Sol: Our Sun | Solar System | Go Astronomy
Dec 6, 2021 · Sol is the star that the planets, comets, and many asteroids in our solar system orbit around. Sol is a class G2 main-sequence yellow dwarf star.
Get Started
Solar Power Plants: Types, Components and
Jun 18, 2023 · Solar power plants are systems that use solar energy to generate electricity. They can be classified into two main types: photovoltaic (PV) power
Get Started
Members of the Solar System
» Jupiter is the biggest and mercury is the smallest planets of our solar system. Classification of Planets » The eight planets have been divided into two groups. All the planets of a particular
Get Started
What are the different classifications of planets?
Jun 16, 2021 · Our solar system has eight major planets and four dwarf planets. The classification of planets is done into four categories – terrestrial, gas
Get Started
Classification of photovoltaic system | Download Scientific
Download scientific diagram | Classification of photovoltaic system from publication: Performance of grid-connected solar photovoltaic power plants in the Middle East and North Africa | A
Get Started
(PDF) An Objective Classification Scheme for Solar-System
Nov 6, 2024 · We introduce succinct and objective definitions of the various classes of objects in the solar system. Unlike the formal definitions adopted by the International Astronomical Union
Get Started
Chapter 1: The Solar System
Jan 22, 2025 · The solar system has been a topic of study from the beginning of history. For nearly all that time, people have had to rely on long-range and
Get Started
Solar system | Definition, Planets, Diagram,
3 days ago · Solar system, assemblage consisting of the Sun and those bodies orbiting it: 8 planets with more than 400 known planetary satellites; many
Get Started
Asteroids: Their Origins, Formation, And
Sep 8, 2023 · This classification helps scientists better understand the nature and origin of asteroids and how they interact with other celestial objects in our
Get Started
(PDF) An Objective Classification Scheme for Solar-System
Nov 6, 2024 · Here, we develop a classification method to categorize rocky exoplanets based on their closest Solar system analogue using available data of observed stellar and planetary
Get Started
Solar system classification | PPT
This document discusses the classification of objects in our solar system. It begins by describing memorization of facts without understanding. It then
Get Started
Planetology and classification of the solar system bodies
Jan 1, 2006 · Present terminology and classification of the Solar System (SS) bodies was shaped by many factors: scientific investigation, philosophy, religion and even astrology. Up to the
Get Started
A Proposal for New Definitions of Solar System Bodies
Oct 28, 2013 · Abstract A new classification system for Solar System bodies is proposed which takes into account both physical and dynamical perspectives as well as critiques of the IAU
Get Started
What are the different types, or classes, of flares?
What are the different types, or classes, of flares? Scientists classify solar flares according to their X-ray brightness, in the wavelength range 1 to 8 Angstroms. Flares classes have names: A, B,
Get Started
Planetary classifications | EBSCO Research Starters
2 days ago · Planetary classification refers to the systematic organization of celestial bodies within our solar system based on their characteristics and behaviors. Historically, the term "planet,"
Get Started
Solar system classification | PPT
Oct 24, 2010 · The document discusses the classification of objects in our solar system. It describes the various families of objects based on their size,
Get Started
Geophysical Classification of Planets, Dwarf Planets, and
Aug 2, 2013 · A planetary mass scale and a system of composition codes are presented for describing the geophysical characteristics of exoplanets and Solar System planets, dwarf
Get Started
The Different Types of Solar Photovoltaic Systems
Learn more about the different types of solar photovoltaic systems available and why these systems are promising sources of renewable energy.
Get Started
Planet Classification: How to Group Exoplanets
May 20, 2017 · With thousands of exoplanet candidates discovered, astronomers are starting to figure out how to group them in order to describe them and
Get Started
Planets
Jul 31, 2025 · Planets In 2006, subsequent to several discoveries of several large outer Solar System objects beyond Pluto (one of which was found to be even larger than Pluto) it was
Get Started
Planets of The Solar System Classification Chart
Oct 31, 2011 · The document discusses different ways of classifying the planets in the solar system. Planets can be classified by size as small inner planets or
Get Started
Solar system | Definition, Planets, Diagram, Videos, & Facts
Feb 3, 2022 · In the astronomical community, there are six currently accepted categories for the objects below: star, planet, dwarf planet, moon/satellite, comet, and asteroid. Ceres, dwarf
Get Started
5.1 An Inventory of the Solar System – Fanshawe
5.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The solar system consists of the Sun and many smaller objects: the planets, their moons and rings, and such "debris" as
Get Started
A review on the classifications and applications
Nov 13, 2023 · Our aim of this work is to present a review of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and technologies. The principle of functioning of a PV system
Get Started
Classification of the Planets
Apr 3, 2006 · Here is a brief overview of the modern and ancient classifications of the planets. The planets inside the orbit of the earth are called the Inferior
Get Started
An Objective Classification Scheme for Solar
We introduce succinct and objective definitions of the various classes of objects in the solar system. Unlike the formal definitions adopted by the International
Get Started
Proposed planetary system classifications
Feb 15, 2023 · Astronomers have classified planetary systems into four distinct categories, based on the sizes and arrangements of their planets. As it turns
Get Started
A Proposal for New Definitions of Solar System Bodies
Oct 28, 2013 · In this paper definitions are proposed for the terms planet, moon, and satellite and a classification system is presented with four verified classes of planets in the Solar System:
Get Started
Categorizing Solar System Objects
Feb 3, 2022 · Categories of Solar System Objects In the astronomical community, there are six currently accepted categories for the objects below: star, planet, dwarf planet, moon/satellite,
Get Started
The Solar System-Classification of Planets
1 day ago · Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are the four inner planets of terrestrial planets. On the other hand, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are the four giant planets. The solar
Get Started
Geophysical Classification of Planets, Dwarf Planets, and
Aug 10, 2021 · Abstract AA planetary mass scale and system of composition codes are presented for describing the geophysical characteristics of exoplanets and Solar System planets, dwarf
Get Started
A review on the classifications and applications of solar
Nov 14, 2023 · Solar photovoltaic systems are an excellent choice for generating clean electrical energy without harming the environment. Photovoltaic cells are made up of semi-conductive
Get Started
How Many Planets are in our Solar System?
Sep 29, 2020 · These are the eight planets of our Solar System; however, there is a ninth, or at least, there used to be a ninth planet, namely Pluto.
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Solar System Classification]
How many planets are in the Solar System?
What are the planets in the solar system? There are eight planets in the solar system. The four inner terrestrial planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, all of which consist mainly of rock. The four outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, and Uranus, giant planets that consist mainly of either gases or ice.
Which planets are grouped into different classifications?
This article is focused on the planets of the solar system that are grouped into different classifications. The planets are generally divided into two parts i.e. “The Giant Planets” and “The Terrestrial Planets”. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are the four inner planets of terrestrial planets.
What is a planetary classification?
Planetary classification refers to the systematic organization of celestial bodies within our solar system based on their characteristics and behaviors. Historically, the term "planet," derived from the Greek word for "wanderer," initially included the Sun, Moon, and five visible planets: Mars, Mercury, Jupiter, Venus, and Saturn.
What are the different types of planets?
Here is a brief overview of the modern and ancient classifications of the planets. The planets inside the orbit of the earth are called the Inferior Planets: Mercury and Venus. The planets outside the orbit of the earth are called the Superior Planets: Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto.
What are the main components of the Solar System?
The most important thing is, they all are united with the gravity of the sun. Hydrogen and helium are the primary components of planets Jupiter and Saturn. According to ancient astronomers, the brightest planets or objects of the solar system are easily visible without a telescope.
Why were the Sun and Moon classified as planets?
The Sun and the Moon were classified as planets because they wandered on the celestial sphere, just like Mars and Jupiter and the other planets. A central theme of our initial discussion will be how the "7 planets of the Ancients" (only 5 of which are really planets) evolved into our present list of Solar System planets.
Related Articles
-
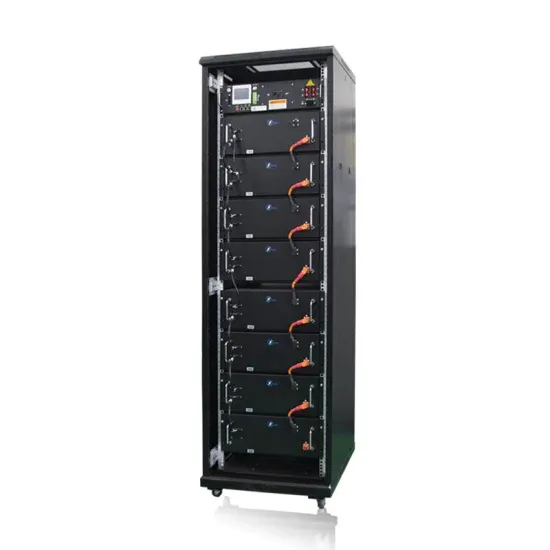 Solar wattage classification
Solar wattage classification
-
 Solar panel water pump classification
Solar panel water pump classification
-
 New solar panel 1000 watts
New solar panel 1000 watts
-
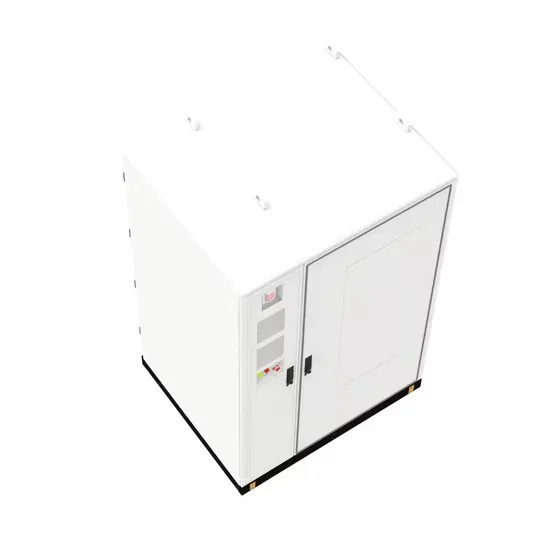
 China Air-Type Solar Energy Storage Cabinet Sales
China Air-Type Solar Energy Storage Cabinet Sales
-
 How much does a 40 watt solar street light cost
How much does a 40 watt solar street light cost
-
 1 5 kw solar inverter factory in Portugal
1 5 kw solar inverter factory in Portugal
-
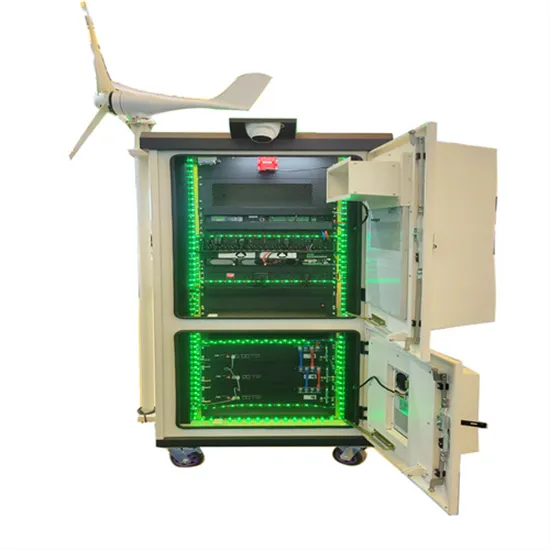
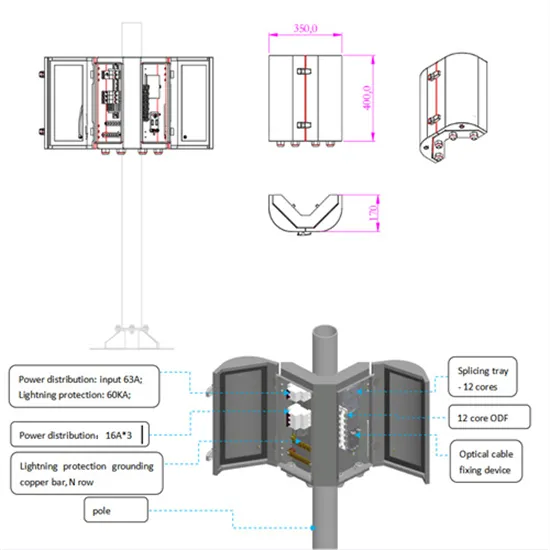 Where are the wind and solar complementary locations for China-Africa communication base stations
Where are the wind and solar complementary locations for China-Africa communication base stations
-
 Energy storage container solar photovoltaic power station
Energy storage container solar photovoltaic power station
-
 Solar panel with 60v water pump
Solar panel with 60v water pump
-
 Bulgaria Solar Container Energy Storage
Bulgaria Solar Container Energy Storage
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


