A comprehensive review on inverter topologies and control strategies
Oct 1, 2018 · In this review, the global status of the PV market, classification of the PV system, configurations of the grid-connected PV inverter, classification of various inverter types, and
Get Started
Topology design and modeling of H6 bridge unidirectional photovoltaic
Based on the analysis of the working mode of H6 bridge inverter, we discuss the trigger mode of the driving signal of each bridge arm switch in H6 bridge inverter and construct the
Get Started
Novel Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Inverter with Neutral
Apr 18, 2025 · In this paper, a battery array neutral point grounded photovoltaic inverter topology is proposed, which consists of three parts: a boost circuit, an intermediate voltage equalization
Get Started
Arm Power Control of the Modular Multilevel
Apr 29, 2019 · The inverter used in photovoltaic (PV) power plants have two main topologies, central and multi-string inverter. The central inverter has relatively
Get Started
Novel Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Inverter with Neutral
Apr 18, 2025 · The inter-mediate voltage balancing circuit maintains the upper and lower bridge arm voltages of the half-bridge inverter circuit equal to improve the output power quality.
Get Started
Grid‐connected inverter bridge arm of A phase
The interface inverter was developed to transfer energy from the PV module into the grid with constant common dc voltage. A 90MW PV system with a 3
Get Started
A review of inverter topologies for single-phase grid
May 1, 2017 · In this review work, some transformer-less topologies based on half-bridge, full-bridge configuration and multilevel concept, and some soft-switching inverter topologies are
Get Started
WO/2012/048518 DIRECT-CURRENT SIDE CONTROL METHOD FOR MIDLINE ARM
Disclosed is a direct-current side control method for a midline arm control model of a four bridge arm photovoltaic inverter. The midline arm control model comprises a photovoltaic direct
Get Started
High frequency inverter topologies integrated with the
Dec 23, 2020 · Abstract: A new topology of the high frequency alternating current (HFAC) inverter bridge arm is proposed which comprises a coupled inductor, a switching device and an active
Get Started
High frequency inverter topologies integrated with the
May 18, 2016 · A new topology of the high frequency alternating current (HFAC) inverter bridge arm is proposed which comprises a coupled inductor, a switching device and an active clamp
Get Started
High frequency inverter topologies integrated with the
Dec 23, 2020 · In this paper, a class of new HFAC inverter topologies are proposed for use of single-phase, three-phase, multi-phase, and multi-levels. A coupled inductor bridge arm is
Get Started
A review on topology and control strategies of high-power inverters
Feb 15, 2025 · A comprehensive analysis of high-power multilevel inverter topologies within solar PV systems is presented herein. Subsequently, an exhaustive examination of the control
Get Started
High frequency inverter topologies integrated with the coupled inductor
May 1, 2016 · Abstract A new topology of the high frequency alternating current (HFAC) inverter bridge arm is proposed which comprises a coupled inductor, a switching device and an active
Get Started
High frequency inverter topologies integrated
May 1, 2016 · Abstract A new topology of the high frequency alternating current (HFAC) inverter bridge arm is proposed which comprises a coupled inductor,
Get Started
Model predictive control for single-phase
Aug 7, 2024 · Firstly, the grid-connected current of the PV inverter should be controlled precisely to maintain the power factor at 1. Secondly, the DC
Get Started
(PDF) Study on neutral-point voltage balancing control in
Mar 11, 2025 · Abstract and Figures Three-level photovoltaic grid-connected inverters are widely used in the photovoltaic grid-connected systems because of their high efficiency and low
Get Started
Causes of photovoltaic inverter bridge arm failure
The central inverter is considered the most important core equipment in the Mega-scale PV power plant which suffers from several partial and total failures. This paper introduces a new
Get Started
High frequency inverter topologies integrated with the
Multiphase and multi-level isolated inverters are also developed using the HFAC bridge arm. Furthermore, based on the proposed HFAC, a front-end DC-DC converter is also developed
Get Started
Improved two-stage boost inverter with integrated control
May 15, 2019 · In this study, an integrated control strategy is proposed which can be widely used in two-stage boost inverters, and an improved two-stage boost inverter is taken as an example
Get Started
A novel cascaded H-bridge photovoltaic inverter with
Jun 21, 2025 · This paper presents a novel approach that simultaneously enables photovoltaic (PV) inversion and flexible arc suppression during single-phase grounding faults verters
Get Started
Analysis and Design of a Transformerless Boost Inverter
Dec 30, 2019 · Abstract—A novel transformerless boost inverter for stand-alone photovoltaic generation systems is proposed in this paper. The proposed inverter combines the boost
Get Started
Research on Double Closed-Loop Control System of NPC Cascaded H-Bridge
Mar 13, 2024 · Aiming at the problems of unstable output voltage and large current harmonic distortion rate of photovoltaic grid-connected, based on three-level H-bridge cascaded inverter,
Get Started
High frequency inverter topologies integrated with the
A new topology of the high frequency alternating current (HFAC) inverter bridge arm is proposed which comprises a coupled inductor, a switching device and an active clamp circuit. Based on
Get Started
Power Balancing Strategy for Cascaded H-Bridge PV Inverter
Oct 24, 2024 · Cascaded H-bridge (CHB) inverter stands out as an ideal solution for a photovoltaic (PV) inverter. However, inherent inter-bridge and inter-phase power imbalanc
Get Started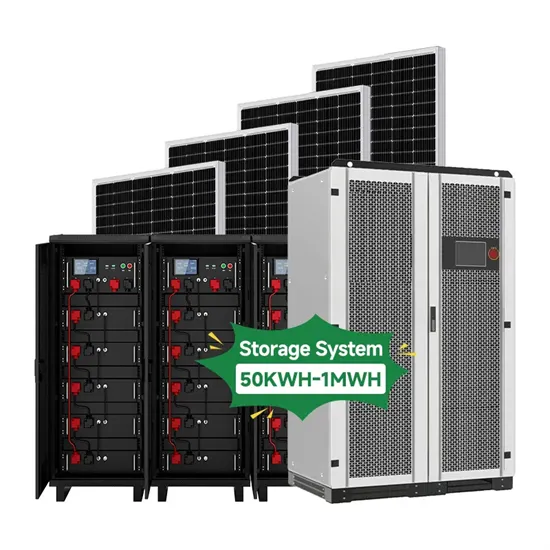
Causes of photovoltaic inverter bridge arm failure
When the power transistor of a certain bridge arm fails, the corresponding faulty bridge arm is isolated by disconnecting the fast fuse Fa, Fb, or Fc; then, the load of the fault
Get Started
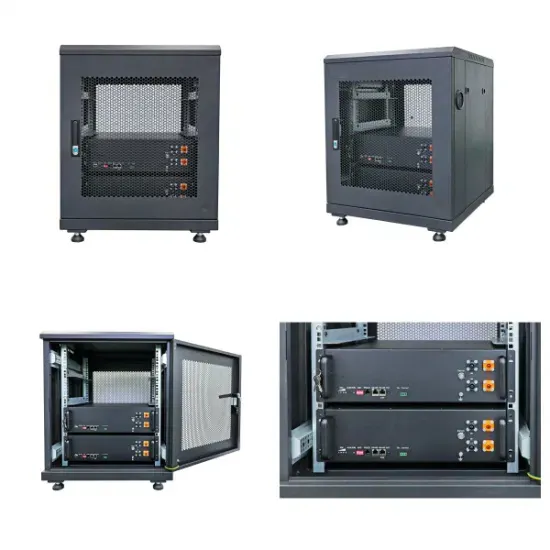
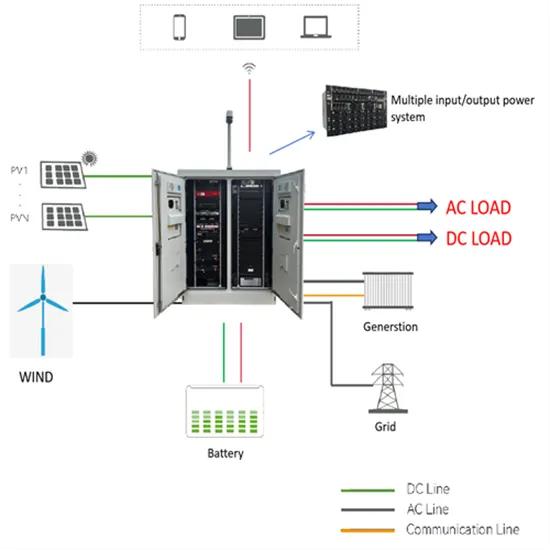
Three-phase four-bridge-arm inverter energy storage
PV system voltage will stay at 1000 V for 3-phase system Mega trends in residential, commercial and utility scale applications - To improve self consumption, Integration of Energy Storage
Get Started
Single-stage three-port isolated H-bridge inverter
Apr 16, 2025 · This paper proposes a single-stage three-port isolated H-bridge inverter. Five operating modes and five switching equivalent circuits of the inverter are studied, and three H
Get Started
A novel cascaded H-bridge photovoltaic inverter with
Aug 1, 2024 · This paper presents a novel approach that simultaneously enables photovoltaic (PV) inversion and flexible arc suppression during single-phase grounding faults. Inverters
Get Started
Grid‐connected inverter bridge arm of A phase
Download scientific diagram | Grid‐connected inverter bridge arm of A phase from publication: Research on the strategy of cooperative control between
Get Started
Analysis on topology derivation of single-phase
Nov 17, 2024 · Based on the researches of above literatures, this paper analyzes single-phase transformerless PV grid-connected inverter topologies in recent years, and divides it into two
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Photovoltaic inverter bridge arm]
How is a cascaded high-voltage direct hanging inverter bridge arm formed?
Finally, Section 4 concludes the study. 1 Working principle of NCHPI A cascaded high-voltage direct hanging inverter bridge arm was formed by connecting the midpoint of the far DC power source bridge arm of each H-bridge unit to that of the near DC power source bridge arm of the next unit (Fig. 1).
Can photovoltaic inversion and flexible arc suppression be used in grounding faults?
513 Abstract: This paper presents a novel approach that simultaneously enables photovoltaic (PV) inversion and flexible arc suppression during single-phase grounding faults. Inverters compensate for ground currents through an arc-elimination function, while outputting a PV direct current (DC) power supply.
How to achieve flexible arc suppression in a PV inverter?
To achieve flexible arc suppression in a PV inverter, the end of it should be connected in Y-type and the neutral point should be grounded. However, grounding creates a zero-sequence current loop, which leads to an increase in the zero-sequence current.
Are full-bridge single-phase PV inverters better?
As mentioned previously, full-bridge single-phase PV inverters have better performance of power density due to their split symmetrical AC inductors structure. The full-bridge PV inverters discussed in this paper can be separated into four groups.
Can a cascaded H-bridge photovoltaic inverter integrate power transmission and flexible arc suppression?
This study combines the functions of a cascaded PV Junyi Tang et al. A novel cascaded H-bridge photovoltaic inverter with flexible arc suppression function 515 inverter and flexible arc-suppression device and proposes a method to integrate power transmission and flexible arc suppression in a novel cascaded H-bridge PV inverter (NCHPI).
What are the different types of PV inverters?
According to the power levels, PV inverters can be classified into three types, including module-level micro-inverters (e.g., residential PV systems) , string inverters for medium and high power applications (e.g., offices or industrial PV power systems) , and utility-scale central inverters (e.g., PV plants) [5, 6].
Related Articles
-
 Photovoltaic inverter lower end bridge production
Photovoltaic inverter lower end bridge production
-
 Photovoltaic bridge and inverter connection
Photovoltaic bridge and inverter connection
-
 Photovoltaic inverter and bridge
Photovoltaic inverter and bridge
-
 Guinea-Bissau Home Photovoltaic Inverter Factory
Guinea-Bissau Home Photovoltaic Inverter Factory
-
 Price per watt of photovoltaic inverter
Price per watt of photovoltaic inverter
-
 Huawei photovoltaic inverter 45kw
Huawei photovoltaic inverter 45kw
-
 Household photovoltaic inverter self-operation
Household photovoltaic inverter self-operation
-
 6mw photovoltaic inverter
6mw photovoltaic inverter
-
 Huawei enters photovoltaic inverter
Huawei enters photovoltaic inverter
-
 The power of photovoltaic inverter
The power of photovoltaic inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


