High frequency versus low inverters
Nov 18, 2019 · I have experience with only one of each, but based on that one experience, a low-frequency inverter can have a significantly higher if for draw and can put out much more heat
Get Started
Power Inverter vs. Frequency Inverter
Jan 20, 2021 · The adapter converts the AC voltage of the mains power grid into a stable 12V DC output, while the inverter converts the 12V DC voltage output
Get Started
Inverter Generators: What You Need To Know.
Sep 18, 2016 · Inverter generators convert the high frequency, three phase AC into DC current via a solid state rectifier, and from there the electricity goes
Get Started
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable
Jan 1, 2025 · There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical
Get Started
How much power does an Inverter use just sitting there idling?
Oct 30, 2020 · Because they generally have less MOSFET''s getting switching at high frequency they have a bit lower idle current. Many inverters have a automatic standby mode. They
Get Started
Inverters High or Low Frequency
Apr 15, 2020 · Not enough to fix what is wrong with modified sine wave inverters, but some. Pretty much all modern inverters are high frequency as in they use high frequency PWM modulation
Get Started
Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions
Dec 11, 2023 · The frequency inverter is a power control equipment that applies frequency conversion technology and microelectronics technology to control
Get Started
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
May 15, 2024 · High frequency inverter: High frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology to chop DC power at high frequency through
Get Started
Adapt high-frequency inverter with addition of transformer?
Jan 28, 2024 · Yes, an autotransformer can help improve the output of a high-frequency inverter when dealing with inductive loads by mitigating the voltage spikes and current surges caused
Get Started
Technical comparison between Low Frequency
Aug 19, 2025 · What internal frequency the inverter circuits operate at – low frequency or high frequency (not to be confused with AC power output
Get Started
What is a High-Frequency Power Inverter?
2 days ago · Introduction A power inverter converts DC power into AC power for operating AC loads and equipment. High-frequency power inverters utilize
Get Started
How to Distinguish High Frequency Inverter and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 11, 2024 · Low frequency inverters produce less electromagnetic interference, but can only produce lower AC power frequencies, while high frequency inverters can produce higher
Get Started
Power Inverters: The Need-to-Know Essentials
Nov 29, 2022 · Inverters are also used for induction heating. AC mains power is first rectified to DC power, and then the inverter converts it to high frequency AC power used for induction
Get Started
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and
4 days ago · A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency,
Get Started
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
Mar 6, 2025 · This is a step-up transformer with more windings in the secondary (yellow zig-zag, right-hand side) than the primary, so it boosts a small AC
Get Started
What are Low Frequency Toroidal Inverters?
Apr 6, 2022 · So here I heard some inverters that are "low frequency toroidal inverters". 1. What are they? Example? 2. What is their advantage vs regular
Get Started
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Conclusion In conclusion, the choice between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters depends largely on the specific needs of the application. High-frequency inverters offer the
Get Started
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Jul 25, 2025 · High-frequency inverters represent a more modern approach, engineered to overcome the size and weight limitations of their line-frequency counterparts. The topology is
Get Started
Which is Better Low Frequency or High
4 days ago · Introduction Inverters convert DC power into AC power to operate AC equipment and devices. They utilize power electronic switching at different
Get Started
Frequency Inverter | inverter
0.75kW single phase output frequency inverter for sale, 1-phase input to 0~input voltage 1-phase output at 220V/230V/240V. Rated current 7A, input voltage single phase AC 220 ± 15%, and
Get Started
Understanding High-Frequency Inverters
Aug 20, 2025 · Benefits of High-Frequency Inverters: Uncover the advantages offered by high-frequency operation, such as reduced size, improved efficiency, and noise suppression.
Get Started
Inverter Current Calculator, Formula, Inverter Calculation
6 days ago · Inverter Current Formula: Inverter current is the electric current drawn by an inverter to supply power to connected loads. The current depends on the power output required by the
Get Started
Introduction to Grid Forming Inverters
Jun 18, 2024 · Why do we need Grid-forming (GFM) Inverters in the Bulk Power System? There is a rapid increase in the amount of inverter-based resources (IBRs) on the grid from Solar PV,
Get Started
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and
2 days ago · High-frequency power inverters utilize high-speed switching at frequencies significantly higher than the standard 50/60 Hz grid frequency. This article provides an
Get Started
Inverter Low Frequency vs High Frequency | How Do I
Mar 31, 2024 · There are two main types of inverters: low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters. Low-frequency inverters operate at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz, which is the same
Get Started
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
Aug 16, 2016 · By definition, Low frequency power inverters got the name of "low frequency" because they use high speed power transistors to invert the DC
Get Started
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and
Oct 1, 2024 · In most regions, the standard inverter frequency for AC power systems is 50 or 60 Hz, representing the number of complete cycles per
Get Started
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and
The low frequency inverters typically operate at ~60 Hz frequency. To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used. These inverters use the
Get Started
Voltage Fed Full Bridge DC-DC & DC-AC Converter High
Apr 1, 2023 · In many applications, it is important for an inverter to be lightweight and of a relatively small size. This can be achieved by using a High-Frequency Inverter that involves an
Get Started
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · The output frequency of a high-frequency inverter is much higher than the power frequency, usually between a few kilohertz and ten kilohertz. With the use of high-frequency
Get Started
6 FAQs about [How much does a high frequency inverter output]
What is the output frequency of a high-frequency inverter?
The output frequency of the high-frequency inverter is much higher than the power frequency, usually between a few kilohertz and tens of kilohertz.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of high frequency inverters?
Benefits of High-Frequency Inverters: Uncover the advantages offered by high-frequency operation, such as reduced size, improved efficiency, and noise suppression. Topologies of High-Frequency Inverters: Examine the different topologies used in high-frequency inverters, including half-bridge, full-bridge, and multilevel.
Are high-frequency inverters a good choice?
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high efficiency, but they also have the problem of relatively poor output waveform quality.
How does a high frequency inverter work?
The inverter bridge contains power switches like IGBTs or MOSFETs. The switches turn on and off at high speed to generate high-frequency pulses. An LC filter smoothens the pulses into sinewave AC output. The output frequency depends on how fast the switches cycle on and off. Common high-frequency inverter circuit configurations include:
What is the range of a high frequency inverter?
High-frequency inverters operate from around 10 kHz up to 1 MHz range, far higher than 50/60 Hz line frequencies. RF inverters can reach up to 30 MHz range. What are some common semiconductor devices used in high-frequency inverters?
What are common high-frequency inverter circuit configurations?
Common high-frequency inverter circuit configurations include: Key design factors for high-frequency inverters: Switching frequency – Higher frequency allows smaller filter components but increases losses. Optimize based on tradeoffs. Filter components – Smaller inductors and capacitors possible at high frequencies. Balance size versus performance.
Related Articles
-
 How many k is the best for high frequency inverter potentiometer
How many k is the best for high frequency inverter potentiometer
-
 High frequency inverter output efficiency
High frequency inverter output efficiency
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
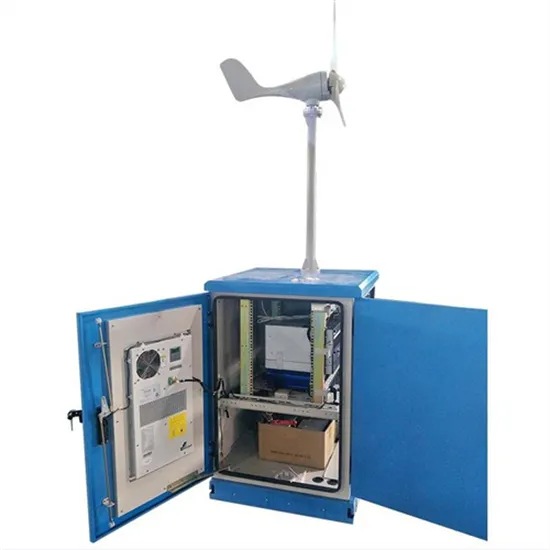 Iraq high frequency inverter device manufacturer
Iraq high frequency inverter device manufacturer
-
 Photovoltaic high frequency parallel inverter
Photovoltaic high frequency parallel inverter
-
 6000W high frequency inverter
6000W high frequency inverter
-
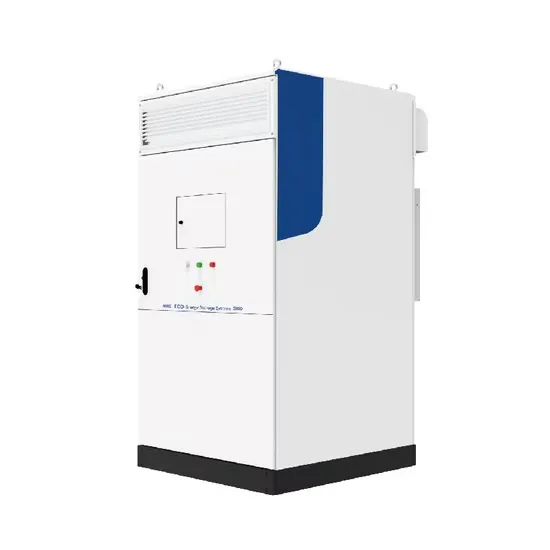 Pure sine wave output power frequency inverter
Pure sine wave output power frequency inverter
-
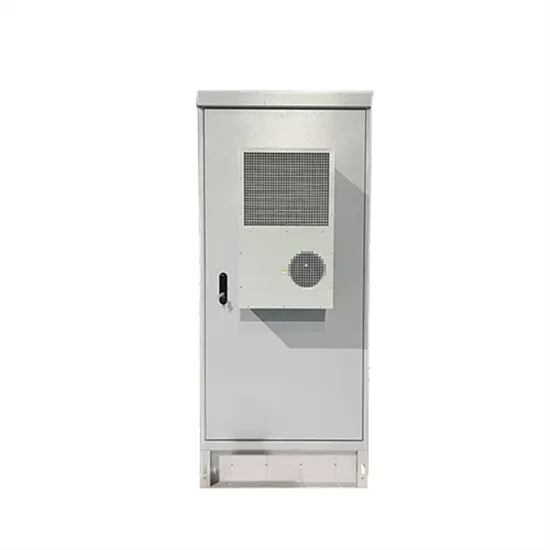 High Frequency Inverter Power Supply Company
High Frequency Inverter Power Supply Company
-
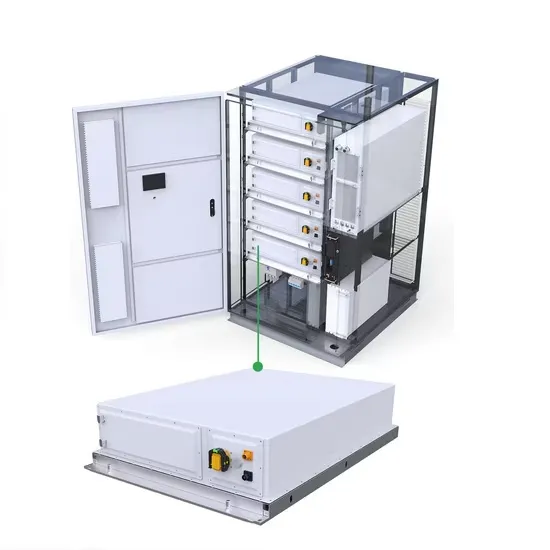 High frequency inverter front stage module
High frequency inverter front stage module
-
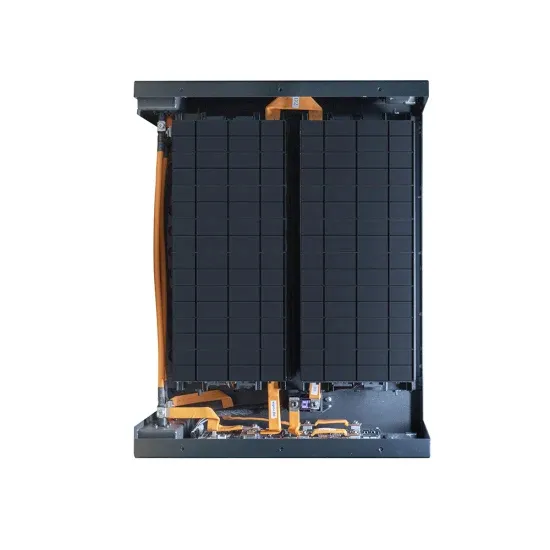 Low frequency inverter output power difference
Low frequency inverter output power difference
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


