Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Jul 25, 2025 · Yet, not all inverters are created equal. One of the most critical architectural decisions an engineer faces is the choice between a line-frequency (or low-frequency) and a
Get Started
Medien Tech Talk
Oct 13, 2021 · Source: Company information. Notes: HV: High Voltage. CO2 savings relate to "tank to wheel" potential vs. pure combustion vehicle based on WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized
Get Started
Inverters, Types and Voltages
Dec 31, 2024 · Key Takeaways Understanding the differences between low voltage and high voltage inverters and low frequency and high frequency inverters ensures you can make an
Get Started
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency
5 days ago · Inverters are essential components of many electrical systems, converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to power various
Get Started
Which is Better Low Frequency or High
3 days ago · This articles examines low frequency inverters operating near the AC line frequency versus high frequency inverters using much higher
Get Started
Low Frequency Inverter – Hybrid Solar Inverter & ESS
Aug 17, 2025 · Low Frequency Off Grid Solar Inverter 1~2KVA | DC 12V,24V | PWM 50A | PV 55V PV2000 PK built-in high efficiency solar controller. AC input voltage range for 140VAC
Get Started
On/Off Grid Hybrid Solar Inverter – Hybrid Solar Inverter
6 days ago · ON/OFF GRID HYBRID SOLAR INVERTER 5~12KW | Three Phase | 380VAC PH1100 EU is brand new three phase hybrid inverter with low battery voltage 48V, ensuring
Get Started
Low Voltage AC Drives/Inverter/Converter
Micno''s low voltage drives/inverter increase plant energy efficiency, flexibility and optimize productivity. Low frequency inverters are widely used in various applications in more than 80
Get Started
Low-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters:
Dec 3, 2024 · Choosing the right inverter is key to maximizing your solar system''s efficiency. Explore the differences between high-frequency and low-frequency
Get Started
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
May 2, 2023 · Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for
Get Started
Demystifying High Frequency vs Low Frequency
Jul 2, 2023 · The main difference between High-frequency and Transformer-based Low-Frequency Inverters/UPS is the frequency at which they operate.
Get Started
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
Feb 6, 2025 · Operating Frequency Low-Frequency Inverter: Operates at a lower frequency, typically around 50Hz or 60Hz. Because its frequency is close to that of utility power, it is
Get Started
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters:
4 days ago · Low-frequency Inverters are designed to handle high-surge loads, typically 2-5 times their rated power output. This makes them perfect for
Get Started
The Ultimate Guide to Low-Frequency Inverters
6 days ago · Advantages of Low-Frequency Inverters The adoption of low-frequency inverters over their high-frequency counterparts hinges on several compelling advantages. Their robust
Get Started
Inverters, Types and Voltages
Dec 31, 2024 · Opt for low voltage inverters if safety, simplicity, and smaller systems are your focus. Choose high voltage inverters if efficiency, scalability, or long-distance transmission is a
Get Started
High Vs Low Frequency Inverters/UPS
Jul 1, 2023 · Why is a Transformer important in a Pure Sinewave Inverter/UPS? Isolation plays a major role in the functioning of the Inverter/UPS during the
Get Started
Very-high-frequency low-voltage power delivery
This thesis introduces elements for hybrid GaN-Si dc-de power converters operating at very high frequencies (VHF, 30-300 MHz) for low-voltage applications. Contributions include
Get Started
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Conclusion In conclusion, the choice between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters depends largely on the specific needs of the application. High-frequency inverters offer the
Get Started
Custom low frequency inverter, low frequency
Dec 16, 2024 · Voltage and Frequency Stabilization A low frequency inverter is specifically designed to maintain stable voltage and frequency levels. This is
Get Started
Reliable Low Frequency Inverter – PowMr
Low-frequency inverter chargers excel with high peak power capacity, resilience to voltage fluctuations and spikes. Ideal for off-grid scenarios, RVs, backup power, construction sites,
Get Started
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters:
Feb 10, 2025 · What are high-frequency inverters? High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency
Get Started
Everything to Know Low Frequency Inverters
Low-frequency inverters, characterized by their use of transformers for electrical isolation, play a crucial role in a variety of high-reliability applications. This
Get Started
High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
Low-Frequency Inverters: Low-frequency inverters use heavy, iron-core transformers to step up the voltage from DC to AC. These transformers operate at the utility grid frequency of 50 Hz or
Get Started
How to Select the Best Low-Frequency Inverter for Your Needs
Aug 15, 2024 · In a world becoming increasingly reliant on portable power, low-frequency inverters have emerged as a crucial tool for converting DC power sources into usable AC
Get Started
Off Grid Solar Inverter – Hybrid Solar Inverter
2 days ago · High Frequency Off Grid Solar Inverter 1.6~6.2KW | PV 400/450/500V | Dual output | DC 12V,24V,48V PV1800 ECO is a multi
Get Started
800VA Pure Sine Wave Inverter''s Reference Design
Apr 1, 2023 · The pure Sine Wave inverter has various applications because of its key advantages such as operation with very low harmonic distortion and clean power like utility-supplied
Get Started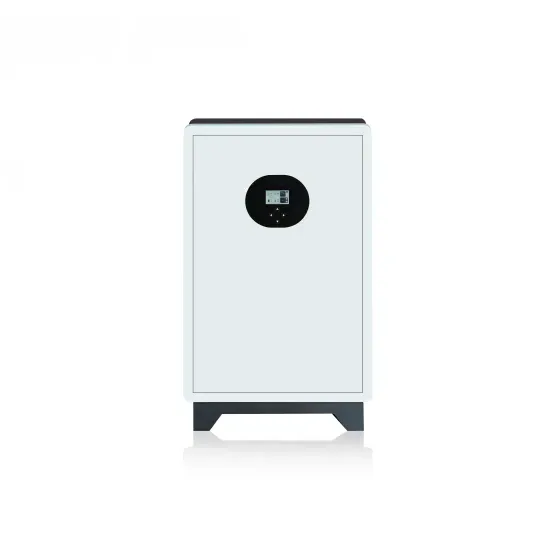
Difference Between High and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 30, 2025 · Understand the difference between high and low frequency inverters (lf vs hf inverter) and what are the main features of Xindun Power''s high frequency inverters?
Get Started
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
May 2, 2023 · Weight: Low-frequency inverters are generally heavier than high-frequency inverters, mainly due to their larger and heavier transformers.
Get Started
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters:
Feb 10, 2025 · High-frequency inverters use high-frequency switches to convert incoming low-voltage DC power to high-frequency low-voltage AC power. This
Get Started
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency
5 days ago · Low-frequency inverters, operating at frequencies below 60 Hz, generally generate a quasi-square wave or a modified sine wave output.
Get Started
Understanding High-Frequency Inverters
6 days ago · In the realm of power electronics, the advent of high-frequency inverters has revolutionized the landscape. These enigmatic devices possess the uncanny ability to
Get Started
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and
3 days ago · A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency,
Get Started
Low-Frequency hybrid Inverter VS High
Jan 29, 2025 · This Article will help you understand some key differences between an low-frequency offgrid hybrid inverter and a high-frequency offgrid
Get Started
Low Frequency Inverter, High Frequency
Jun 5, 2020 · Low frequency inverter can withstand grid input conditions, such as voltage fluctuation, high voltage spike and lightning. However, the high
Get Started
6 FAQs about [Low frequency inverter plus high voltage]
What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency inverters?
Low-frequency Inverters are designed to handle high-surge loads, typically 2-5 times their rated power output. This makes them perfect for refrigerators, compressors, or air conditioners requiring extra power during startup. High-frequency inverters typically have 1.5-2 times their rated power, which limits their surge capacity.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Efficiency: Low-frequency inverters are known for their robustness and ability to handle high surge currents, making them suitable for powering heavy-duty appliances or equipment with high starting currents, such as motors and compressors.
Should you buy a low-frequency inverter?
If you need to power appliances with high surge requirements, like refrigerators, compressors, or industrial machinery, a low-frequency inverter is a better choice due to its ability to handle high starting currents.
What is the main issue with low frequency power inverters?
Low frequency power inverters suffer from a low frequency hum. This hum is caused by the fact that they use high speed power transistors to invert the DC to AC, but drive transistors at the same frequency (60 Hz or 50Hz) as the AC sine wave output.
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a low frequency inverter?
The advantages of a low frequency inverter include: relatively simple structure, stable and reliable operation, strong overload capacity, and impact resistance. However, its disadvantages are: heavier, larger, more expensive, and less efficient than high-frequency inverters of the same power.
Related Articles
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
 Inverter input voltage is too high or too low
Inverter input voltage is too high or too low
-
 Latvian high quality low voltage inverter manufacturer
Latvian high quality low voltage inverter manufacturer
-
 Inverter from high frequency to low frequency
Inverter from high frequency to low frequency
-
 Low voltage to high voltage inverter for construction sites
Low voltage to high voltage inverter for construction sites
-
 Inverter high frequency and low frequency
Inverter high frequency and low frequency
-
 Santo Domingo high frequency inverter price
Santo Domingo high frequency inverter price
-
 Imported high frequency inverter manufacturers
Imported high frequency inverter manufacturers
-
 6000W high frequency inverter
6000W high frequency inverter
-
 Industrial frequency and high frequency inverter for RV
Industrial frequency and high frequency inverter for RV
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


