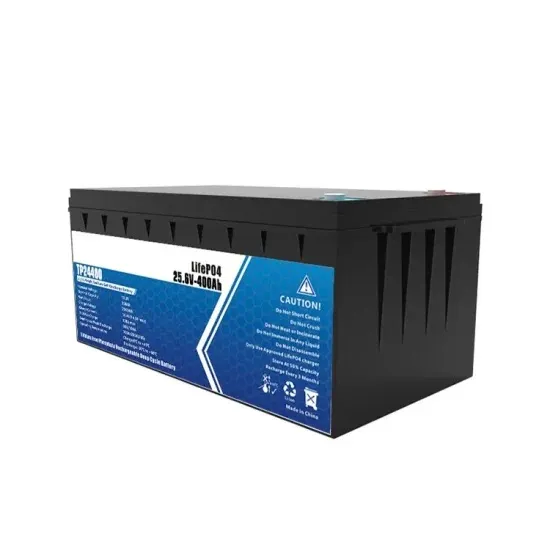
What is a High-Frequency Power Inverter?
1 day ago · Introduction A power inverter converts DC power into AC power for operating AC loads and equipment. High-frequency power inverters utilize
Get Started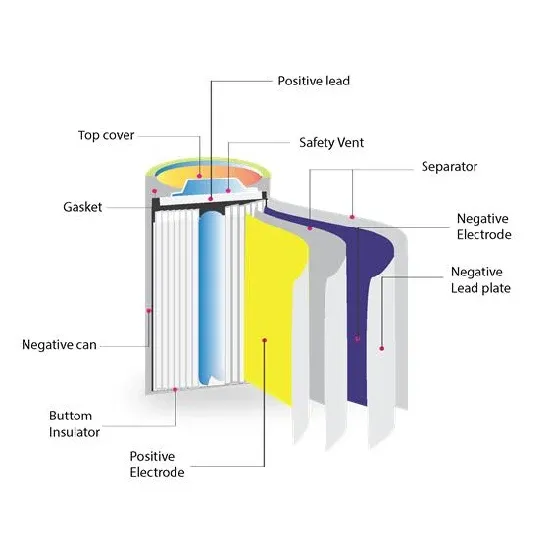
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters:
Feb 10, 2025 · An inverter is a key component that converts DC power into AC power for household appliances and is commonly used in solar energy
Get Started
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key
Aug 15, 2025 · Low frequency inverters are larger and handle surges better, while high frequency inverters are compact and cost-effective. Which inverter is
Get Started
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency
Aug 18, 2025 · Discover the disparities between high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter in this concise article, aiding your decision-making process.
Get Started
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · If you are looking for an inverter for fixed power stations, precision instruments, or other related fields, then go with power-frequency inverters. However, a high-frequency
Get Started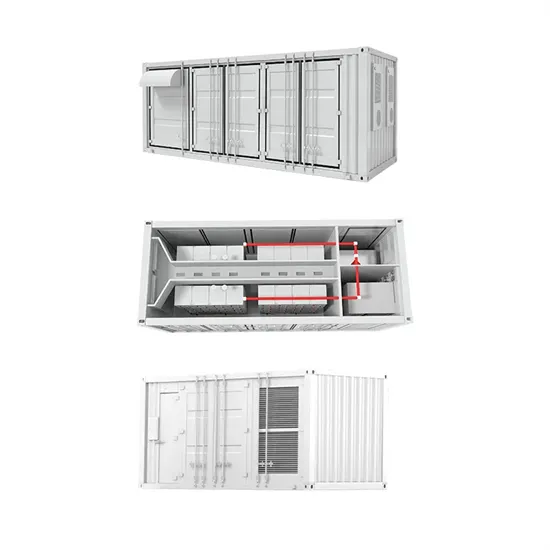
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
May 15, 2024 · High frequency inverter: High frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology to chop DC power at high frequency through
Get Started
Difference Between High-Frequency (HF) and
Dec 25, 2023 · Are you trying to figure out the differences between High-Frequency (HF) and Low Frequency (LF) Solar Inverters? Choosing the right
Get Started
Frequency Inverter | inverter
A frequency inverter also called frequency converter, is a power control conversion device to convert normal power supply (50Hz or 60Hz) to another frequency power by inner power
Get Started
Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions
Dec 11, 2023 · The frequency inverter is a power control equipment that applies frequency conversion technology and microelectronics technology to control
Get Started
Understanding the Difference Between Low
Mar 7, 2023 · There are two types of inverters, low frequency and high frequency inverters. Inverters are used in solar power systems, wind turbines, and
Get Started
Low-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters:
Dec 3, 2024 · Choosing the right inverter is key to maximizing your solar system''s efficiency. Explore the differences between high-frequency and low-frequency
Get Started
Key Differences Between Frequency Inverters and Inverters
Power inverters, on the other hand, are generally more affordable. High-frequency models offer cost-effective solutions for portable or residential applications. Weighing the initial investment
Get Started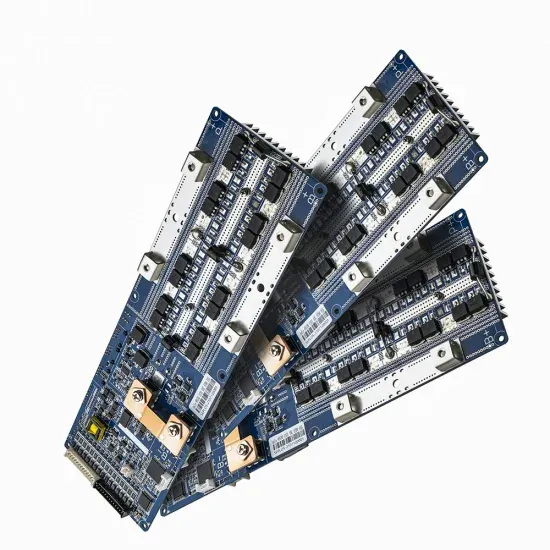
Low-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters: Technical
Jul 17, 2025 · This analysis evaluates the performance characteristics of low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) inverters based on current industry data and technical literature.
Get Started
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and
Oct 1, 2024 · Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments In today''s world, inverters play a vital role in various applications, such as home
Get Started
Low frequency inverter vs high frequency
Mar 12, 2025 · More Durable & Reliable: The transformer-based design enhances longevity and stability, making it more resistant to power fluctuations. Easier to
Get Started
High-frequency versus low-frequency inverters which is right
Jun 13, 2025 · Compare high-frequency and low-frequency frequency inverters to find the best fit for your power needs, efficiency, surge capacity, and reliability.
Get Started
Complete Comparison: High Frequency vs Low Frequency Inverters
May 7, 2025 · 🏋️♂️ Low-Frequency Inverters: Durable and Powerful Key Benefits 🔸 Superior Durability Perfect for Pakistan''s high temperatures and dust. These inverters handle tough
Get Started
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
2. Low Frequency Inverters: Robust and Durable: Low frequency inverters are better suited for applications requiring high power output and reliability. Their robust design allows them to
Get Started
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters:
4 days ago · High-frequency inverters are more budget-friendly, making them a cost-effective solution for budget-conscious buyers with modest power
Get Started
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Learn the key differences between high frequency inverters and low frequency inverters. Discover which one suits your power needs for efficiency and surge capacity.
Get Started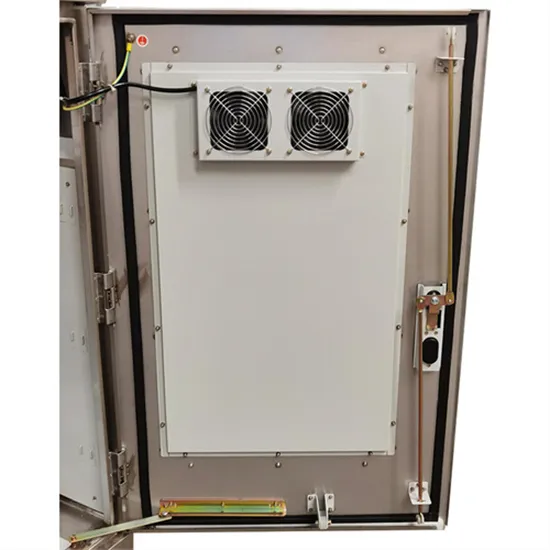
Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of power frequency
Apr 14, 2024 · High-frequency inverters, whose operating frequency significantly exceeds traditional power frequency inverters, specifically refer to a device that can convert low-voltage
Get Started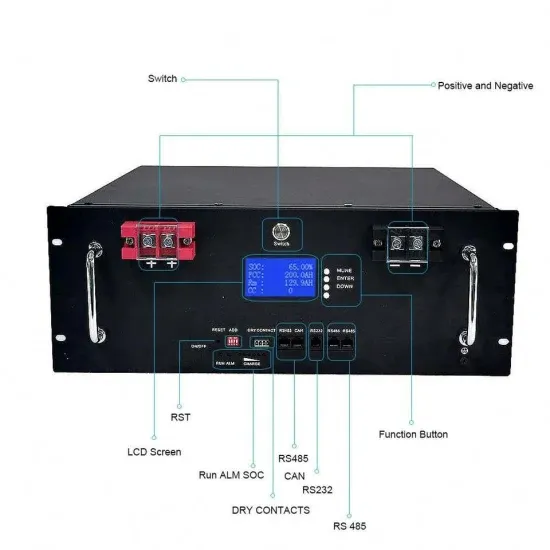
Low-frequency Inverter Vs. High Frequency
The high-frequency inverter uses MOSFETs, which use electronic switching and are more prone to damage, especially at high power levels. On the other
Get Started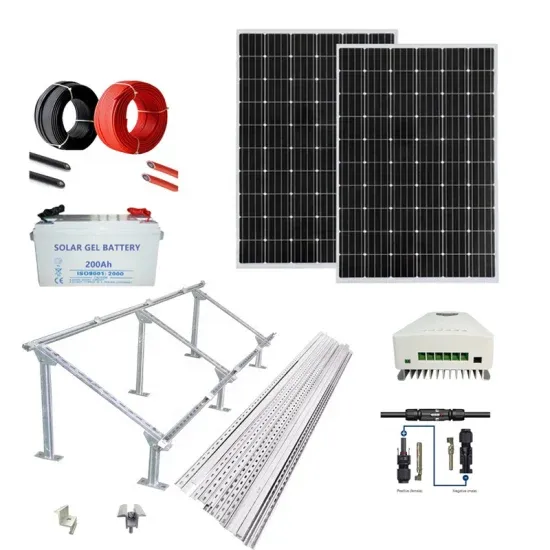
Which is better, power frequency inverter or high-frequency inverter?
Sep 20, 2024 · If the installation space is sufficient and the durability of the equipment is considered, choose a pure sine wave power frequency inverter, and so on. If there is a greater
Get Started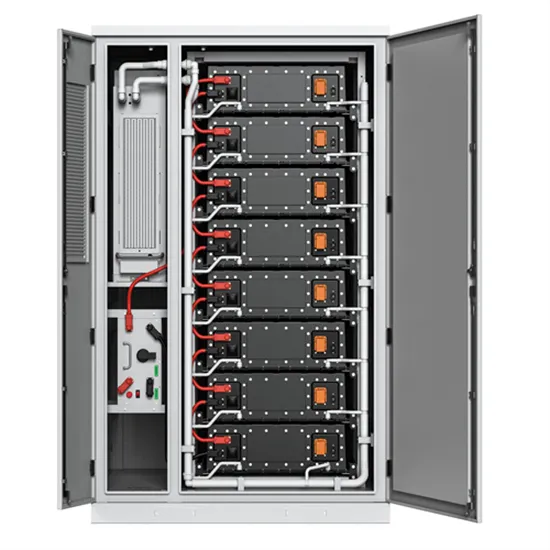
High-frequency Power Inverter
When comparing high-frequency power inverters with traditional low-frequency inverters, several differences become apparent. First, HF power inverters are generally more compact and
Get Started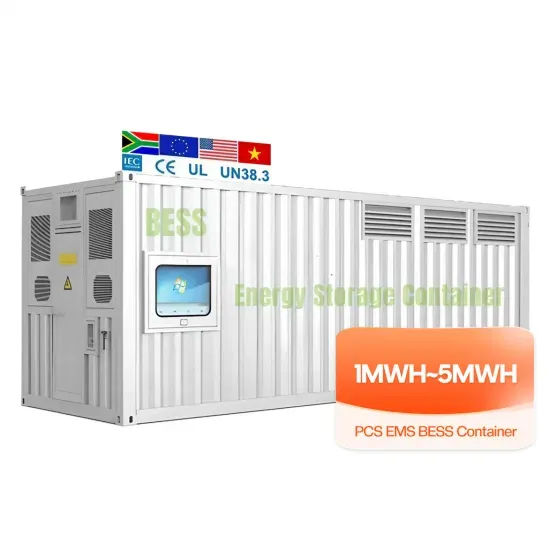
HIGH VS LOW FREQUENCY INVERTERS
Nov 28, 2022 · The second main difference is reliability: low-frequency inverters operate using powerful transformers, which are more reliable and sturdy than the high-frequency inverter''s
Get Started
What''s the difference between a high frequency and Low frequency inverter?
Low-frequency inverters use powerful transformers that are more reliable than high-frequency MOSFETs which use electronic switching, and more susceptible to damage at higher power
Get Started
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
Aug 16, 2016 · By definition, Low frequency power inverters got the name of "low frequency" because they use high speed power transistors to invert the DC
Get Started
Comparing High Frequency UPS and Low Frequency UPS
Mar 27, 2025 · Low-frequency inverters are more durable, handle higher surge loads, and provide better power quality but are bulkier and more expensive. High-frequency inverters are lighter,
Get Started
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters:
4 days ago · On the other hand, a high-frequency inverter is efficient for light to medium loads. Its advanced switching technology minimizes energy losses,
Get Started
Low-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters: Technical
Jul 17, 2025 · This analysis evaluates the performance characteristics of low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) inverters based on current industry data and technical literature. Key
Get Started
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · High-frequency inverters consume less power from the battery at zero load than power-frequency inverters. Power-frequency inverters are best for their robustness and
Get Started
Understanding the Differences
3 days ago · Conclusion Whether opting for a low-frequency or high-frequency solar inverter depends on the individual''s specific requirements and priorities. Low-frequency inverters offer
Get Started
What''s The Difference between A High Frequency And Low Frequency
Cost Considerations The cost of solar inverters plays a significant role in determining which type of inverter is best for your solar power system. High-frequency (HF) and low-frequency (LF)
Get Started
Ultimate Guide to the 3kW LF Inverter: Power, Battery Sizing,
May 2, 2025 · High Frequency Technology: Compared to other types of inverters, high frequency inverters seem to be more compact and lightweight, and more affordable, but then, its surge
Get Started
Inverter vs. Generator: Which One Is More Durable?
Feb 14, 2025 · Choosing between an Inverter vs. Generator? This guide answers Inverter vs. Generator: Which One Is More Durable?by exploring their durability, maintenance, and
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Which high-frequency power frequency inverter is more durable]
What is a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverter: High frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology to chop DC power at high frequency through high-frequency switching tubes (such as IGBT, MOSFET, etc.), and then convert high-frequency pulses into stable alternating current through high-frequency transformers and filter circuits.
What are the advantages of high frequency inverters?
Volume and weight: Since high frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology and compact circuit design, their size and weight are usually much smaller than power frequency inverters. This gives high frequency inverters significant advantages in mobile power supplies, aerospace, electric vehicles, and other fields.
What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency inverters?
Low-frequency Inverters are designed to handle high-surge loads, typically 2-5 times their rated power output. This makes them perfect for refrigerators, compressors, or air conditioners requiring extra power during startup. High-frequency inverters typically have 1.5-2 times their rated power, which limits their surge capacity.
Why are frequency drive inverters more efficient?
Efficiency and energy consumption: Because frequency drive inverters use high-frequency switching technology, their switching losses and iron losses are relatively small, so their efficiency is usually higher than that of power frequency inverters.
Are high-frequency inverters a good choice?
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high efficiency, but they also have the problem of relatively poor output waveform quality.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a low frequency inverter?
The advantages of a low frequency inverter include: relatively simple structure, stable and reliable operation, strong overload capacity, and impact resistance. However, its disadvantages are: heavier, larger, more expensive, and less efficient than high-frequency inverters of the same power.
Related Articles
-
 Is the photovoltaic power frequency inverter durable
Is the photovoltaic power frequency inverter durable
-
 Low frequency inverter output power difference
Low frequency inverter output power difference
-
 SG8010 sine wave power frequency inverter production
SG8010 sine wave power frequency inverter production
-
 High Frequency Inverter Power Supply Company
High Frequency Inverter Power Supply Company
-
 Bulgaria power frequency inverter price
Bulgaria power frequency inverter price
-
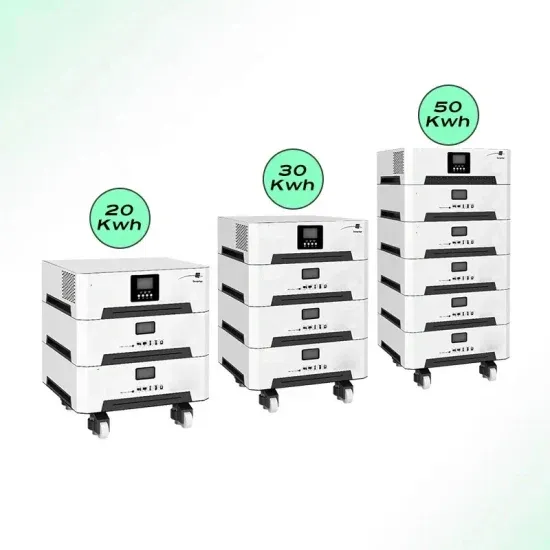 High-efficiency power frequency isolation inverter manufacturer
High-efficiency power frequency isolation inverter manufacturer
-
 Luxembourg power frequency off-grid inverter supply
Luxembourg power frequency off-grid inverter supply
-
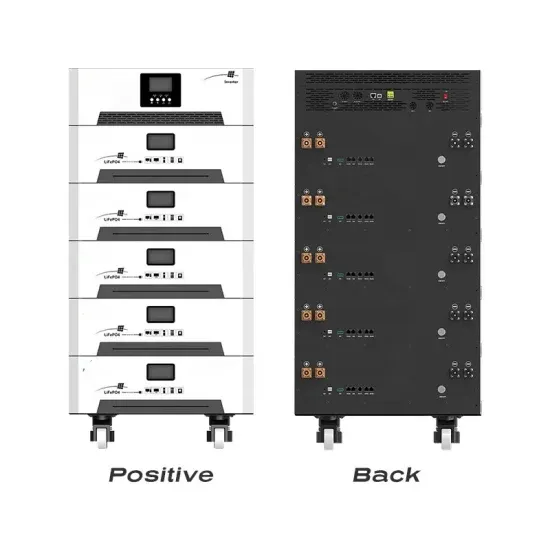 Pure sine wave output power frequency inverter
Pure sine wave output power frequency inverter
-
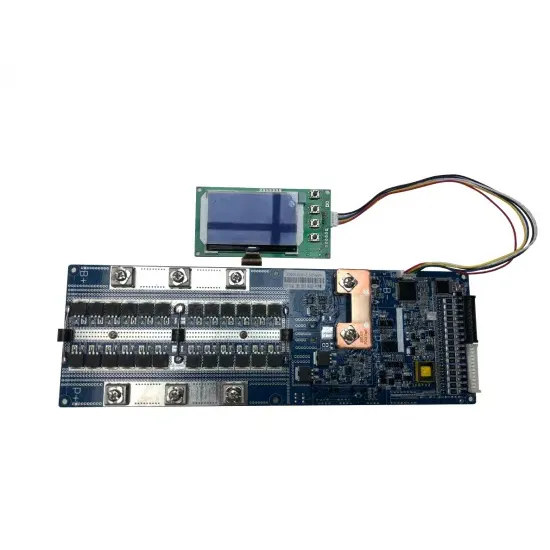 Power frequency AC inverter price
Power frequency AC inverter price
-
 High frequency power supply and industrial frequency inverter
High frequency power supply and industrial frequency inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

