Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
4 days ago · Understand the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters with this quick article.
Get Started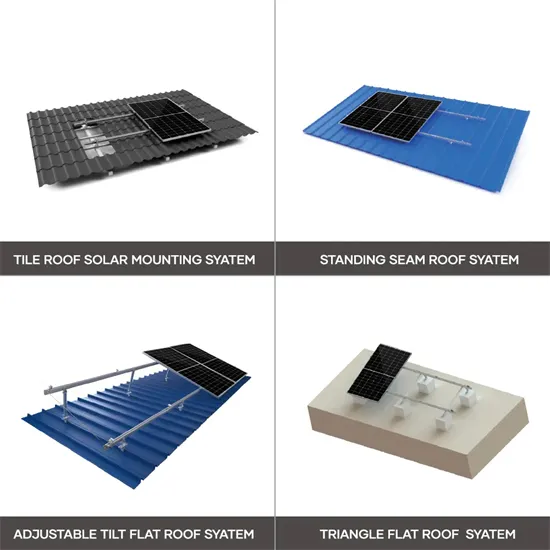
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters:
4 days ago · There are two main types of frequencies to be compared: low frequency vs high frequency inverters. The inverter frequency determines the
Get Started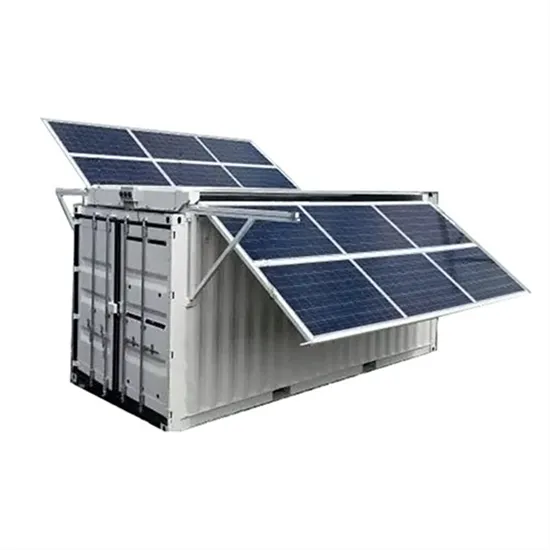
Power Inverter vs. Frequency Inverter
Jan 20, 2021 · There are many differences between a power inverter and a frequency inverter. Power inverters and frequency inverters serve different
Get Started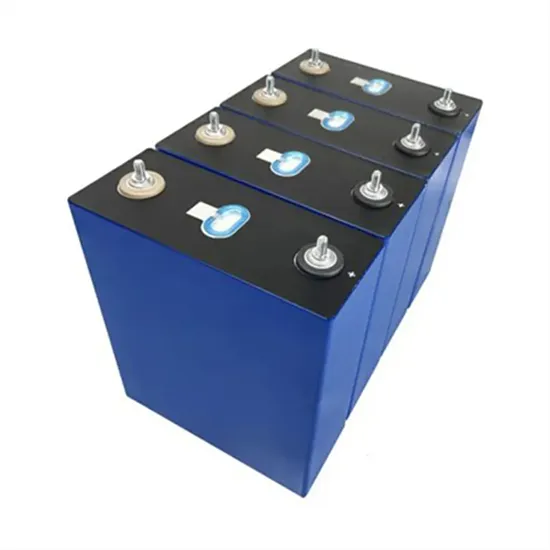
The difference between frequency converter and
Apr 2, 2024 · The inverter with adjustable frequency and voltage of the inverter power supply is called a frequency converter. The waveform output by the
Get Started
Understanding Frequency Inverters: A Comprehensive Guide
Feb 23, 2025 · A frequency inverter, also known as a variable frequency drive (VFD), is an essential device used to control the speed and torque of electric motors by adjusting the input
Get Started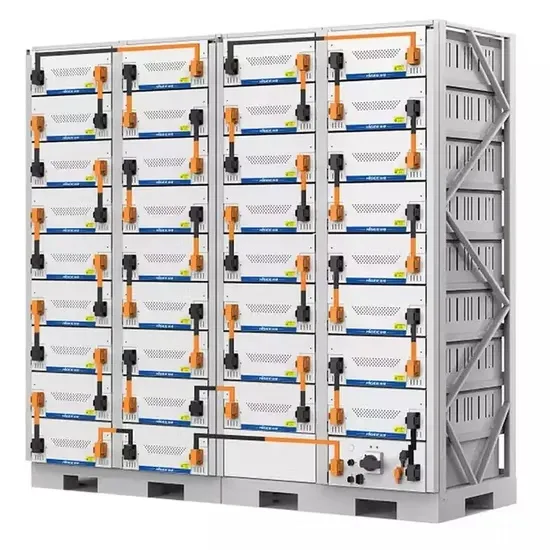
The difference between high frequency and industrial frequency of inverter
What is the difference between industrial and high-frequency inverters? Industrial frequency inverters have high stability and are suitable for high-demand occasions; high-frequency
Get Started
What is the difference between a high frequency
Apr 25, 2024 · Since the high-frequency inverter uses small-sized, lightweight high-frequency magnetic core materials, the power density of the circuit is
Get Started
Teach you how to choose industrial frequency inverter and high
Structurally, the difference between industrial frequency inverters and high frequency inverters is mainly reflected in the isolation transformer, and the use of isolation transformers by industrial
Get Started
Motor Inverter vs VFD: What''s the Real Difference? | Mingch
Aug 4, 2025 · Knowing the difference between frequency inverter vs VFD matters because your choice affects: Motor performance – A full VFD offers smoother starts, better torque control,
Get Started
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
Feb 6, 2025 · The primary distinctions between low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters lie in their operating frequencies, design structures, and performance characteristics
Get Started
What is the difference between an industrial frequency
Jun 18, 2025 · What is the difference between an industrial frequency compressor and an inverter compressor? What are the benefits of inverter compressors?VSD (Variable Speed Drive)
Get Started
Which is Better: Low Frequency or High Frequency Inverter?
Mar 20, 2025 · High-frequency inverters use smaller, high-speed switching devices like MOSFETs or IGBTs and typically do not require bulky transformers, which reduces their size and weight.
Get Started
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Nov 14, 2024 · High-frequency inverters consume less power from the battery at zero load than power-frequency inverters. Power-frequency inverters are best for their robustness and
Get Started
What''s The Difference between A High Frequency And Low Frequency
What''s The Difference between A High Frequency And Low Frequency Solar Inverter? Solar power has become an increasingly popular and environmentally friendly way to generate
Get Started
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
Feb 6, 2025 · Application Scenarios Low-Frequency Inverter: More suitable for industrial applications, large equipment power supply, and other scenarios requiring high reliability and
Get Started
High frequency inverter vs low frequency
Nov 2, 2023 · This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size
Get Started
Difference Between High and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 30, 2025 · Understand the difference between high and low frequency inverters (lf vs hf inverter) and what are the main features of Xindun Power''s high frequency inverters?
Get Started
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
May 2, 2023 · The difference between low and high-frequency inverters impacts their weight, efficiency, and applications. Here''s a brief overview of the two
Get Started
The differences and similarities between high-frequency inverters
Industrial frequency inverters are usually used for higher power applications, such as home power systems, industrial power, etc. High frequency inverters are often used in applications that
Get Started
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key
Aug 15, 2025 · Explore the key differences in low frequency vs high frequency inverters including their applications, advantages, and which is best for your
Get Started
Frequency Inverter | inverter
The Difference between Power Inverter and Frequency Inverter The power inverter is a device that can convert DC into AC and the frequency inverter is a component used to change the AC
Get Started
What is the Difference Between a Transformer and a Frequency Inverter
May 23, 2022 · The difference between transformer and frequency inverter Transformer technical parameters have corresponding technical requirements for different types of transformers, and
Get Started
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Conclusion In conclusion, the choice between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters depends largely on the specific needs of the application. High-frequency inverters offer the
Get Started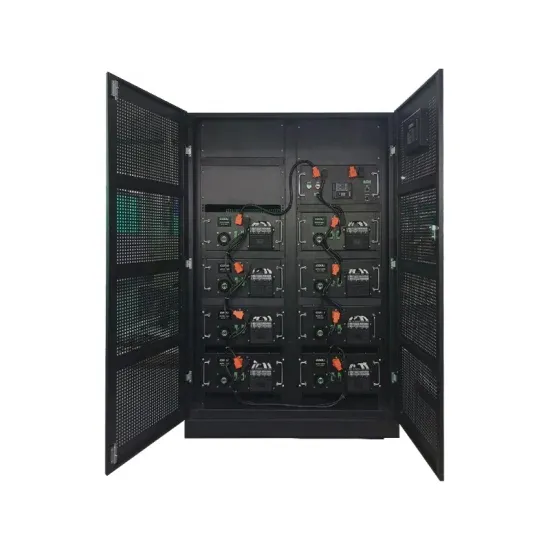
Low frequency inverter vs high frequency
Mar 12, 2025 · In this article, we''ll explore their differences, benefits, and ideal use cases to help you make an informed decision. Understanding the Difference
Get Started
Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions
Dec 11, 2023 · Function of Frequency Inverter Speed Regulation Function: Frequency inverters can change the speed of the motor by adjusting the
Get Started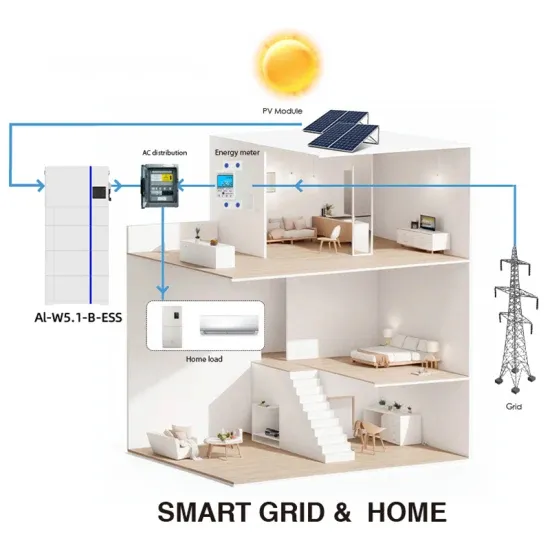
What are the Types of Frequency Inverter?
Oct 22, 2023 · These frequency converters are typically used in low-power applications and high-frequency applications. Frequency inverters are
Get Started
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
4 days ago · There are two distinct types of industrial grade power inverters distinguished by the size of their transformers, and the switching speed of their transistors. The ability of an inverter
Get Started
The differences and similarities between high-frequency inverters
The frequency range of the inverter is affected by the application needs and specific requirements. Industrial frequency inverters are usually used for higher power applications, such as home
Get Started
The difference between frequency converter and
Mar 7, 2023 · What is a frequency converter? Introduction to frequency converter: mainly to change the frequency. The inverter is mainly composed of
Get Started
Technical comparison between Low Frequency
Aug 19, 2025 · The second main difference is reliability: low-frequency inverters operate using powerful transformers, which are more reliable and sturdy than
Get Started
Understanding the Difference Between
Jan 21, 2025 · Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power
Get Started
Difference Between High-Frequency and Low
Sep 6, 2024 · FAQs Q: Can I use high-frequency UPS for industrial equipment? While high-frequency UPS systems are more suitable for home and office use,
Get Started
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
Dec 17, 2024 · Understanding the differences between a high and low frequency inverter helps you make informed decisions. High frequency inverters offer compactness and efficiency,
Get Started
6 FAQs about [The difference between inverter high frequency and industrial frequency]
What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency inverters?
Low-frequency Inverters are designed to handle high-surge loads, typically 2-5 times their rated power output. This makes them perfect for refrigerators, compressors, or air conditioners requiring extra power during startup. High-frequency inverters typically have 1.5-2 times their rated power, which limits their surge capacity.
What is a high frequency inverter?
The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency. They are typically less expensive, have smaller footprints, and have a lower tolerance for industrial loads. HF inverters have over twice the number of components and use multiple, smaller transformers.
What is a frequency inverter?
A frequency inverter, also known as a variable frequency drive (VFD), is a device that converts fixed frequency AC to variable frequency AC. It is based on traditional principles of analog circuit design and uses components like thyristors (SCR), IGBTs, and transformers. Its operating frequency can be adjusted, typically from 0 to 50Hz.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Low-frequency inverters are known for their durability and ability to handle high surge loads. The heavy transformers inside these inverters allow them to deliver much power for short bursts, which is essential for starting devices like refrigerators, air conditioners, or power tools that need extra energy to start running.
Should you buy a high-frequency inverter?
On the other hand, if you’re looking for a portable solution for RVs, boats, or small solar setups, a high-frequency inverter is ideal for powering lighter loads, such as laptops, LED lights, and small electronics.
Does a high frequency inverter need a battery converter?
A high-frequency inverter will typically have a separate battery voltage converter configured. When the mains power is normal, the battery converter reduces the bus voltage to 800V. In case of mains failure or overrun, the battery pack voltage converter raises the high bus voltage to 800V.
Related Articles
-
 Industrial frequency machine and high frequency machine inverter
Industrial frequency machine and high frequency machine inverter
-
 Household high frequency or industrial frequency inverter
Household high frequency or industrial frequency inverter
-
 High frequency inverter rcd
High frequency inverter rcd
-
 High frequency inverter front stage module
High frequency inverter front stage module
-
 High frequency sine wave inverter
High frequency sine wave inverter
-
 Inverter high frequency control
Inverter high frequency control
-
 High frequency inverter front stage output
High frequency inverter front stage output
-
 High frequency protection setting value of photovoltaic inverter
High frequency protection setting value of photovoltaic inverter
-
 3600V high frequency inverter
3600V high frequency inverter
-
 How much does a high frequency inverter output
How much does a high frequency inverter output
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


