High Frequency vs. Low Frequency Inverter
Jul 29, 2022 · A lot of the most popular AIO inverters are High Frequency Transformerless. How important is it to use the correct family of transformer (high vs. low freq) for to power devices
Get Started
Understanding the Differences
3 days ago · Conclusion Whether opting for a low-frequency or high-frequency solar inverter depends on the individual''s specific requirements and priorities. Low-frequency inverters offer
Get Started
High frequency inverter vs low frequency
Nov 2, 2023 · This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size
Get Started
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters:
Feb 10, 2025 · An inverter is a key component that converts DC power into AC power for household appliances and is commonly used in solar energy
Get Started
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
2. Low Frequency Inverters: Robust and Durable: Low frequency inverters are better suited for applications requiring high power output and reliability. Their robust design allows them to
Get Started
Inverter Low Frequency vs High Frequency | How Do I
Mar 31, 2024 · There are two main types of inverters: low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters. Low-frequency inverters operate at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz, which is the same
Get Started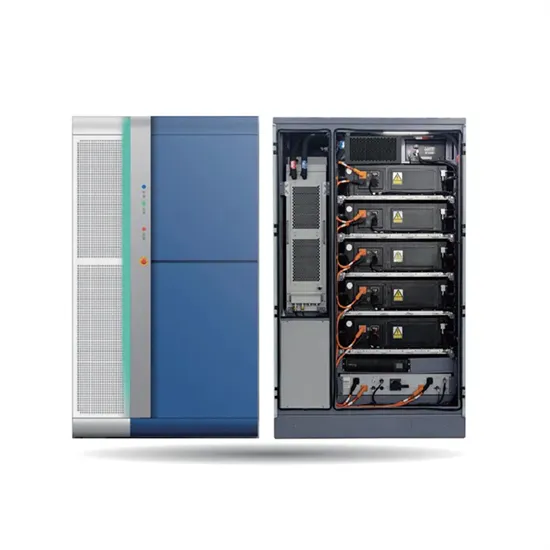
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter: How to
Aug 18, 2025 · High frequency inverters and low frequency inverters are two common types of inverters with distinct differences in their application, operating principles, and characteristics:
Get Started
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Conclusion In conclusion, the choice between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters depends largely on the specific needs of the application. High-frequency inverters offer the
Get Started
High-frequency versus low-frequency inverters which is right
Jun 13, 2025 · Compare high-frequency and low-frequency frequency inverters to find the best fit for your power needs, efficiency, surge capacity, and reliability.
Get Started
Understanding Low Frequency Power Inverters
6 days ago · – Higher efficiency: Low frequency inverters typically exhibit higher efficiency than high frequency inverters, which can result in significant energy savings over time. – Lower
Get Started
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
High frequency inverters are compact and efficient, making them ideal for applications where space is limited, such as solar power systems and portable devices. Low frequency inverters
Get Started
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Oct 26, 2024 · Understanding the differences between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters is vital for anyone involved in renewable energy or considering an uninterrupted
Get Started
What is a Frequency Inverter? A Complete Guide to How It
4 days ago · A frequency inverter is an electronic device that converts the fixed frequency and fixed voltage from your electrical supply (e.g.,50Hz or 60Hz,240V or 480V)into a variable
Get Started
Introduction to Low-Frequency Inverters :: Articles :: 12V
Introduction to Low-Frequency Inverters For those who are unaware, the purpose of an off-grid inverter is simple, yet incredibly important for anyone who is looking to set up an off-grid or
Get Started
Which is Better Low Frequency or High
3 days ago · Low frequency inverters are simpler, more robust and easier to control. High frequency inverters enable miniaturization, fast response,
Get Started
Inverters High or Low Frequency ? | DIY Solar Power Forum
Apr 15, 2020 · Low-frequency inverters use high-speed switches to invert (or change) the DC to AC, but drive these switches at the same frequency as the AC sine wave which is 60 Hz (60
Get Started
Understanding the Difference Between Low
Mar 7, 2023 · There are two types of inverters, low frequency and high frequency inverters. Inverters are used in solar power systems, wind turbines, and
Get Started
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Operation: High-frequency inverters convert DC to AC at a much higher frequency than the standard 50 or 60 Hz (often in the range of tens of kHz to hundreds of kHz). They use
Get Started
Voltage Fed Full Bridge DC-DC & DC-AC Converter High
Apr 1, 2023 · ABSTRACT The High-Frequency Inverter is mainly used today in uninterruptible power supply systems, AC motor drives, induction heating and renewable energy source
Get Started
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and
3 days ago · A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency,
Get Started
Low Frequency Inverter, High Frequency
Jun 5, 2020 · Compared with high-frequency inverters, low-frequency inverters have larger peak power capacity to handle large loads with power spikes. In
Get Started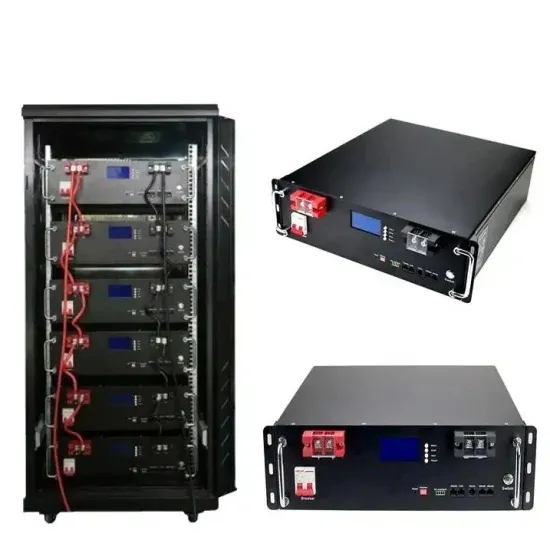
Low frequency pure sine inverter??
May 18, 2022 · Halló, I noticed that some inverter manufacturers produce a type of pure sine inverter "low frequency". They are expensive and extremely heavy! 30 kg for 2000 watts! Waht
Get Started
Difference Between High and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 30, 2025 · Understand the difference between high and low frequency inverters (lf vs hf inverter) and what are the main features of Xindun Power''s high frequency inverters?
Get Started
High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
High-Frequency Inverters: High-frequency inverters can handle moderate surges, but their surge capacity is generally lower than low-frequency inverters. They may struggle to run devices with
Get Started
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
Feb 6, 2025 · Operating Frequency Low-Frequency Inverter: Operates at a lower frequency, typically around 50Hz or 60Hz. Because its frequency is close to that of utility power, it is
Get Started
Low frequency inverter vs high frequency
Mar 12, 2025 · When choosing an inverter for your solar system, one of the key decisions is whether to use a low-frequency inverter or a high-frequency
Get Started
HIGH VS LOW FREQUENCY INVERTERS
Nov 28, 2022 · The second main difference is reliability: low-frequency inverters operate using powerful transformers, which are more reliable and sturdy than the high-frequency inverter''s
Get Started
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · Low-frequency power inverters have much better peak power capability to manage large loads with power spikes than high-frequency inverters. In fact, low-frequency inverters
Get Started
High Vs Low Frequency Inverters/UPS
Jul 1, 2023 · Let us compare High Vs Low-Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison. Two kinds of commonly used Inverters/UPS; High Frequency and Low
Get Started
Everything to Know Low Frequency Inverters
Low-frequency inverters, characterized by their use of transformers for electrical isolation, play a crucial role in a variety of high-reliability applications. This
Get Started
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Low-frequency inverters, on the other hand, operate at frequencies typically below 1 kHz. They rely on more traditional transformer-based technology to perform the DC to AC conversion.
Get Started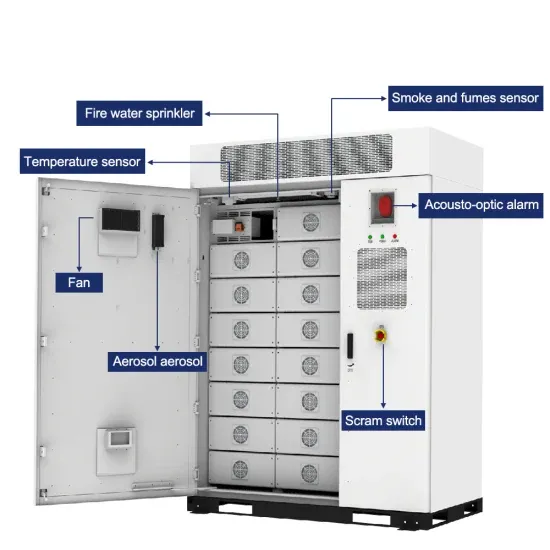
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
May 15, 2024 · In the field of power electronics and energy conversion, inverters, as key equipment for power conversion, play a vital role. Inverters are capable
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Inverter from high frequency to low frequency]
What is a low frequency inverter?
Low-frequency inverters, operating at frequencies below 60 Hz, generally generate a quasi-square wave or a modified sine wave output. These inverters are less efficient and can introduce harmonics into the power supply. Size and Weight High-frequency inverters are typically smaller and lighter than low-frequency inverters.
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
High-frequency inverters generally have higher efficiency than low-frequency inverters. This is because the higher operating frequency reduces the size of transformers, capacitors, and other components, leading to lower power losses. Low-frequency inverters have lower efficiency due to higher losses in magnetic components and switching devices.
What is a high frequency inverter?
The efficiency of an inverter refers to the ratio of AC power output to DC power input. High-frequency inverters generally have higher efficiency than low-frequency inverters. This is because the higher operating frequency reduces the size of transformers, capacitors, and other components, leading to lower power losses.
How do I choose a high-frequency or low-frequency inverter?
Choosing between a high-frequency and low-frequency inverter depends on several factors, including efficiency, size, budget, and application needs. Here’s a quick guide: Residential Users: High-frequency inverters are ideal for home use, especially in solar systems, due to their efficiency and compact size.
Why should you choose a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverters enable miniaturization, fast response, efficiency and ultra-quiet operation. The choice depends on the specific size, performance, cost, reliability and noise criteria for the application. Hybrid inverters running at medium frequencies can balance the tradeoffs.
Why is a low frequency inverter so difficult to install?
Size and Weight: The low-frequency transformer is large and heavy, making the overall inverter bulky and more challenging to install and transport. Efficiency: Generally, they have lower efficiency due to the energy losses associated with the larger transformer and the lower switching speeds.
Related Articles
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
 Inverter from high frequency to low frequency
Inverter from high frequency to low frequency
-
 High frequency sine wave inverter
High frequency sine wave inverter
-
 Low frequency inverter output power difference
Low frequency inverter output power difference
-
 High frequency inverter in Douala Cameroon
High frequency inverter in Douala Cameroon
-
 Stockholm High Frequency Inverter Installation
Stockholm High Frequency Inverter Installation
-
 High frequency inverter life
High frequency inverter life
-
 Armenia high frequency sine wave inverter
Armenia high frequency sine wave inverter
-
 Belgian high frequency inverter manufacturer
Belgian high frequency inverter manufacturer
-
 Papua New Guinea high frequency inverter price
Papua New Guinea high frequency inverter price
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.