Can A Micro Inverter Be Plugged Directly Into An
Jan 17, 2024 · Addressing Safety and Code Compliance One big question is: how do we plug directly into the grid safely? There''s a risk of back-feeding the grid
Get Started
Resiliency improvement through grid forming inverter
Oct 23, 2024 · Passive filters play a vital role in ensuring that grid-connected inverters comply with grid rules. The inverter output voltage and current are going to have ripple components (Kim
Get Started
DESIGNING OF GRID CONNECTED INVERTER FOR PV
Jun 7, 2021 · The second category is a grid-connected PV system where the generated electricity is directly used and there is no need for storage. This study investigates this category since
Get Started
Grid-Connected Inverter System
4 Grid-connected inverter control techniques Although the main function of the grid-connected inverter (GCI) in a PV system is to ensure an efficient DC-AC energy conversion, it must also
Get Started
Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes,
Jan 1, 2024 · Auxiliary functions should be included in Grid-connected PV inverters to help maintain balance if there is a mismatch between power generation and load demand. The goal
Get Started
Optimised configuration of multi-energy systems
Dec 30, 2024 · Additionally, exploring the integration of communication base stations into the system''s flexibility adjustment mechanisms during the configuration is important to address the
Get Started
An Overview of the Roles of Inverters and Converters in
Feb 28, 2024 · Microgrids signify a transformative approach in energy distribution, pivoting away from traditional power grids toward a more decentralized, efficient, and sustainable model.
Get Started
Control and Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected Inverters in
Jan 14, 2025 · Increasing the penetration of grid-connected inverters and integration of single-phase microgrids (MG) and unbalanced loads into three-phase MGs result in power quality
Get Started
Smart Inverters for Microgrid Applications: A
Mar 4, 2019 · In a microgrid, with several distributed generators (DGs), energy storage units and loads, one of the most important considerations is the
Get Started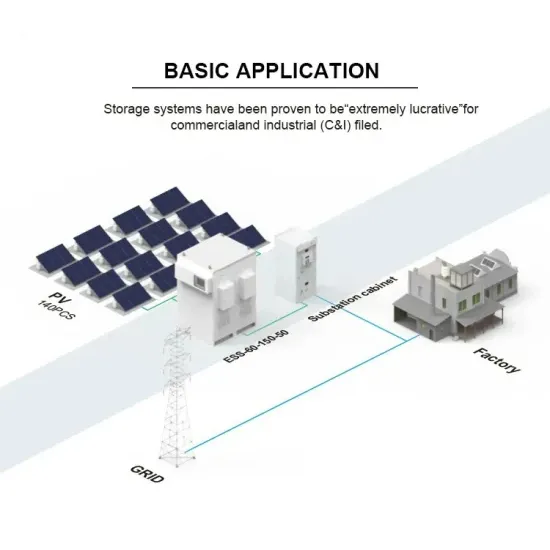
A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
Oct 1, 2018 · The requirements for the grid-connected inverter include; low total harmonic distortion of the currents injected into the grid, maximum power point tracking, high efficiency,
Get Started
Synchronization of Inverters in Grid Forming Mode
Apr 14, 2022 · Abstract: This article compares two strategies for seamless (re)connection of grid-forming inverters to a microgrid powered by droop-controlled inverters. While an incoming
Get Started
Overcurrent Limiting in Grid-Forming Inverters: A
Jul 18, 2024 · Grid-forming (GFM) inverters are increasingly recognized as a solution to facilitate massive grid integration of inverter-based resources and enable 100% power-electronics
Get Started
Grid-Forming Inverters for Grid-Connected Microgrids:
Mar 4, 2022 · The electric power grid is in transition. For nearly 150 years it has supplied power to homes and industrial loads from synchronous generators (SGs) situated in large, centrally
Get Started
A Review of Current Control Schemes in Grid Connected Inverters
Dec 5, 2024 · Abstract: Grid connected inverters (GCI)s are attracting the attention of the researchers and industrialists due to the advantages it offers to the grid, such as providing
Get Started
Grid Forming Inverters: EPRI Tutorial (2021)
In most cases, commercially available BESS inverters will operate in grid following mode when grid connected and transition to grid forming mode when islanded. Larger scale grid forming
Get Started
Communication Base Station Innovation Trends | HuiJue
Rethinking Infrastructure for the 5G-Advanced Era As global mobile data traffic surges 35% annually, communication base stations face unprecedented demands. Can traditional tower
Get Started
Grid-Forming Inverters: Project Demonstrations and Pilots
Feb 23, 2024 · Power system operators around the world are pushing the limits of integrating inverter-based resources (IBRs) to very high levels, approaching 100% instantaneous
Get Started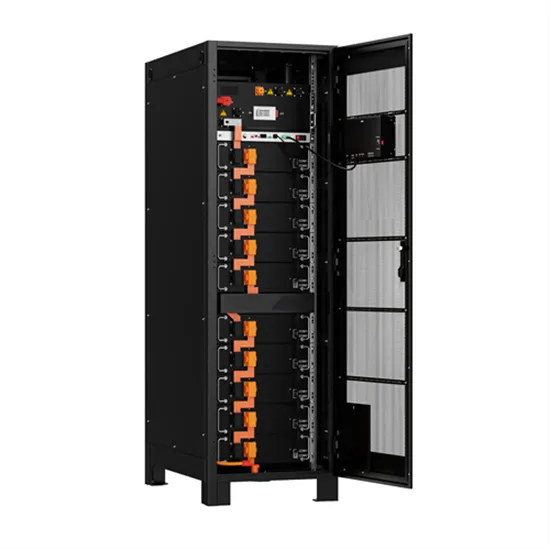
Design Power Control Strategies of Grid-Forming
Jan 28, 2022 · Strategy II has good tracking performance for both active and reactive power with an acceptable settling time. The low PCC voltage has a larger impact for Strategy I because
Get Started
Inverter communication mode and application scenario
Jul 15, 2025 · When using GPRS/4G communication mode, each inverter needs to be equipped with a data collector with GPRS/4G communication module, built-in SIM card or use an
Get Started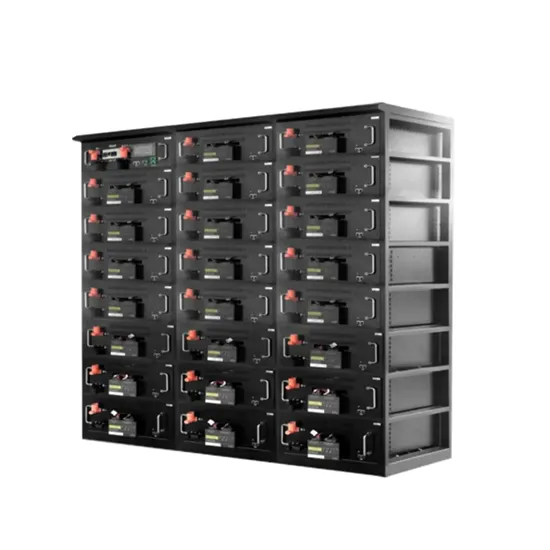
Inverter-based islanded microgrid: A review on
Jan 1, 2022 · In the classification based on the mode of operation, inverters can be classified into three broad categories: autonomous inverters (supplies stable voltage and frequency to load),
Get Started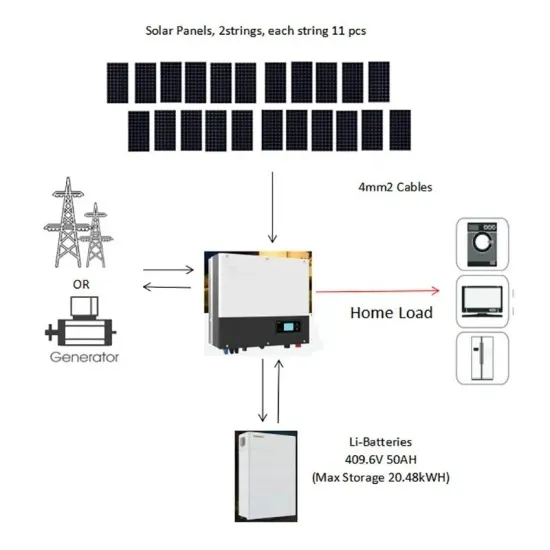
How Does a Solar Farm Connect to the Grid?
All solar farms connect to a specific point on the electrical grid, the vast network of wires that connects every power generation plant to every home and business
Get Started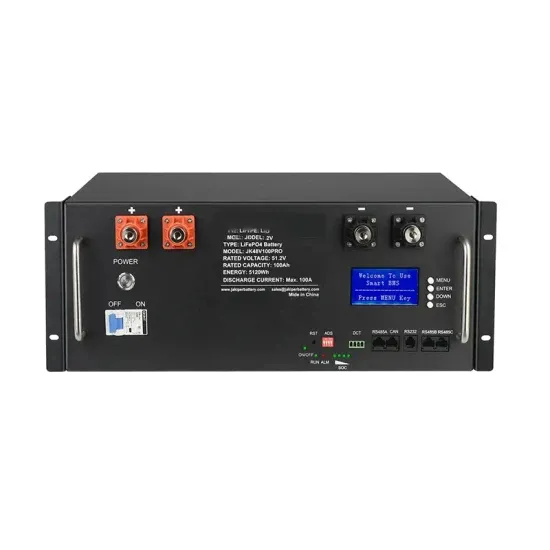
Running Inverters in Parallel: A Comprehensive
Jul 14, 2023 · Inverters are vital for converting DC to AC in solar and renewable energy systems. Running inverters in parallel is indeed possible. This article
Get Started
Inverter Transformers for Photovoltaic (PV) power plants:
Dec 22, 2022 · I. INTRODUCTION Utility scale photovoltaic (PV) systems are connected to the network at medium or high voltage levels. To step up the output voltage of the inverter to such
Get Started
Design Power Control Strategies of Grid-Forming
Jan 28, 2022 · Background grid-forming inverter control: PQ in grid-connected (current and VF in islanded mode (voltage source) phase jump during microgrid transition operation use grid
Get Started
2MW_PCS_BESS2010 dd
Mar 15, 2024 · The demand for battery systems will grow as the benefits of using them on utility grid networks is realized. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) can store energy from
Get Started
Solar Transformers: Sizing, Inverters, and E
May 29, 2024 · Learn all about transformer sizing and design requirements for solar applications—inverters, harmonics, DC bias, overload, bi-directionality,
Get Started
Analysis of Solar Powered Micro-Inverter Grid
Oct 27, 2023 · In Nigeria where most of the site stations are not directly connected to the electricity grid and if the grid fails as in most of the time, these sites are powered by diesel
Get Started
Synchronization of Three Phase Inverter with Electrical Grid
Mar 8, 2022 · Abstract - Phase, frequency, and amplitude of phase voltages are the most important and basic parameters need to be controlled or grid-connected applications. The aim
Get Started
Transformerless Photovoltaic Inverters Connected to the Grid
Feb 25, 2007 · Renewable energy sources are getting more and more widespread, mainly due to the fact that they generate energy by keeping the environment clean. Most of these systems
Get Started
Synchronization of Inverters in Grid Forming Mode
ABSTRACTThis article compares two strategies for seamless (re)connection of grid-forming inverters to a microgrid powered by droop-controlled inverters.
Get Started
SoC–Based Inverter Control Strategy for Grid-Connected
Jan 23, 2025 · By mimicking the behavior of the synchronous generators, droop control enables the decentralized and autonomous operation of multiple inverters in a microgrid (MG) [16]. The
Get Started
Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study
Mar 20, 2025 · This approach ensures stable operation in both islanded and grid-connected modes, providing essential grid support functions such as
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Are there any communication base station inverters connected to the grid in Micronesia ]
Can grid-forming inverters be reconnected to a microgrid powered by droop-controlled inverter?
Abstract: This article compares two strategies for seamless (re)connection of grid-forming inverters to a microgrid powered by droop-controlled inverters. While an incoming inverter must be synced to the microgrid, seamless syncing and power-sharing are technical challenges for grid-forming inverters.
What is an inverter based microgrid?
An inverter-based MG consists of micro-sources, distribution lines and loads that are connected to main-grid via static switch. The inverter models include variable frequencies as well as voltage amplitudes. In an inverter-based microgrid, grid-connected inverters are responsible for maintaining a stable operating point [112, 113].
How do grid-forming inverters work?
While an incoming inverter must be synced to the microgrid, seamless syncing and power-sharing are technical challenges for grid-forming inverters. In the first strategy, called the output-sync method, an incoming inverter is synced to the microgrid, and then the circuit breaker is closed for power-sharing.
Are inverter-based energy sources the same as SGS?
Today, we have more and more renewable energy sources—photovoltaic (PV) solar and wind—connected to the grid by power electronic inverters. These inverter-based resources (IBRs) do not have the same characteristics as SGs, such as inertia and high fault current. This mismatch has not been a problem until now.
How does active power control work in a Bess inverter?
Step changes in the inverter’s reference power show the strategy’s quick adaptation to reactive power demands, while maintaining a stable active power supply. Furthermore, active power control disconnects the BESS when it approaches its lower SoC limit in a near-depleted battery scenario.
Why do inverters mismatch the power grid?
This mismatch has not been a problem until now. Inverters have assumed that the grid is strong and will provide a stable and clean voltage and that they are able to inject real power into the grid without undue impact on its operation. The electric power grid is in transition.
Related Articles
-
 There are communication base station inverters connected to the grid around the house
There are communication base station inverters connected to the grid around the house
-
 The first batch of communication base station inverters in Panama are connected to the grid
The first batch of communication base station inverters in Panama are connected to the grid
-
 What to do if the communication base station inverter is connected to the grid and is struck by lightning
What to do if the communication base station inverter is connected to the grid and is struck by lightning
-
 What types of inverters are connected to the grid for communication base stations
What types of inverters are connected to the grid for communication base stations
-
 Guatemala communication base station inverter connected to the grid on residents roofs
Guatemala communication base station inverter connected to the grid on residents roofs
-
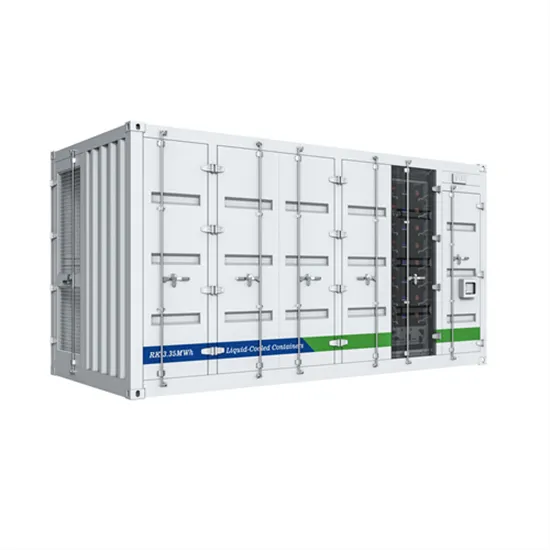 A small communication base station inverter in Georgetown is connected to the grid
A small communication base station inverter in Georgetown is connected to the grid
-
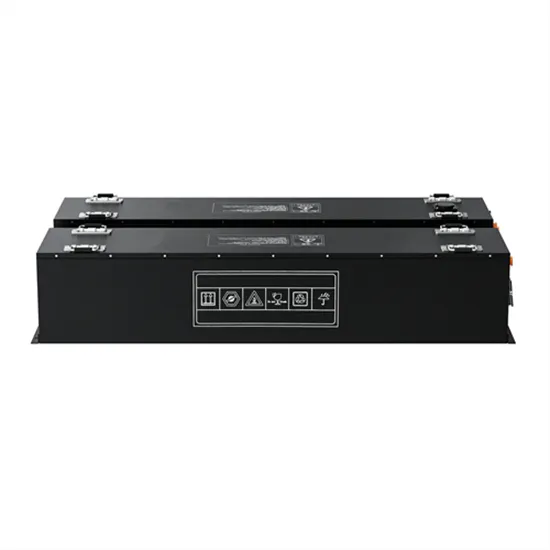 Luxembourg communication base station inverter grid connection construction bidding
Luxembourg communication base station inverter grid connection construction bidding
-
 Portable test communication base station inverter grid connection construction
Portable test communication base station inverter grid connection construction
-
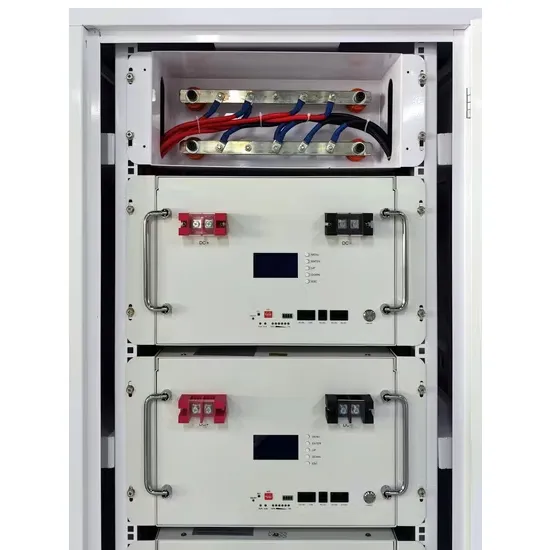 The highest communication base station inverter grid connection
The highest communication base station inverter grid connection
-
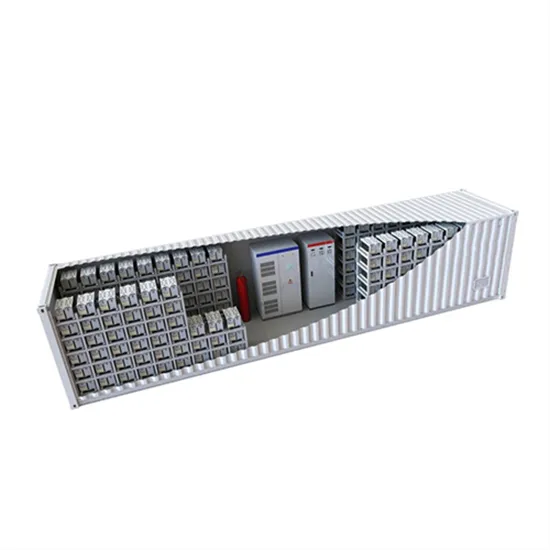 Tendering for the communication base station inverter grid connection project
Tendering for the communication base station inverter grid connection project
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.