
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in
High-frequency inverters generate less heat due to their high efficiency and reduced energy loss, which simplifies thermal management requirements.
Get Started
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Conclusion In conclusion, the choice between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters depends largely on the specific needs of the application. High-frequency inverters offer the
Get Started
CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
Mar 27, 2016 · A frequency that is set to maintain a stable output by not changing the output frequency to within a specified frequency zone and thus avoid a resonance frequency of a
Get Started
What is a High-Frequency Power Inverter?
1 day ago · This article provides an overview of high-frequency inverter topologies, design considerations, applications, and advantages versus
Get Started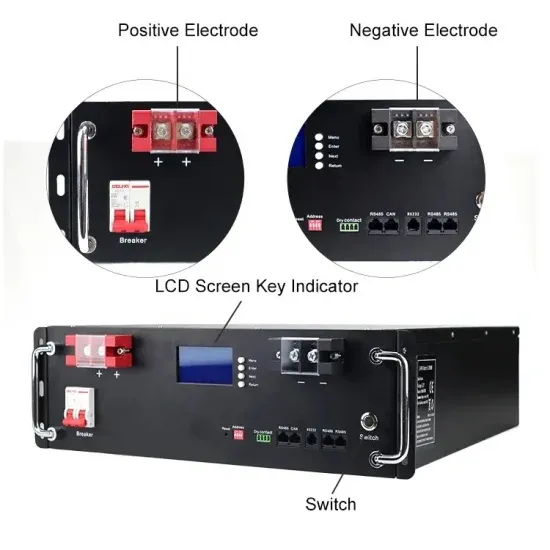
How High-Frequency Inverters Improve Energy Efficiency
4 days ago · High-frequency inverters are revolutionizing energy efficiency, unlocking substantial savings in various electrical systems. By embracing the transformative power of high
Get Started
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and
3 days ago · A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency,
Get Started
6.5. Efficiency of Inverters | EME 812: Utility Solar
High frequency inverters are usually more efficient than low-frequency. Inverter efficiency depends on inverter load. Figure 11.8. Typical generic inverter
Get Started
Mastering Inverter Switching Frequencies: A
Apr 25, 2024 · High-frequency switching can result in more efficient operation and smoother output waveforms, but also leads to increased heat generation and
Get Started
High-Frequency Inverters: From Photovoltaic, Wind, and
Jul 26, 2022 · (3) efficiency, and (4) power density. Conventional approach to inverter design is typically based on the architecture illustrated in Fig. 29.1a. A problematic feature of such an
Get Started
Performances assessment of very high frequency class E inverters
Apr 28, 2025 · Class E inverters are widely used in very high frequency power converters due to their ease of driving, their high efficiency and their low component count. A generic design
Get Started
(PDF) A bidirectional, sinusoidal, high-frequency
Aug 1, 2001 · The inverter is controlled by two minimum-time feedback loops, providing relatively low output voltage distortion (less than 2% for DC input
Get Started
Inverter Transformers for High-Efficiency
Jul 18, 2024 · High-frequency operation reduces transformer size and weight, improving system compactness and efficiency. High-frequency transformers
Get Started
High-efficiency inverter for photovoltaic applications | IEEE
Nov 1, 2010 · We introduce a circuit topology and associated control method suitable for high efficiency DC to AC grid-tied power conversion. This approach is well matched to the
Get Started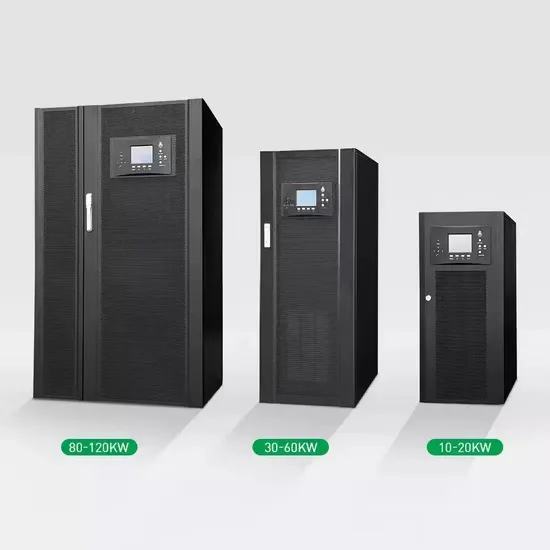
High Frequency Power Inverter: Efficiency, Reliability, and
Discover the benefits of high frequency power inverters for efficient power conversion, space-saving designs, and unparalleled reliability in protecting your electronics.
Get Started
Pure Sine Wave Inverter (12v/24v/48v)
High efficiency 300W pure sine wave ups inverter with a good price for sale, DC input voltage can select 12V, 24V, 48V, with uninterruptible power source,
Get Started
High-Efficiency Inverter Technologies
Jun 11, 2025 · High-efficiency inverter technologies are pivotal in the modern energy landscape, enabling more effective conversion of direct current to alternating current while...
Get Started
Voltage Fed Full Bridge DC-DC & DC-AC Converter High
Apr 1, 2023 · In many applications, it is important for an inverter to be lightweight and of a relatively small size. This can be achieved by using a High-Frequency Inverter that involves an
Get Started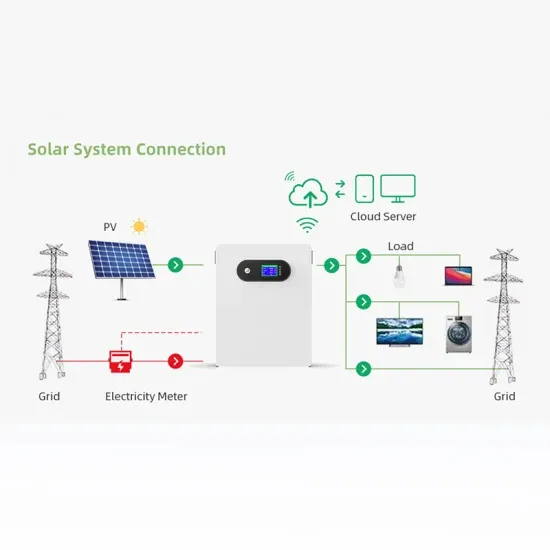
5 kW High-Efficiency Fan-less Inverter
Nov 11, 2021 · 5 kW High-Efficiency Fan-less Inverter We employ trans-linked interleaved circuits as inverter circuits that utilize the high frequency switching performance of silicon carbide (SiC)
Get Started
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · With the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the benefits of compact size, high efficiency, and lightweight but also have the
Get Started
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
Aug 16, 2016 · By definition, Low frequency power inverters got the name of "low frequency" because they use high speed power transistors to invert the DC
Get Started
Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions
Dec 11, 2023 · The frequency inverter is a power control equipment that applies frequency conversion technology and microelectronics technology to control
Get Started
Design and Development of High Frequency Inverter for
The use of high frequency in wireless power transfer allows for more efficient and precise transfer of energy, as well as potentially reducing interference and allowing for smaller size of the
Get Started
What is Inverter Efficiency? | inverter
Jul 26, 2020 · European efficiency: It refers to inverter efficiency measured at different ac output power points, then multiplied by different weighted number,
Get Started
Which is Better Low Frequency or High
3 days ago · Introduction Inverters convert DC power into AC power to operate AC equipment and devices. They utilize power electronic switching at different
Get Started
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters: Enhanced Efficiency High-frequency inverters are known for their high efficiency, which is one of their most
Get Started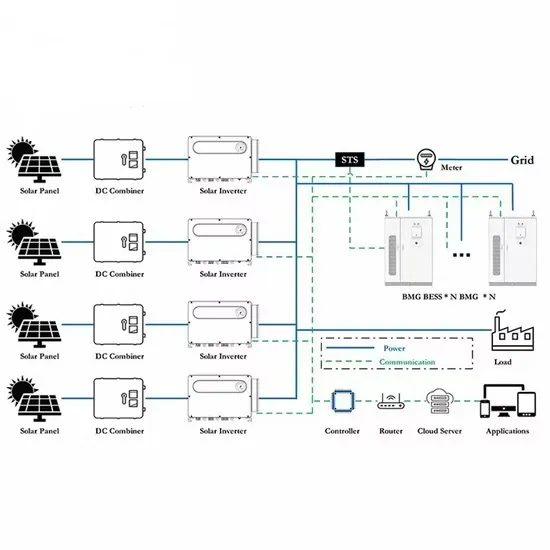
High-Efficiency Inverter for Photovoltaic Applications
Dec 4, 2023 · Abstract—We introduce a circuit topology and associated con-trol method suitable for high efficiency DC to AC grid-tied power conversion. This approach is well matched to the
Get Started
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters:
Feb 10, 2025 · The use of high-frequency switching technology greatly improves the efficiency of high-frequency inverters, and their peak conversion efficiency
Get Started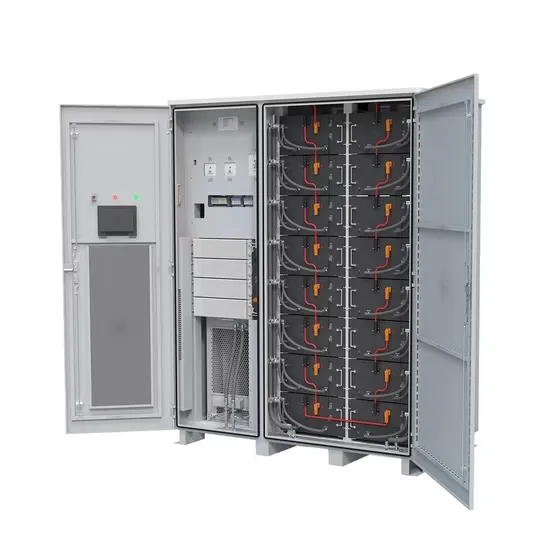
Understanding the Difference Between Low
Mar 7, 2023 · Low frequency inverters are ideal for applications that require high power output and can handle heavy-duty appliances. High frequency inverters
Get Started
A Review on the Recent Development of High
Oct 16, 2024 · This paper reviews the high-frequency inverters for WPT systems, summarizes the derived topologies based on power amplifiers and H-bridge
Get Started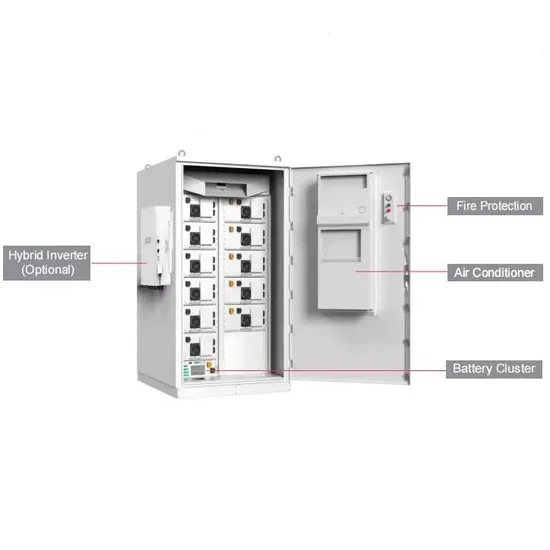
6 FAQs about [High frequency inverter output efficiency]
What is a high frequency inverter?
In many applications, it is important for an inverter to be lightweight and of a relatively small size. This can be achieved by using a High-Frequency Inverter that involves an isolated DC-DC stage (Voltage Fed Push-Pull/Full Bridge) and the DC-AC section, which provides the AC output.
What percentage of power does an inverter have a high efficiency?
Below 10-15% of power output, efficiency is quite low. At high output power, the efficiency is steadily high with some small variations. The behavior in Figure 11.8 partially results from the fact that stand-by losses for an inverter are the same for all output power levels, so the efficiency at lower outputs is affected more.
What is a typical generic inverter efficiency curve?
Typical generic inverter efficiency curve. Below 10-15% of power output, efficiency is quite low. At high output power, the efficiency is steadily high with some small variations.
Are modified sine wave inverters more efficient?
Lower quality modified sine wave inverters are less efficient - 75-85%. High frequency inverters are usually more efficient than low-frequency. Inverter efficiency depends on inverter load. Figure 11.8. Typical generic inverter efficiency curve. Below 10-15% of power output, efficiency is quite low.
How do you calculate the efficiency of an inverter?
The efficiency of an inverter indicates how much DC power is converted to AC power. Some of the power can be lost as heat, and also some stand-by power is consumed for keeping the inverter in powered mode. The general efficiency formula is: ηinv = PAC PDC η i n v = P A C P D C
What is the efficiency of a sine wave inverter?
High quality sine wave inverters are rated at 90-95% efficiency. Lower quality modified sine wave inverters are less efficient - 75-85%. High frequency inverters are usually more efficient than low-frequency. Inverter efficiency depends on inverter load. Figure 11.8. Typical generic inverter efficiency curve.
Related Articles
-
 How much does a high frequency inverter output
How much does a high frequency inverter output
-
 High frequency inverter front stage output
High frequency inverter front stage output
-
 Inverter high frequency vibration
Inverter high frequency vibration
-
 High frequency inverter power loss
High frequency inverter power loss
-
 Canberra One High Frequency Inverter
Canberra One High Frequency Inverter
-
 Special function high efficiency inverter by12-8
Special function high efficiency inverter by12-8
-
 High frequency protection setting value of photovoltaic inverter
High frequency protection setting value of photovoltaic inverter
-
 Vatican high frequency inverter quotation
Vatican high frequency inverter quotation
-
 High frequency inverter for RV
High frequency inverter for RV
-
 50 Hz high frequency inverter
50 Hz high frequency inverter
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


