CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
Mar 27, 2016 · An inverter uses this feature to freely control the speed and torque of a motor. This type of control, in which the frequency and voltage are freely set, is called pulse width
Get Started
Inverter Types & Working Principle
2 days ago · The article provides an overview of inverter technology, explaining how inverters convert DC to AC power and detailing the different types of
Get Started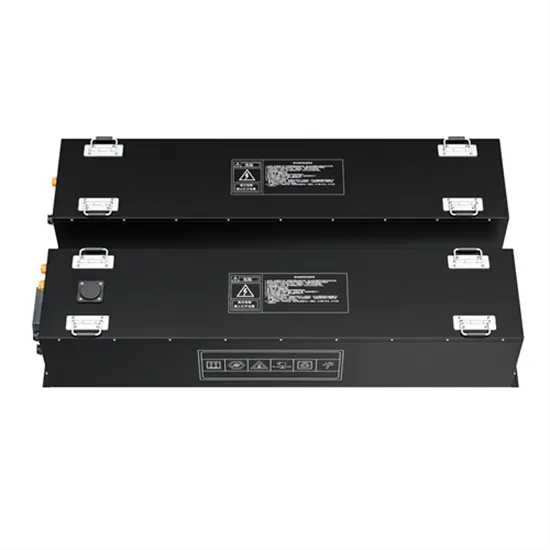
Voltage Converter: Basics, Types and
Jun 13, 2022 · Applications of Voltage Converters 1. Power Transmission and Distribution: In power systems, voltage converters are widely used in high
Get Started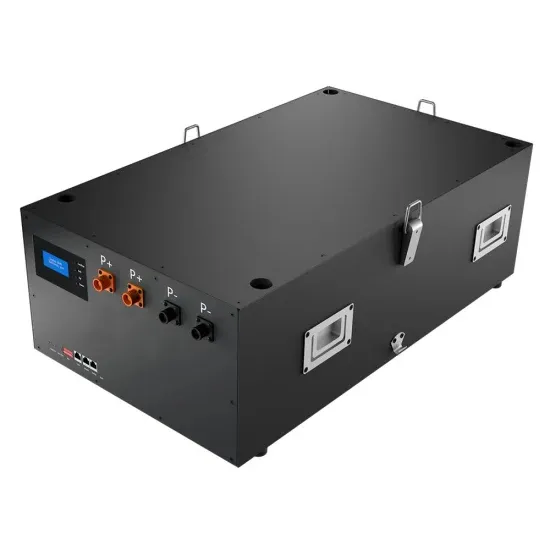
Understanding inverter voltage
Jan 10, 2024 · Inverter voltage typically falls into three main categories: 12V, 24V, and 48V. These values signify the nominal direct current (DC) input voltage required for the inverter to function
Get Started
What is Inverter? – Meaning, Types and
Jul 26, 2020 · The DC power input to the inverter is obtained from an existing power supply source or from a rotating alternator through a rectifier or a
Get Started
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They
Dec 17, 2019 · Key learnings: Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for
Get Started
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
Dec 17, 2019 · Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working
Get Started
Types of Inverters in context of inverter voltage
Aug 31, 2024 · The type of inverter used can significantly impact the voltage characteristics of the output waveform. This article provides an overview of various types of inverters, focusing on
Get Started
Inverters, Types and Voltages
Dec 31, 2024 · Browse our recommended inverters for every type of setup—from low voltage off-grid systems to high voltage, grid-tied solutions. Each product is reviewed to ensure it meets
Get Started
What Is Inverter Voltage?
Inverters are crucial components in energy systems, converting direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for household appliances. Understanding inverter voltage —both input and
Get Started
Voltage Control Methods of Inverter – PWM
Feb 12, 2022 · The voltage control is primarily achieved by varying the firing angle of the ac voltage controller that feeds the ac load. In this method, there is a
Get Started
What Is Inverter Voltage?
Understanding inverter voltage —both input and output—is key to selecting the right inverter for your system. This guide explains the different types of inverter voltages and how to choose the
Get Started
3-Phase Inverter
Feb 27, 2024 · Types of Three Phase Inverter Three phase inverters are classified many types according to their features and characteristics . Some of
Get Started
Types of Power Inverters And How To Choose
Apr 15, 2024 · Discover the different types of power inverters and learn how to choose the right one for your needs. Expert advice from Junchipower.
Get Started
Inverter types and classification | AE 868: Commercial Solar
Inverters based on PV system type Considering the classification based on the mode of operation, inverters can be classified into three broad categories: Stand-alone inverters (supplies stable
Get Started
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
Dec 18, 2024 · What is a 12VDC to 120VAC inverter? 12VDC to 120VAC Inverter is a common device that converts 12V DC power to AC power with a nominal
Get Started
multilevel inverters introduction types
Introduction to multilevel inverters, types of multilevel inverters, their applications, comparison of different types with advantages and disadvantages.
Get Started
Power Electronics
Single Phase Inverter There are two types of single phase inverters − full bridge inverter and half bridge inverter. Half Bridge Inverter This type of inverter is the
Get Started
AKX00057-1
Jul 26, 2018 · The switching of a voltage-type PWM inverter generates a neutral-point voltage, which is divided by the capacitance distributed in a motor and appears as a motor shaft voltage.
Get Started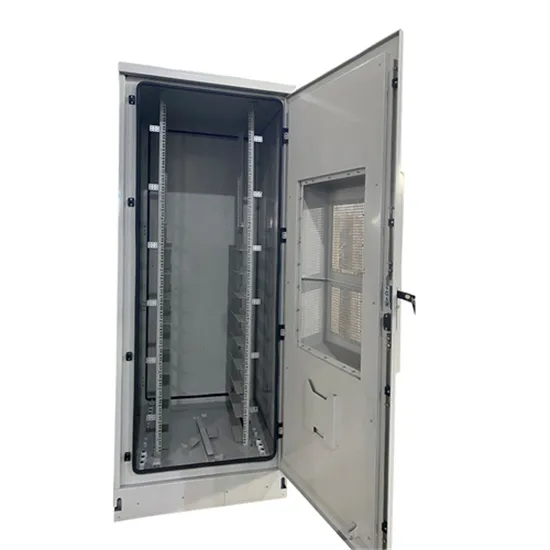
Voltage Source Inverter
Voltage Source Inverters abbreviated as VSI are the type of inverter circuits that converts a dc input voltage into its ac equivalent voltage at the output. It is
Get Started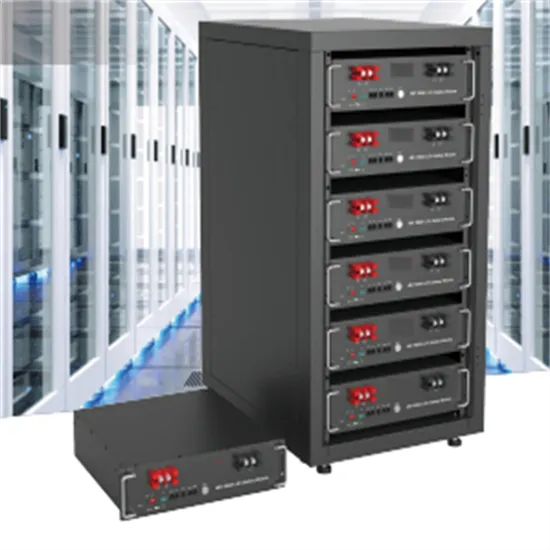
Complete Guide to Inverter Batteries – NPP POWER
Oct 23, 2024 · What exactly is an inverter battery? Inverter batteries perform several critical functions: Energy Storage They store electrical energy for future use, offering backup power
Get Started
Inverters, Types and Voltages
Dec 31, 2024 · Understanding Low Voltage vs. High Voltage Inverters and Low Frequency vs. High Frequency Inverters When setting up a solar energy system, choosing the right inverter is
Get Started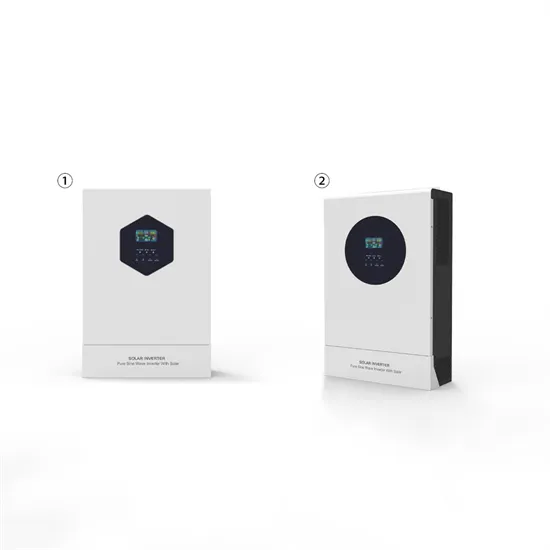
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What
3 days ago · Inverters are devices that play an important role in modern, green, and clean electrical systems. They work by converting the power obtained
Get Started
Inverter types and classification | AE 868: Commercial Solar
Now that we understand why we need an inverter for PV systems, it is time to introduce the different types of inverters that exist in the market and discover the advantages and
Get Started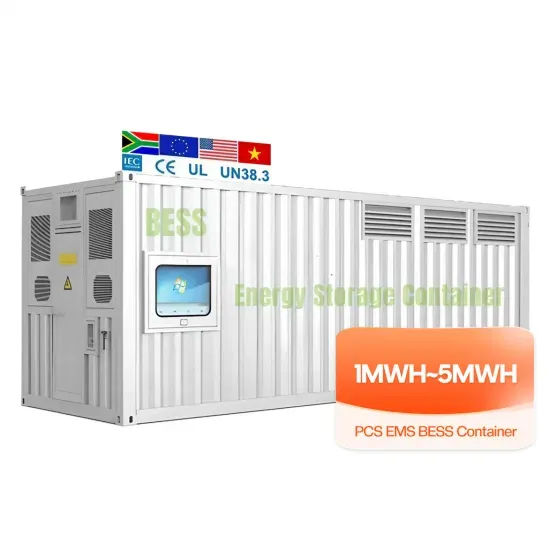
Types of Inverters
Jul 23, 2025 · Regular two-level inverters produce an output voltage that switches between two voltage levels either the positive DC voltage or the negative DC voltage. They use switches
Get Started
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
2 days ago · For inverters designed for residential use, the output voltage is 120 V or 240 V at 60 Hz for North America. It is 230 V at 50 Hz for many other
Get Started
Introduction to 17 types of inverter – TYCORUN
Oct 17, 2023 · Based on the application''s input source, connection method, output voltage waveform, etc.,there are 17 types of inverter. Different types of
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Inverter voltage type]
What are the different types of inverters?
Inverters are classified into many different categories based on the applied input source, connection wise, output voltage wise etc. In this article, we will see some of the categories. The inverter can be defined as the device which converts DC input supply into AC output where input may be a voltage source or current source.
What is the input voltage of an inverter?
Understanding the inverter voltage is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your power system. Inverter voltage typically falls into three main categories: 12V, 24V, and 48V. These values signify the nominal direct current (DC) input voltage required for the inverter to function optimally. What is the rated input voltage of an inverter?
What is an example of a power inverter?
Common examples are refrigerators, air-conditioning units, and pumps. AC output voltage This value indicates to which utility voltages the inverter can connect. For inverters designed for residential use, the output voltage is 120 V or 240 V at 60 Hz for North America. It is 230 V at 50 Hz for many other countries.
What is a DC inverter?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working Principle: Inverters use power electronics switches to mimic the AC current’s changing direction, providing stable AC output from a DC source.
What is a voltage source inverter?
The inverter is known as voltage source inverter when the input of the inverter is a constant DC voltage source. The input to the voltage source inverter has a stiff DC voltage source. Stiff DC voltage source means that the impedance of DC voltage source is zero. Practically, DC sources have some negligible impedance.
What voltage is a 12V inverter?
Inverters come in various configurations, each designed for specific power systems. Common rated input voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V. The choice depends on the application, the size of the power system, and the available power source. A 12V inverter is commonly used for smaller applications, such as in vehicles or small off-grid setups.
Related Articles
-
 Bangi high voltage inverter
Bangi high voltage inverter
-
 The inverter has low voltage when working for a long time
The inverter has low voltage when working for a long time
-
 Inverter voltage conversion
Inverter voltage conversion
-
 What is the input voltage of the inverter
What is the input voltage of the inverter
-
 Multi-function inverter high voltage
Multi-function inverter high voltage
-
 Bulgaria low voltage inverter price
Bulgaria low voltage inverter price
-
 Photovoltaic inverter connected to high voltage system
Photovoltaic inverter connected to high voltage system
-
 High voltage inverter accessories
High voltage inverter accessories
-
 Is there a voltage comparator in the inverter
Is there a voltage comparator in the inverter
-
 Low frequency inverter plus high voltage
Low frequency inverter plus high voltage
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


