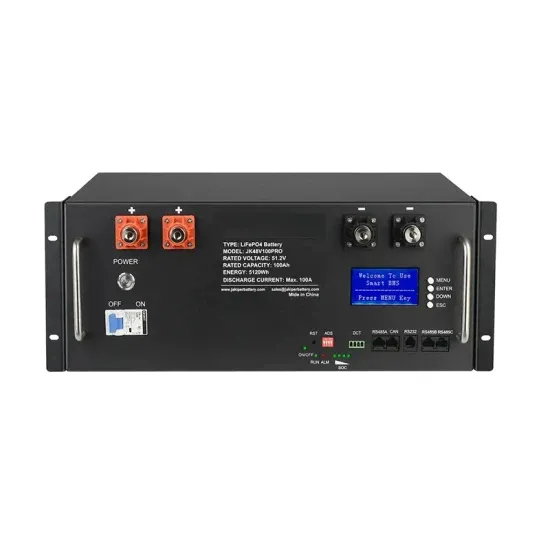
What is an inverter? | inverter
Aug 11, 2019 · The power inverter can provide AC household power on the move, ideal for charging the electronics or appliances such as mobile phones, iPad, computers, TV, washing
Get Started
Types of Inverters and their Applications
3 days ago · Related Post: Difference between Inverter & UPS – Uninterruptible Power Supply Different Types of Inverters Inverters are classified into many
Get Started
Power Inverters Explained
Apr 25, 2020 · Learn the basic working principle of power inverters, how they work, what they are used for, where we use them and their importance along
Get Started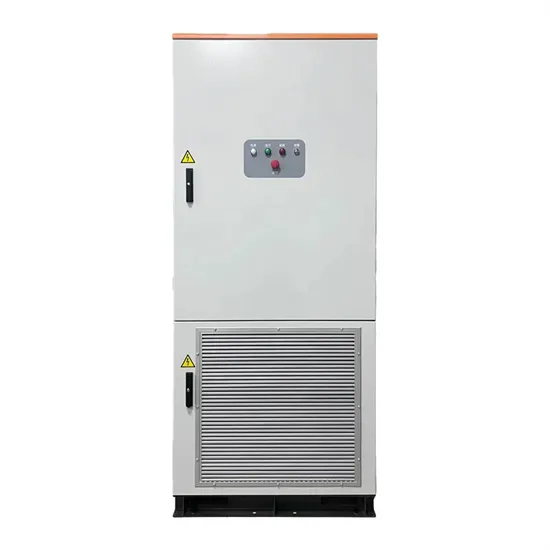
Types of Power Inverters And How To Choose
Apr 15, 2024 · Discover the different types of power inverters and learn how to choose the right one for your needs. Expert advice from Junchipower.
Get Started
Inverter | Efficiency & Output Waveform
Jan 15, 2019 · The article provides an overview of inverters in renewable energy systems, focusing on their role in converting DC to AC, their efficiency, and
Get Started
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters:
May 10, 2024 · Unlock the potential of power supply with our comprehensive guide on all about inverters - discover types, benefits, and tips for the perfect
Get Started
What Is An Inverter
Sep 12, 2023 · What Is An Inverter, And How Does It Work? In simple terms, an inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into
Get Started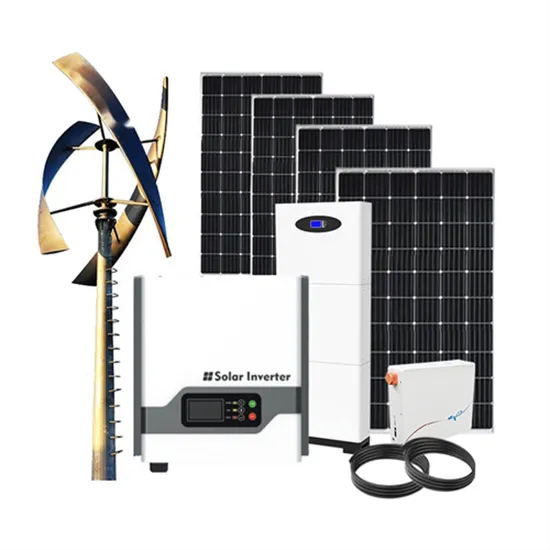
How to Calculate the Power Requirements for an Inverter | ehow
Mar 29, 2010 · While most plug-in electrical appliances are designed to run on alternating current (AC) power, batteries and emergency generators produce direct current (DC) power. To
Get Started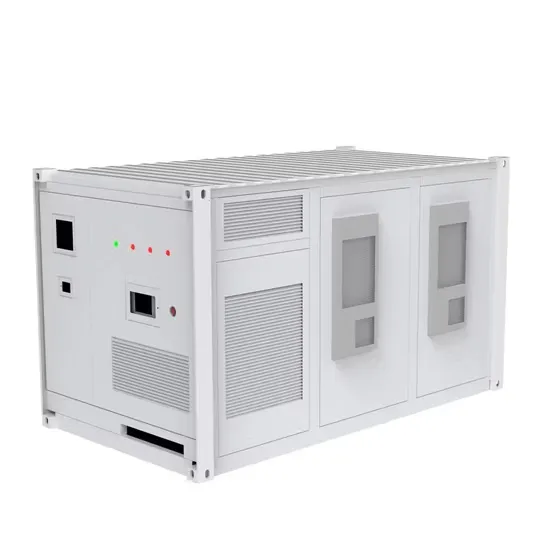
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Jul 8, 2025 · Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
Get Started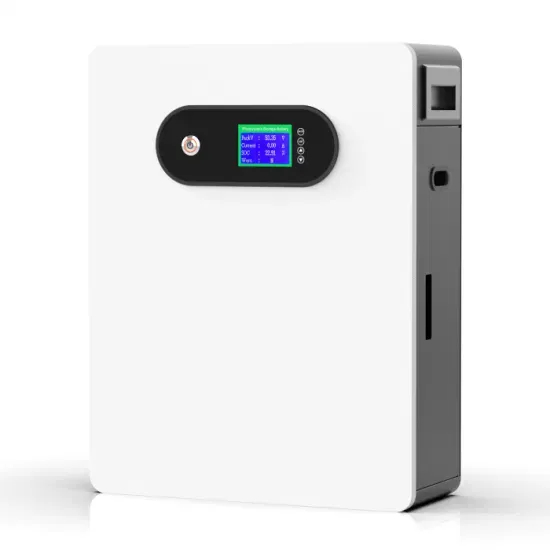
What Are The Components Of An Inverter
Jan 27, 2025 · Discover what are the components of an inverter, including the DC input source, power electronics circuit, and control systems. Learn how
Get Started
Everything You Need to Know About the Split Phase Inverter
Mar 13, 2025 · One big advantage of split phase inverters is their high power output; they are perfect for big electrical needs like industrial machines or large homes; in addition, they work
Get Started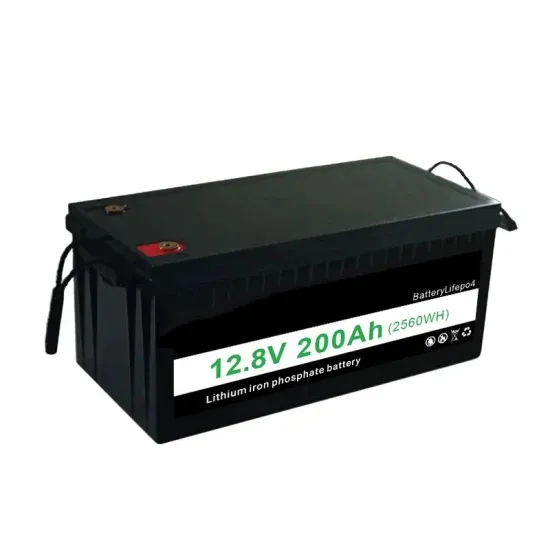
What is the Peak Output Power of a Power Inverter?
May 25, 2022 · What is an inductive load? High-power electrical products made by electromagnetic induction, such as motors, compressors, relays, fluorescent lamps, etc.,
Get Started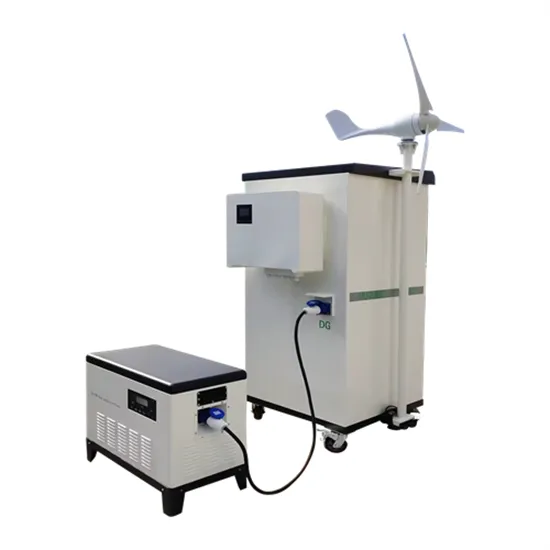
Power Inverters: The Need-to-Know Essentials
Nov 29, 2022 · Solar inverters convert the variable DC output of photovoltaic solar panel cells into AC that is then fed into a commercial electrical grid. Solar inverters are either stand-alone
Get Started
Solar Integration: Inverters and Grid Services Basics
4 days ago · Inverters are just one example of a class of devices called power electronics that regulate the flow of electrical power. Fundamentally, an
Get Started
Power Inverter Calculator
Dec 28, 2023 · The Power Inverter Calculator is a valuable tool for engineers and enthusiasts working with electrical systems. Its ease of use and accurate calculations make it
Get Started
What is an Inverter?
2 days ago · Grid Tie inverters In case of Grid Tie inverters, as their name indicates, the output AC power is supplied to a grid type network, i.e. a larger
Get Started
Introduction to Inverters
Jul 23, 2025 · Inverter is an important device because it provides power source when there are power cuts. It can turn on electrical appliances and can be an
Get Started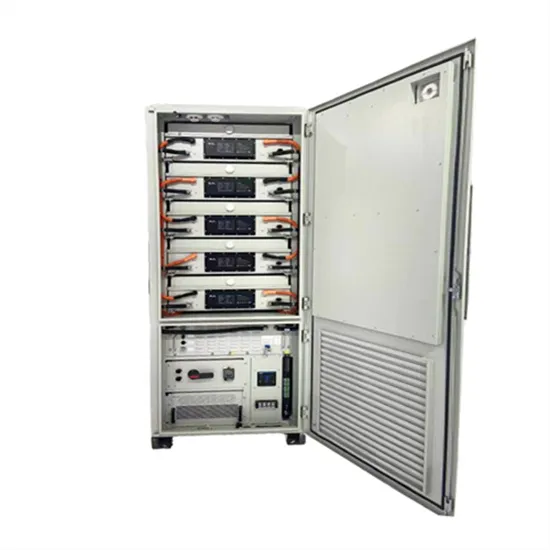
Types of Power Inverters And How To Choose
Apr 15, 2024 · Grid-tied inverters (GTI) can be used with batteries and the public grid. It converts DC power from the battery (from the solar system) into AC
Get Started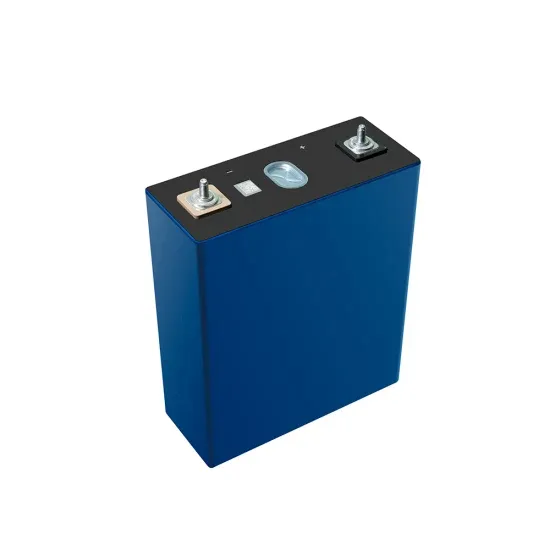
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What
3 days ago · The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input source into alternating current
Get Started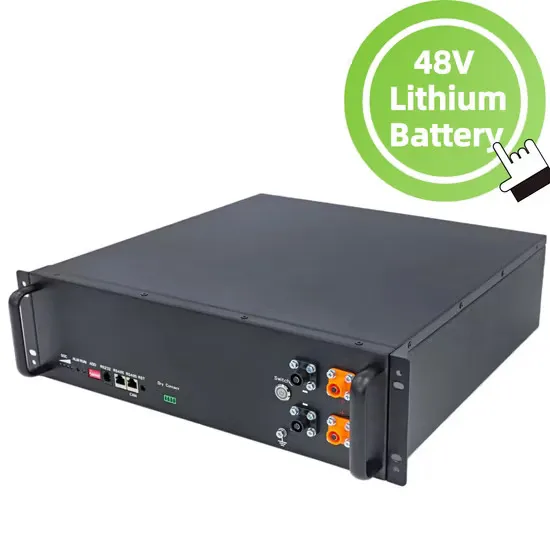
CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
Mar 27, 2016 · The inverter first converts the input AC power to DC power and again creates AC power from the converted DC power using PWM control. The inverter outputs a pulsed
Get Started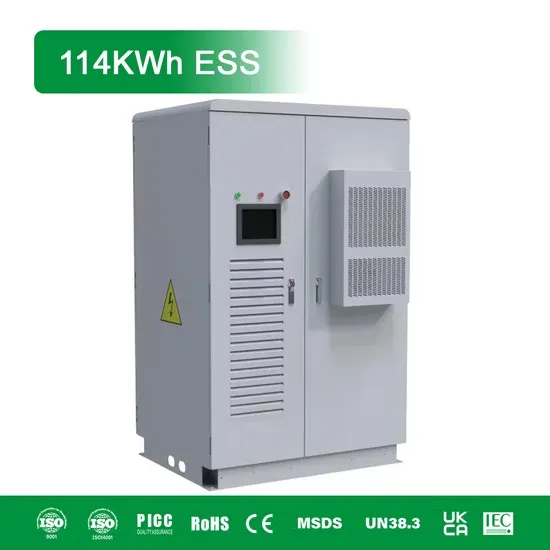
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
2 days ago · The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an
Get Started
How Inverters Work
Dec 15, 2017 · How do Inverters work? In this article we''ll be learning how inverters work, starting from the very basics. We''ll cover Pulse Width
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Inverter electrical output power]
What is inverter output?
The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input source into alternating current (AC).
What is a power inverter?
A power inverter, or inverter, is an electronic device or circuitry that converts DC to AC. You might find these chapters and articles relevant to this topic. Abolfazl Ghasemi, ... Sherif Abdelwahed, in Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013 A power inverter is used to maintain the flow of energy from DC to AC buses .
What is a DC inverter?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working Principle: Inverters use power electronics switches to mimic the AC current’s changing direction, providing stable AC output from a DC source.
How do inverters work?
Working Principle: Inverters use power electronics switches to mimic the AC current’s changing direction, providing stable AC output from a DC source. Types of Inverters: Inverters are categorized by their output waveforms (square wave, modified sine wave, and sine wave) and by their load type (single-phase and three-phase).
How does inverter input voltage work?
Inverter input voltage depends on input from batteries or sources such as PV arrays or wind turbines. Smaller systems supplying less power will have less current and the voltage supplying the inverter, and larger systems with more power will have higher current and voltage inputs.
What power sources use an inverter to change DC to AC?
The outputs of PV cells, fuel cells, some wind turbine generators, and other renewable energy devices are DC, but most of the world uses AC power. Therefore, DC power sources use an inverter to change DC to AC. Early inverters were rotary motor–generators, connected by a shaft, and they mechanically converted/inverted DC to AC.
Related Articles
-
 PV inverter output power
PV inverter output power
-
 Output power discrete rate inverter
Output power discrete rate inverter
-
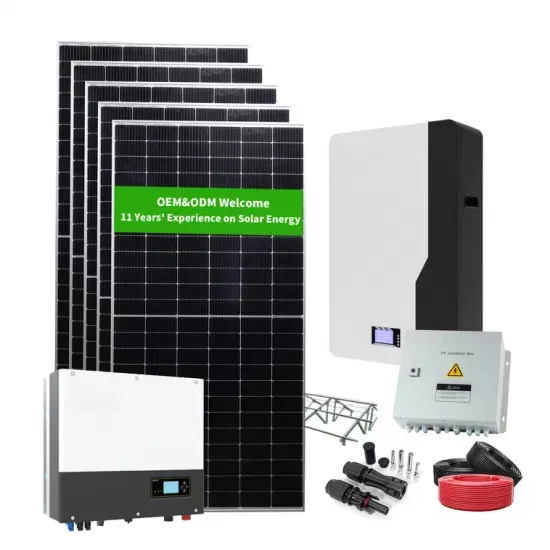 Pure sine wave output power frequency inverter
Pure sine wave output power frequency inverter
-
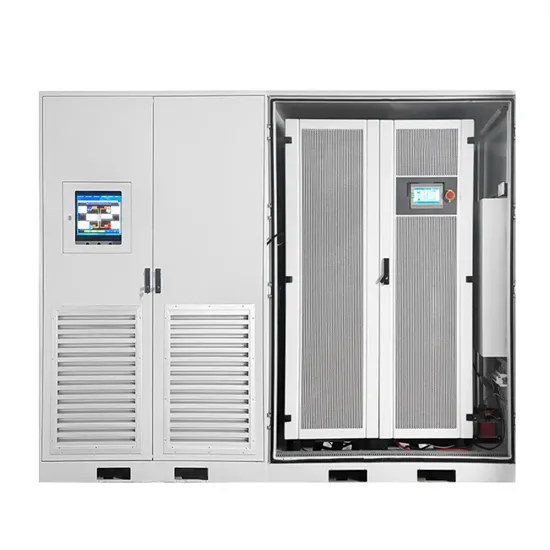 Inverter output power is too low
Inverter output power is too low
-
 Andorra City three-phase output power frequency inverter
Andorra City three-phase output power frequency inverter
-
 Inverter rated power 1500
Inverter rated power 1500
-
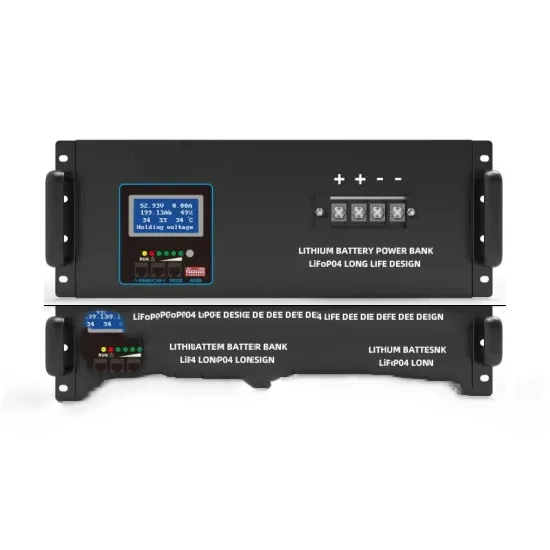 Can the power of photovoltaic inverter be adjusted
Can the power of photovoltaic inverter be adjusted
-
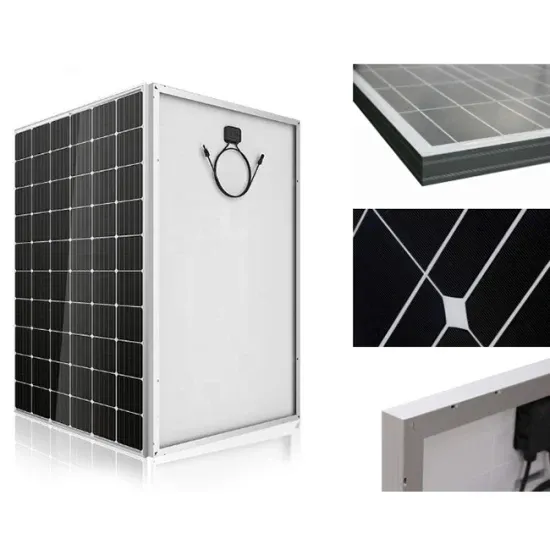 Portable power supply with stable output of 24V
Portable power supply with stable output of 24V
-
 UPS uninterruptible power supply does not output
UPS uninterruptible power supply does not output
-
 Small outdoor power supply with large output
Small outdoor power supply with large output
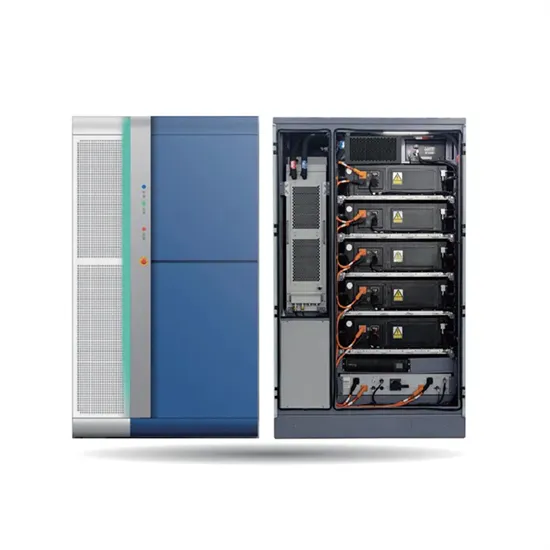
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
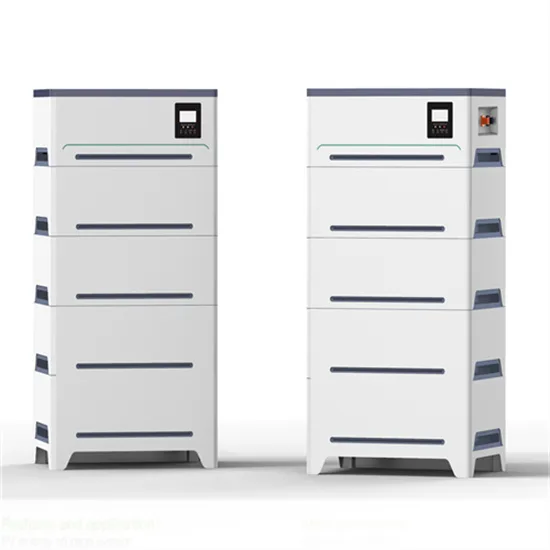
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


