Inverter vs converter: What''s the difference?
Mar 29, 2024 · Key differences between inverters vs converters The fundamental difference between inverters and converters can be found in their functionality. Converters change the
Get Started
简单聊一下用来反转电压的inverting converter-电
Apr 4, 2023 · 我们花了十多次的篇幅,说明了常用的交换式 电源 的原理。从可以升压的 boost conver te r 开始,到降压用的 buck converter,我们用
Get Started
Converter vs. Inverter: What''s the Difference?
Jan 6, 2024 · A converter is a device that changes the voltage of an electrical power source, either stepping it up or down, but it doesn''t alter the current
Get Started
Power Inverter vs. Frequency Inverter
Jan 20, 2021 · There are many differences between a power inverter and a frequency inverter. Power inverters and frequency inverters serve different
Get Started
Inverters Vs. Converters | What''s The Difference?
An inverter converts DC (direct current) into AC (alternating current), whereas a converter modifies voltage and current within the same current type (AC to
Get Started
What is an inverter? | inverter
Aug 11, 2019 · The inverter is made of inverting circuit, logic control circuit and filtering circuit, mainly including input interface, voltage start circuit, MOS switch, PWM controller, DC
Get Started
Understanding inverter voltage
Jan 10, 2024 · Inverter voltage typically falls into three main categories: 12V, 24V, and 48V. These values signify the nominal direct current (DC) input voltage required for the inverter to function
Get Started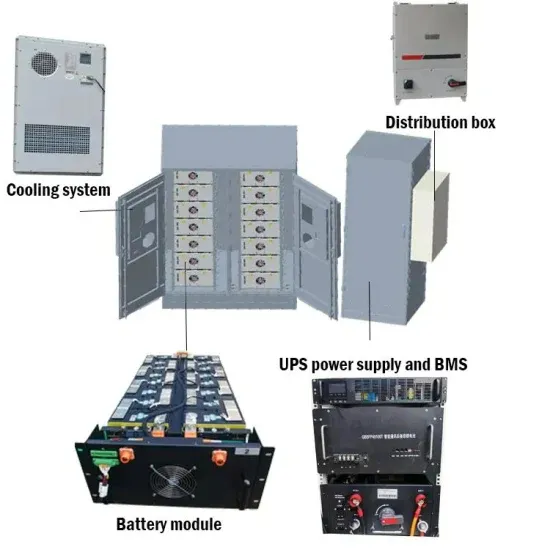
What to Know about DC to AC Voltage Conversion?
Feb 10, 2025 · Learn everything you need to know about DC to AC voltage conversion, including why it''s necessary, how it works, the role of inverters, and common applications like solar
Get Started
3000 Watt Voltage Converter, 220/240v to
3000w voltage converter transformer, input voltage is available for 110v, 120v, 220v, 230v, 240v, converting 120v to 240v, 220v to 110v for home appliances.
Get Started
Inverter Voltage Calculator, Formula, Inverter Voltage
3 days ago · Inverter Voltage Formula: Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes
Get Started
Converter vs. Inverter
A converter is primarily used to convert the voltage level of an electrical signal, either stepping it up or down, while maintaining the same type of current. On the other hand, an inverter is
Get Started
How does an inverter work?
3 days ago · How does an inverter work? How and what does an inverter take control of? A brief explanation to grasp the basic structure. Starting off from
Get Started
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They
Dec 17, 2019 · An inverter (or power inverter) is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage. While DC power is common
Get Started
Inverter AC to DC Amperage Conversion
Feb 24, 2025 · For this, you need a DC-to-AC power inverter that takes the DC voltage a battery provides and inverts it to AC voltage so that you can run an
Get Started
Low Voltage Drives & Inverters
2 days ago · Nidec Conversion Low Voltage Drives improve plants'' energy efficiency, increasing flexibility and optimizing productivity. Send us your request.
Get Started
What Devices Need a Voltage Converter? | inverter
Nov 4, 2024 · A voltage converter is a power conversion device that is mainly used to convert input voltage to the required output voltage. A variety of devices and scenarios require voltage
Get Started
What Are the Differences Between Voltage Converters and
Jan 31, 2025 · While voltage converters and transformers can both achieve voltage conversion, they differ significantly in working principles, application scenarios, and input/output power types.
Get Started
Power Inverter vs. Converter
Jan 26, 2020 · Power inverters and converters are both electrical devices to play a role of electrical power conversion in our life. The power inverter is actually
Get Started
3-Phase Inverter
Feb 27, 2024 · An inverter is a fundamental electrical device designed primarily for the conversion of direct current into alternating current . This versatile
Get Started
Inverters and converters
5 days ago · In a broad sense, an inverter inputs alternating current with a constant voltage or frequency (for example, AC100V/50Hz or 60Hz supplied
Get Started
DC to AC Conversion (INVERTER)
May 23, 2013 · Voltage source inverter (VSI) with variable DC link • DC link voltage is varied by a DC -to DC converter or controlled rectifier. • Generate "square wave" output voltage. • Output
Get Started
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
May 28, 2024 · This article investigates the basic principles of inverters, different types of DC-to-AC conversion, and common applications for generating AC
Get Started
你似乎来到了没有知识存在的荒原
知乎,中文互联网高质量的问答社区和创作者聚集的原创内容平台,于 2011 年 1 月正式上线,以「让人们更好的分享知识、经验和见解,找到自己的解答」为品牌使命。知乎凭借认真、专业
Get Started
When do You Need a Voltage Converter? | inverter
Nov 6, 2024 · A voltage converter is a power conversion device mainly used to convert input voltage into the required output voltage. The voltage converter uses the transformer principle
Get Started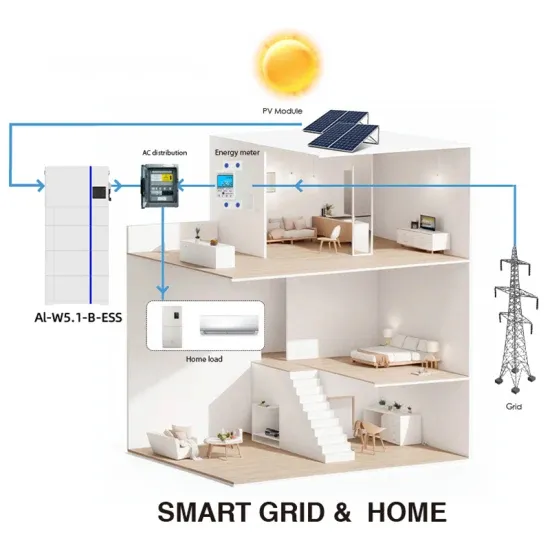
Inverter voltage conversion
Dec 15, 2021 · I have a 24 Vdc battery that I have connected to an inverter to. Using the Vrms to Vac equation (i.e. multiplying by sqrt (2)) I would find the peak value of the Vac. So it would be
Get Started
5000 Watt Voltage Converter, 110/120v to
Favorable price 5000 watt voltage converter (step up and step down transformer), change 110v (120v) to 220 volts, step-down 230/240 volt to 120v, the best
Get Started
Inverter Vs. Converter – When Do We Need One
3 days ago · Power inverter only inverts the power from 12/24v dc to 12/24v AC, then it uses a step-up transformer or even converter to step-up voltage into
Get Started
Inverter Basics: Classification and Applications
Jan 3, 2021 · Voltage fed inverter carry the characteristics of buck-converter as the output rms voltage is always lower than the input DC voltage. Current-fed
Get Started
Understanding the Differences: Inverter vs
May 25, 2024 · Have you ever found yourself scratching your head, trying to decipher the difference between an inverter and a converter? These two
Get Started
Converter vs Inverter
Nov 25, 2023 · What''s the difference between Converter and Inverter? Converters and inverters are electrical devices that convert current. Converters convert
Get Started
Converter vs Inverter: Which is Better for Your
May 31, 2024 · Choosing between a converter and an inverter is a crucial decision that impacts how well your power system works, especially if you''re
Get Started
DC-to-AC Converters (Inverters): Design,
May 20, 2023 · HVDC Systems: High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission systems use inverters to convert DC back to AC at the receiving
Get Started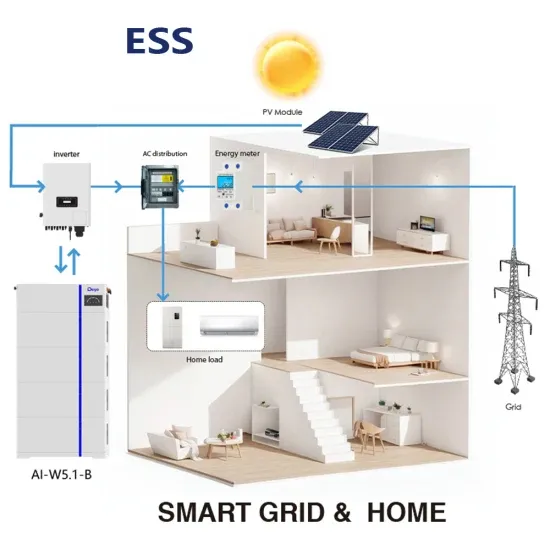
6 FAQs about [Inverter voltage conversion]
How do inverters convert DC voltage to AC voltage?
Most inverters rely on resistors, capacitors, transistors, and other circuit devices for converting DC Voltage to AC Voltage. In alternating current, the current changes direction and flows forward and backward. The current whose direction changes periodically is called an alternating current (AC). It has non-zero frequency.
What is inverter voltage?
Inverter voltage (VI) is an essential concept in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and operation of power electronics systems. It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC).
What is the difference between an inverter and a converter?
An inverter converts DC (direct current) into AC (alternating current), whereas a converter modifies voltage and current within the same current type (AC to DC, DC to DC, or AC to AC). Inverters are commonly used in renewable energy systems, while converters regulate power supply in electronic devices. 2. Can an inverter work without a battery?
What is DC to AC converter (inverter)?
Power Electronics and Drives: Dr. Zainal Salam, FKE, UTM Skudai, JB 2 DC to AC Converter (Inverter) • DEFINITION: Converts DC to AC power by switching the DC input voltage (or current) in a pre -determined sequence so as to generate AC voltage (or current) output . • TYPICAL APPLICATIONS: – UPS, Industrial drives, Traction, HVDC
What is a 12V to 240V inverter?
A 12V to 240V inverter is a pivotal device designed to convert direct current (DC) power from a 12-volt battery into alternating current (AC) power with a nominal output of 240 volts. This conversion is vital for running household appliances, electronic devices, and other equipment that require standard AC power.
What is a converter circuit & inverter circuit?
An inverter is composed of the front part and the rear part. The front part, the “converter circuit” converts AC to DC while the rear part, the “inverter circuit” converts DC to AC. From a broad perspective, the converter circuit and inverter circuit are used as a set to perform AC to AC conversion.
Related Articles
-
 How does the inverter achieve voltage conversion
How does the inverter achieve voltage conversion
-
 Bangi high voltage inverter
Bangi high voltage inverter
-
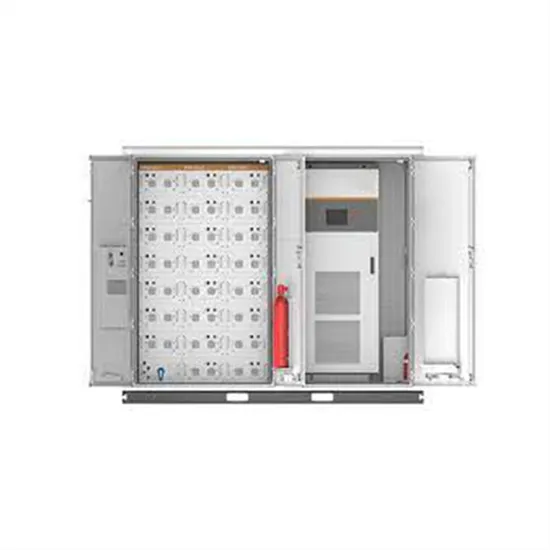 Solar Panel High Voltage Inverter
Solar Panel High Voltage Inverter
-
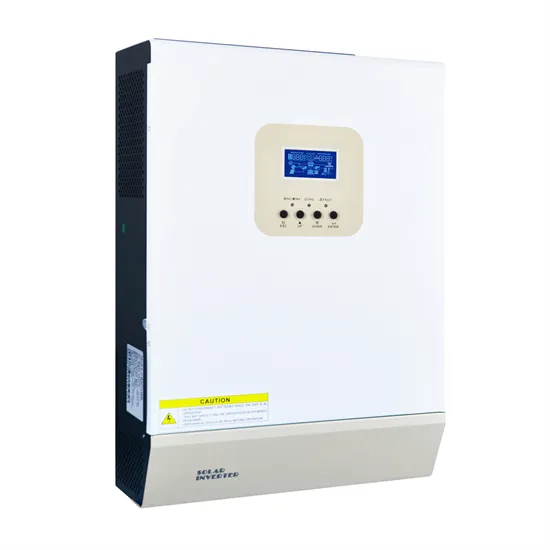 72v inverter applicable voltage range
72v inverter applicable voltage range
-
 The higher the inverter frequency the lower the voltage
The higher the inverter frequency the lower the voltage
-
 The front-stage output voltage of the inverter
The front-stage output voltage of the inverter
-
 Maximum voltage of the inverter
Maximum voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the input voltage of the communication inverter
What is the input voltage of the communication inverter
-
 Can the inverter high voltage capacitor be charged
Can the inverter high voltage capacitor be charged
-
 Inverter string voltage to ground
Inverter string voltage to ground
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


